目录
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-all-adjacent-duplicates-in-string/
题目:232.用栈实现队列
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/
使用栈实现队列的下列操作:
push(x) -- 将一个元素放入队列的尾部。
pop() -- 从队列首部移除元素。
peek() -- 返回队列首部的元素。
empty() -- 返回队列是否为空。示例:
MyQueue queue = new MyQueue(); queue.push(1); queue.push(2); queue.peek(); // 返回 1 queue.pop(); // 返回 1 queue.empty(); // 返回 false说明:
- 你只能使用标准的栈操作 -- 也就是只有 push to top, peek/pop from top, size, 和 is empty 操作是合法的。
- 你所使用的语言也许不支持栈。你可以使用 list 或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个栈,只要是标准的栈操作即可。
- 假设所有操作都是有效的 (例如,一个空的队列不会调用 pop 或者 peek 操作)。
思路:用两个栈实现队列,一个输入栈,一个输出栈,注意要将输入栈中的所有数据全部导入到输出栈中。
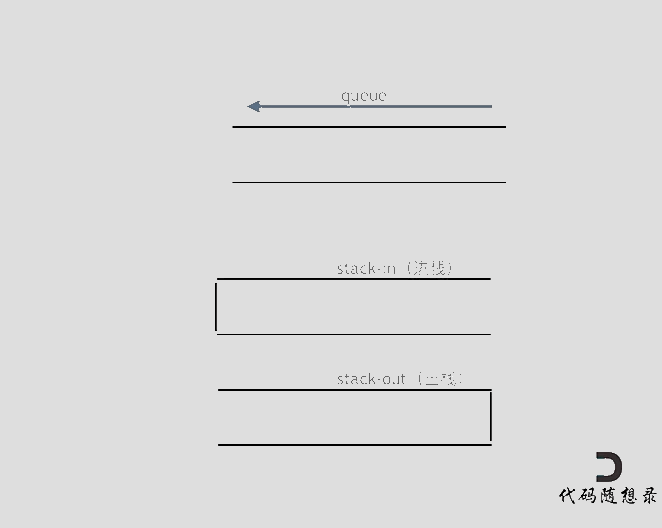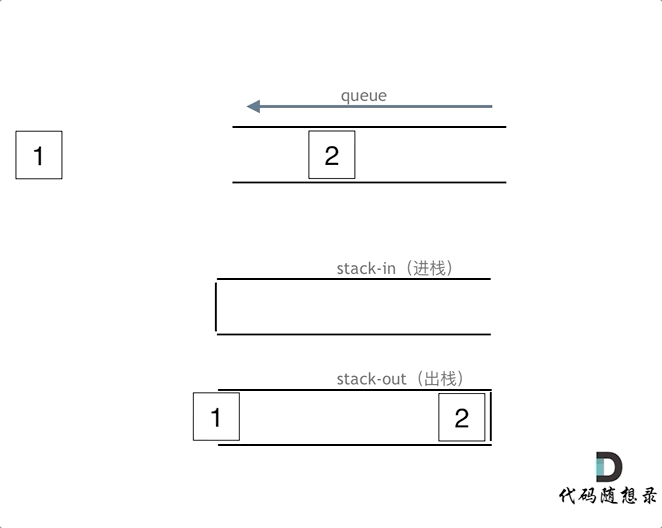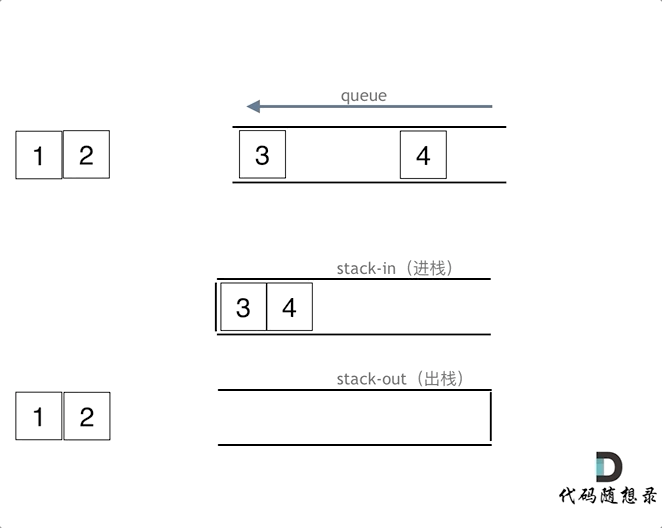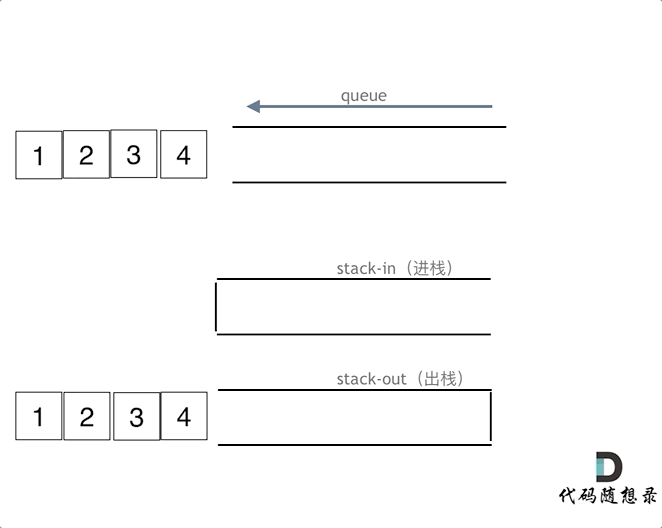
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stIn;
stack<int> stOut;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
stIn.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
// 只有当stOut为空的时候,再从stIn里导入数据(导入stIn全部数据)
if (stOut.empty()) {
// 从stIn导入数据直到stIn为空
while(!stIn.empty()) {
stOut.push(stIn.top());
stIn.pop();
}
}
int result = stOut.top();
stOut.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
int res = this->pop(); // 直接使用已有的pop函数
stOut.push(res); // 因为pop函数弹出了元素res,所以再添加回去
return res;
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return stIn.empty() && stOut.empty();
