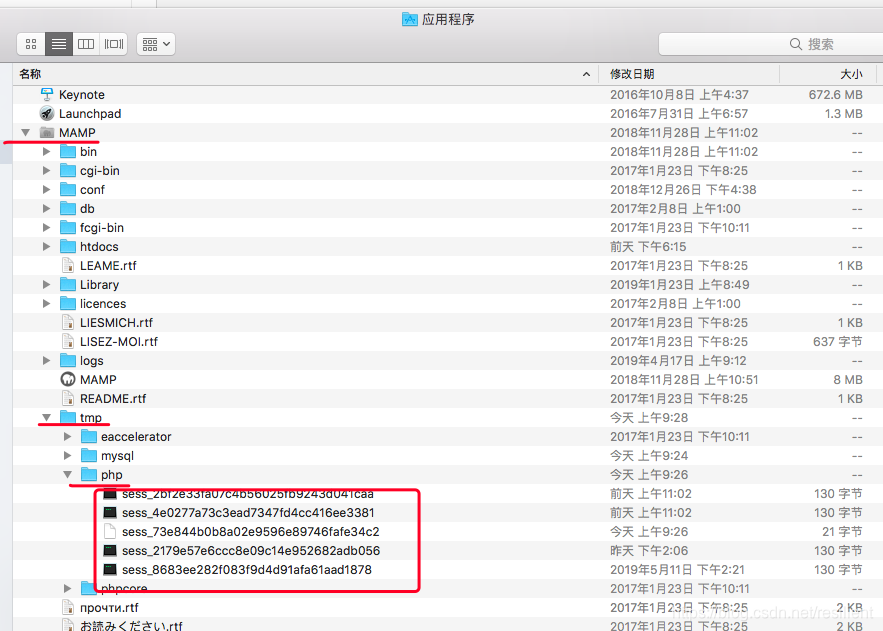
mamp中session存储位置为/Applications/MAMP/tmp/php
可以查看配置文件
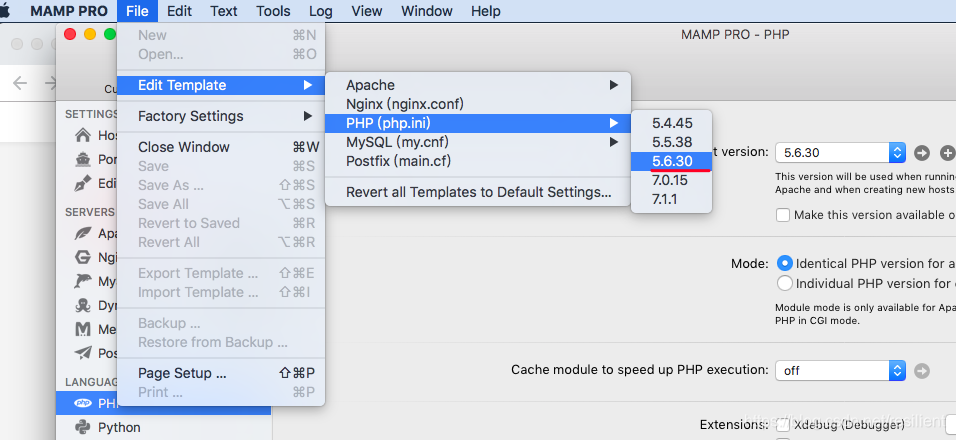
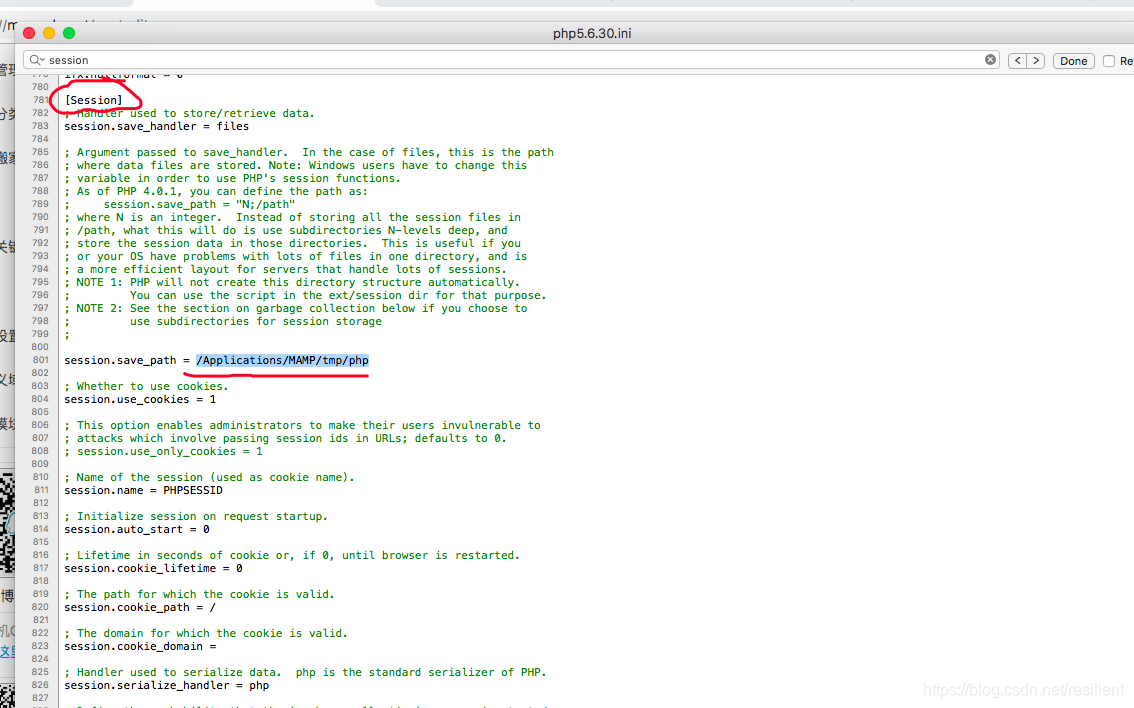
session相关的配置
[Session]
; Handler used to store/retrieve data.
session.save_handler = files
; Argument passed to save_handler. In the case of files, this is the path
; where data files are stored. Note: Windows users have to change this
; variable in order to use PHP's session functions.
; As of PHP 4.0.1, you can define the path as:
; session.save_path = "N;/path"
; where N is an integer. Instead of storing all the session files in
; /path, what this will do is use subdirectories N-levels deep, and
; store the session data in those directories. This is useful if you
; or your OS have problems with lots of files in one directory, and is
; a more efficient layout for servers that handle lots of sessions.
; NOTE 1: PHP will not create this directory structure automatically.
; You can use the script in the ext/session dir for that purpose.
; NOTE 2: See the section on garbage collection below if you choose to
; use subdirectories for session storage
;
session.save_path = /Applications/MAMP/tmp/php
; Whether to use cookies.
session.use_cookies = 1
; This option enables administrators to make their users invulnerable to
; attacks which involve passing session ids in URLs; defaults to 0.
; session.use_only_cookies = 1
; Name of the session (used as cookie name).
session.name = PHPSESSID
; Initialize session on request startup.
