1、自定义注解
package com.logPrint;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 自定义注解,用于打印业务日志
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface BusinessLog {
/**
* 功能描述
*/
String description() default "";
}
2、自定义切面类
package com.logPrint;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 自定义切面类
*/
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
/**
* 自定义切点
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.logPrint.BusinessLog)")
public void logPointCut() {
}
/**
* 自定义切面
*/
@Around("logPointCut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
String description = "";
try {
// 获取HttpServletRequest
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
assert requestAttributes != null;
HttpServletRequest request = requestAttributes.getRequest();
// 获取注解参数
Method method = ((MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature()).getMethod();
description = method.getAnnotation(BusinessLog.class).description();
if (description == null || description.isEmpty()) {
description = method.getName();
}
// 获取方法参数名以及参数值
Map<String, Object> argList = getParams(joinPoint);
// 打印日志
log.info("业务日志:{},请求方法:{},请求参数:{}", description, request.getMethod(), JSON.toJSONString(argList));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("日志记录出错", e);
}
// 执行原方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 打印响应日志
log.info("业务日志:{},响应结果:{}", description, JSON.toJSONString(result));
return result;
}
/**
* 从 JoinPoint 中获取方法参数名和参数值
*
* @param joinPoint 切点对象
* @return 参数名和参数值的Map
*/
public static Map<String, Object> getParams(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Map<String, Object> paramMap = new HashMap<>();
// 获取方法参数名
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
String[] parameterNames = signature.getParameterNames();
// 获取参数值
Object[] parameterValues = joinPoint.getArgs();
// 将参数名和参数值存入Map
for (int i = 0; i < parameterNames.length; i++) {
// 过滤掉HttpServletRequest、HttpServletResponse、MultipartFile参数类型
if (parameterValues[i] instanceof HttpServletRequest || parameterValues[i] instanceof HttpServletResponse || parameterValues[i] instanceof MultipartFile) {
continue;
}
paramMap.put(parameterNames[i], parameterValues[i]);
}
return paramMap;
}
}
3、调试类
package com.logPrint;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/log")
public class LogController {
@BusinessLog(description = "日志打印测试")
@GetMapping(value = "/test")
public Map<String, String> logTest(String message, String phone) {
log.info("方法执行:log test message:{} phone:{}", message, phone);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "张三");
map.put("age", "18");
return map;
}
}
4、测试结果
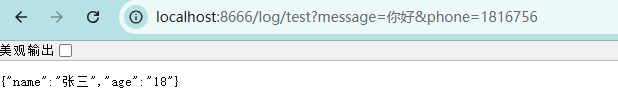
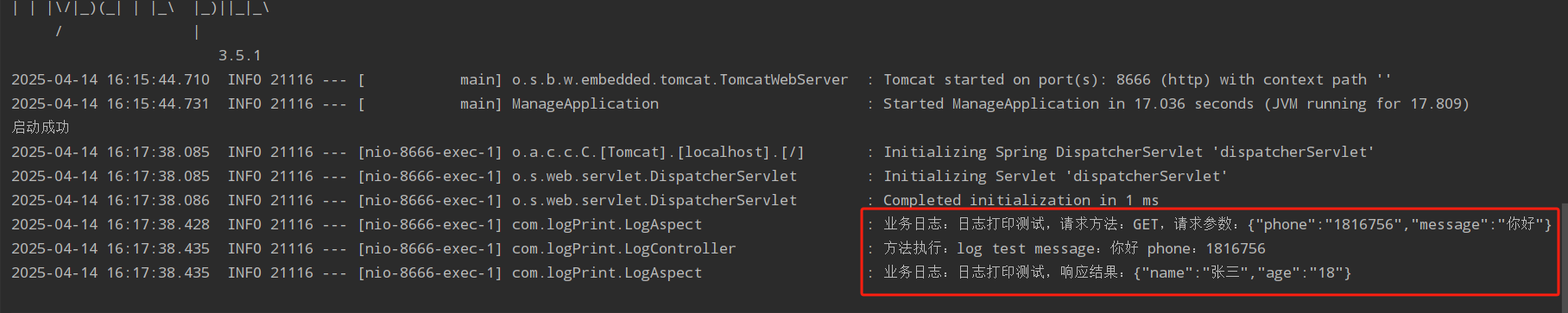

























 3226
3226

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