}
};题目:225. 用队列实现栈
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/implement-stack-using-queues/
请你仅使用两个队列实现一个后入先出(LIFO)的栈,并支持普通栈的全部四种操作(push、top、pop 和 empty)。
实现 MyStack 类:
void push(int x) 将元素 x 压入栈顶。
int pop() 移除并返回栈顶元素。
int top() 返回栈顶元素。
boolean empty() 如果栈是空的,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
注意:
你只能使用队列的基本操作 —— 也就是 push to back、peek/pop from front、size 和 is empty 这些操作。
你所使用的语言也许不支持队列。 你可以使用 list (列表)或者 deque(双端队列)来模拟一个队列 , 只要是标准的队列操作即可。
思路:一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时在去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了
que.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};
题目:20. 有效的括号
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/valid-parentheses/
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串 s ,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
思路:通过栈来实现括号匹配,分析不匹配的情况有三种:
- 左括号多了
- 右括号多了
- 左右括号一样多,但是类型不匹配
在遍历字符串时,每遇到左括号,就相应地往栈中放相同类型的右括号,当遍历到右括号时,就与栈中的存在的括号进行比对,如果相同则弹出数据。这样对应的不匹配的情况总共有三种:
- 栈不为空(左括号多了)
- 栈为空,但是字符串还没有遍历完(右括号多了)
- 类型不匹配
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if (s.size() % 2 != 0) return false; // 如果s的长度为奇数,一定不符合要求
stack<char> st;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) {
if (s[i] == '(') st.push(')');
else if (s[i] == '{') st.push('}');
else if (s[i] == '[') st.push(']');
// 第三种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,栈已经为空了,没有匹配的字符了,说明右括号没有找到对应的左括号 return false