session.auto_start = 0
; Lifetime in seconds of cookie or, if 0, until browser is restarted.
session.cookie_lifetime = 0
; The path for which the cookie is valid.
session.cookie_path = /
; The domain for which the cookie is valid.
session.cookie_domain =
; Handler used to serialize data. php is the standard serializer of PHP.
session.serialize_handler = php
; Define the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started
; on every session initialization.
; The probability is calculated by using gc_probability/gc_divisor,
; e.g. 1/100 means there is a 1% chance that the GC process starts
; on each request.
session.gc_probability = 1
session.gc_divisor = 100
; After this number of seconds, stored data will be seen as 'garbage' and
; cleaned up by the garbage collection process.
session.gc_maxlifetime = 1440
; NOTE: If you are using the subdirectory option for storing session files
; (see session.save_path above), then garbage collection does *not*
; happen automatically. You will need to do your own garbage
; collection through a shell script, cron entry, or some other method.
; For example, the following script would is the equivalent of
; setting session.gc_maxlifetime to 1440 (1440 seconds = 24 minutes):
; cd /path/to/sessions; find -cmin +24 | xargs rm
; PHP 4.2 and less have an undocumented feature/bug that allows you to
; to initialize a session variable in the global scope, albeit register_globals
; is disabled. PHP 4.3 and later will warn you, if this feature is used.
; You can disable the feature and the warning seperately. At this time,
; the warning is only displayed, if bug_compat_42 is enabled.
session.bug_compat_42 = 1
session.bug_compat_warn = 1
; Check HTTP Referer to invalidate externally stored URLs containing ids.
; HTTP_REFERER has to contain this substring for the session to be
; considered as valid.
session.referer_check =
; How many bytes to read from the file.
session.entropy_length = 0
; Specified here to create the session id.
session.entropy_file =
;session.entropy_length = 16
;session.entropy_file = /dev/urandom
; Set to {nocache,private,public,} to determine HTTP caching aspects
; or leave this empty to avoid sending anti-caching headers.
session.cache_limiter = nocache
; Document expires after n minutes.
session.cache_expire = 180
; trans sid support is disabled by default.
; Use of trans sid may risk your users security.
; Use this option with caution.
; - User may send URL contains active session ID
; to other person via. email/irc/etc.
; - URL that contains active session ID may be stored
; in publically accessible computer.
; - User may access your site with the same session ID
; always using URL stored in browser's history or bookmarks.
session.use_trans_sid = 0
; The URL rewriter will look for URLs in a defined set of HTML tags.
; form/fieldset are special; if you include them here, the rewriter will
; add a hidden <input> field with the info which is otherwise appended
; to URLs. If you want XHTML conformity, remove the form entry.
; Note that all valid entries require a "=", even if no value follows.