// 第二种情况:遍历字符串匹配的过程中,发现栈里没有我们要匹配的字符。所以return false
else if (st.empty() || st.top() != s[i]) return false;
else st.pop(); // st.top() 与 s[i]相等,栈弹出元素
}
// 第一种情况:此时我们已经遍历完了字符串,但是栈不为空,说明有相应的左括号没有右括号来匹配,所以return false,否则就return true
return st.empty();
}
};题目:1047. 删除字符串中的所有相邻重复项
题目链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-all-adjacent-duplicates-in-string/
给出由小写字母组成的字符串 S,重复项删除操作会选择两个相邻且相同的字母,并删除它们。
在 S 上反复执行重复项删除操作,直到无法继续删除。
在完成所有重复项删除操作后返回最终的字符串。答案保证唯一。
示例:
输入:"abbaca"
输出:"ca"
解释:
例如,在 "abbaca" 中,我们可以删除 "bb" 由于两字母相邻且相同,这是此时唯一可以执行删除操作的重复项。之后我们得到字符串 "aaca",其中又只有 "aa" 可以执行重复项删除操作,所以最后的字符串为 "ca"。
提示:
1 <= S.length <= 20000
S 仅由小写英文字母组成。
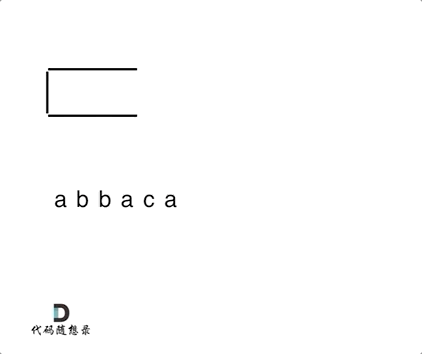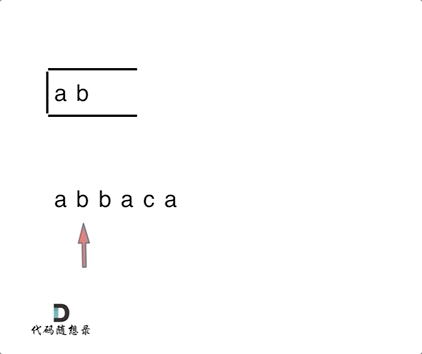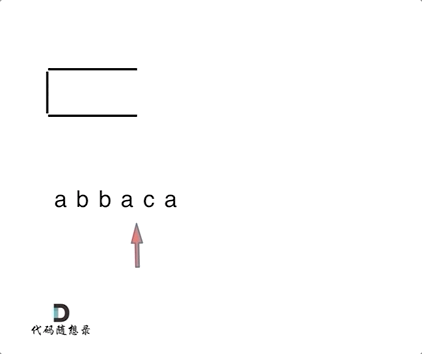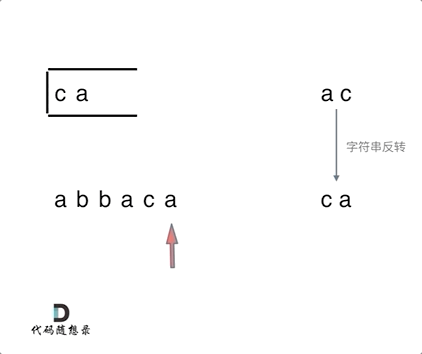
思路:将遍历过的元素存放在栈中,当前遍历的元素与栈中的元素进行比对,如果相同,就弹出栈顶元素,反之,则将当前遍历的元素加入到栈中。最终将栈中所有元素弹出,然后利用reverse反转一下。
class Solution {
public:
string removeDuplicates(string S) {
stack<char> st;
for (char s : S) {
if (st.empty() || s != st.top()) {
st.push(s);
} else {
st.pop(); // s 与 st.top()相等的情况
}
}
string result = "";
while (!st.empty()) { // 将栈中元素放到result字符串汇总
result += st.top();
st.pop();
}
reverse (result.begin(), result.end()); // 此时字符串需要反转一下
return result;
}
};





















 709
709

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