url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=,fieldset="
一、Session和Cookie的区别
Session是在服务器端保持会话数据的一种方法(通常用于pc端网站保持登录状态,手机端通常会使用token方式实现),存储在服务端。
Cookie是在客户端保持用户数据,存储位置是客户端(浏览器或者手机端)。
二、原理
1、当代码session_start(); 运行的时候,就在服务器上产生了一个session文件,随之也产生了与之唯一对应的一个session_id。
2、定义的Session变量以一定形式存储在刚才产生的session文件中。客户端将session_id传递给服务端,服务端根据session_id找到对应的文件,读取的时候,对文件内容进行反序列化就能得到session的值,保存的时候先序列化再写入。由此通过session_id可以取出之前定义的变量。
3、也就是说,Session_id是取得存储在服务器端Session变量的身份证。
注:PHP中的Session在默认的情况下,是使用客户端的Cookie来保存session_id的(session_start();之后,会自动将session_id存储在cookie中),但是必须注意,Session不一定必须依赖Cookie,这也就是Session相比于Cookie的高明之处。当客户端的Cookie被禁用或出现问题时,PHP会自动把session_id附着在URL中,这样再通过session_id就能实现跨页使用session变量了。但是这种附着也是有一定条件的,即php.ini文件中的“session.use_trans_sid=1”或者编译时打开了--enable-trans-sid选项。
三、实验cookie禁用后,session的传递
TP5中简单写一个demo
1、cookie未禁用时的结果
public function index()
{
session_start();
$_SESSION['name'] = "session_name测试";
echo $_SESSION['name'];
echo "<hr>";
var_dump($_COOKIE);
echo "<hr>";
return $this->fetch();
}
public function classadd()
{
session_start();
echo $_SESSION['name'];
echo "<hr>";
var_dump($_COOKIE);
$res = Db::name('goods_class')->field("*,concat(path,',',pid) as paths")->order('paths')->select();
// var_dump($res);exit();
foreach ($res as $k => $v) {
$res[$k]['name'] = str_repeat('|---', $v['level']) . $v['name'];
}
// var_dump($res);
$this->assign('data', $res);
return $this->fetch();
}
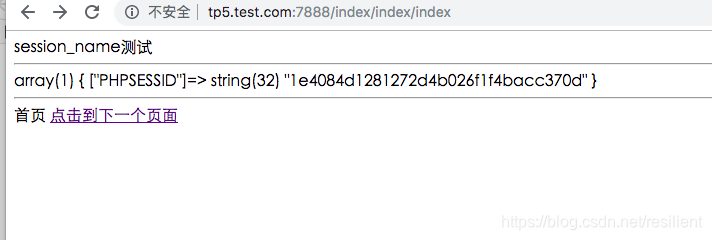
(2)此时,运行index.php代码在浏览器会得到类似下面结果:
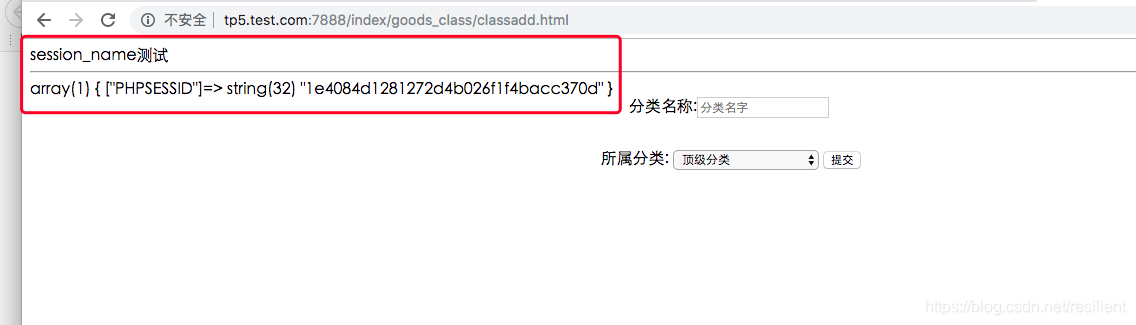
(3)此时点击“ 点击到下一页页面”,跳转到GoodsClass.php
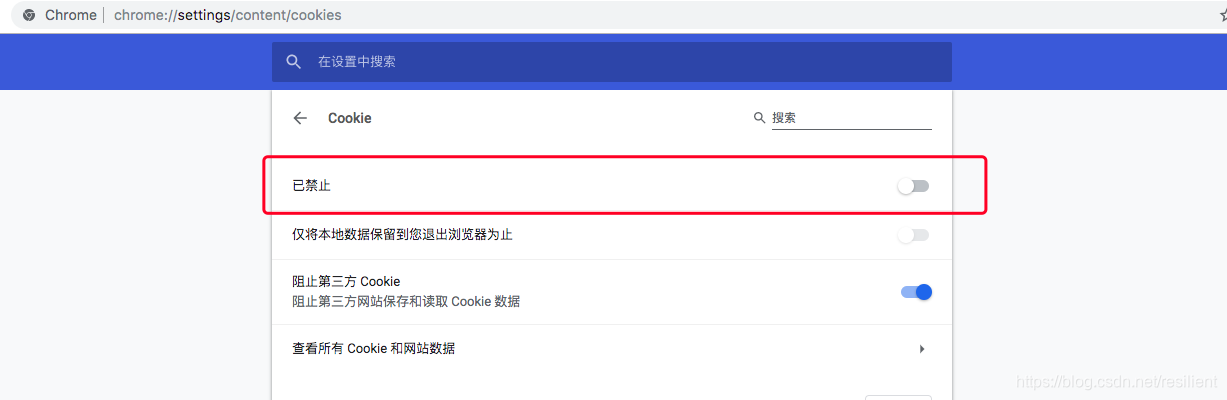
2、禁用掉cookie之后,重新运行代码
注:禁用cookie位置:chrome://settings/content/cookies
得到的结果:
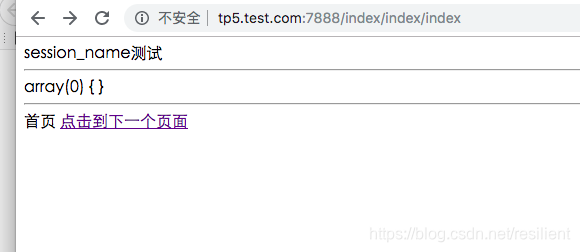
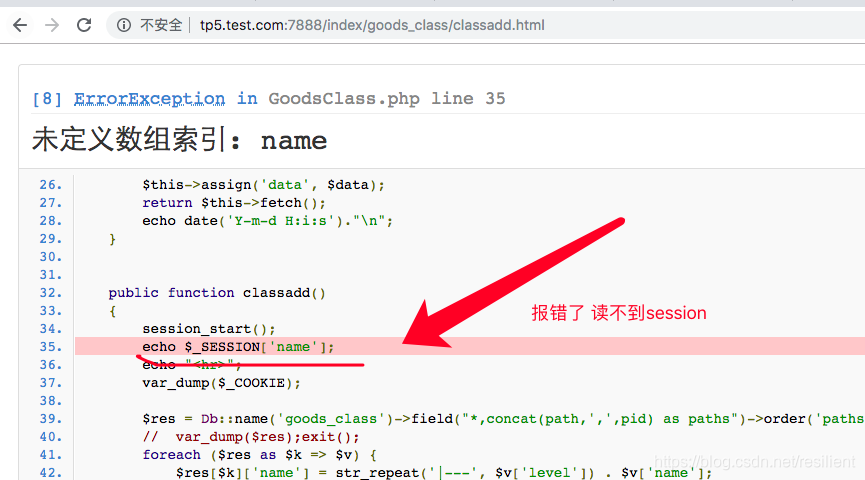
也就是说,在不更改php.ini配置文件的前提下,禁用掉cookie之后,默认session是无法跨页传输的
3、解决禁用掉cookie之后,让session仍然可以正常传输
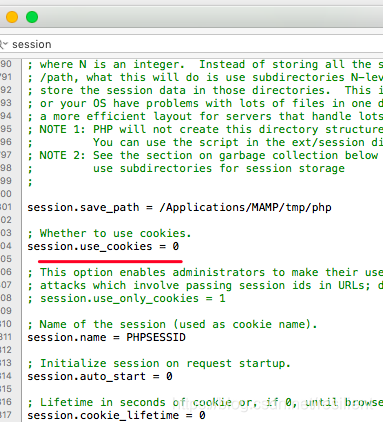
(1)关闭php.ini配置文件中 session.use_only_cookies,打开php.ini配置文件中session.use_trans_sid,如下:
session.use_trans_sid = 1
session.use_only_cookies = 0
(2)重新运次Index.php
点击下一页进入GoodsClass.php
可以看到,在浏览器禁用cookie之后,session仍然是可以继续传输的,只不过需要进行配置而已。
但事实上,并不太建议,也不需要这么做。毕竟是存在安全风险的。而且目前浏览器基本也不会主动禁用cookie。
四、Session在大型网站应用中需要注意的问题
1、如何解决Session文件过多,消耗IO性能
建议:可以更改php.ini的 session.save_handler 参数为redis或memcache等内存缓存数据库。
2、解决Session的同步问题
我们前端可能有很多台服务器,用户在A服务器上登录了,种下了session信息,然后访问网站的某些页面没准跳到B服务器上去了,如果这个时候B服务器上没有session信息又没有做特殊处理,可能就会出问题了。
解决方案:
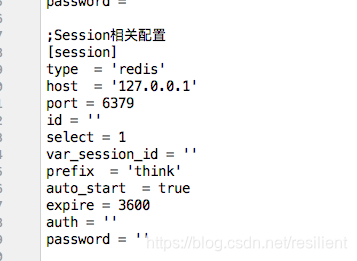
(1)更改php.ini的 session.save_handler 参数为redis或memcache等内存缓存数据库
方法一
session.save_handler = redis
session.save_path = “tcp://127.0.0.1:6379″
修改后重启php-fpm或nginx,phpinfo()方法二
ini_set(“session.save_handler”,”redis”);
ini_set(“session.save_path”,”tcp://127.0.0.1:6379″);
我在tp5配置文件是这么配置的
(2)还有一种方式是通过加密的cookie来实现,用户在A服务器上登录成功,在用户的浏览器上种上一个加密的cookie,当用户访问B服务器时,检查有无 session,如果有当然没问题,如果没有,就去检验cookie是否有效,cookie有效的话就在B服务器上重建session。这种方法其实很有 用,如果网站有很多个子频道,服务器也不在一个机房,session没办法同步又想做统一登录那就太有用了。
(3)当然还有一种方法就是在负载均衡那一层保持会话,把访问者绑定在某个服务器上,他的所有访问都在那个服务器上就不需要session同步了(比如负载均衡中的ip_hash)。





 本文深入解析Session和Cookie的工作原理及区别,演示了在Cookie禁用情况下Session的传递方法,探讨了Session在大型网站中的应用挑战及解决方案。
本文深入解析Session和Cookie的工作原理及区别,演示了在Cookie禁用情况下Session的传递方法,探讨了Session在大型网站中的应用挑战及解决方案。

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










