前言:
在使用Penpot前,我们尝试过多种协作工具,但没有一个能同时满足三个需求:完全私有化部署、支持组件库共享、低带宽流畅操作。Penpot的离线优先设计解决了网络波动问题,即使在4G环境下也能编辑矢量图形。最让我惊喜的是它的"客户演示模式",能临时隐藏编辑界面只展示最终效果,这个细节比商业软件更懂设计服务流程。
配合cpolar固定域名后,我们的印度分公司同事终于能流畅访问总部的设计系统。上周产品发布会前夜,纽约客户通过穿透链接直接标注修改意见,北京团队实时调整,这种跨时区协作在以前需要3轮邮件往返。现在我的设计稿更新不再受地域限制,灵感来了随时可以在平板上修改。
本篇文章讲解如何在Linux系统使用Docker部署一款开源的设计和原型创作平台Penpot,并结合Cpolar内网穿透软件配置公网地址,轻松实现异地远程访问本地设计平台。
本例中,我们在Linux系统使用Docker快速进行本地部署。
目录
1. 安装Docker
本教程操作环境为Linux Ubuntu系统,在开始之前,我们需要先安装Docker与docker-compose。
在终端中执行下方命令安装docker:
```shell
sudo curl -fsSL https://github.com/tech-shrimp/docker_installer/releases/download/latest/linux.sh| bash -s docker --mirror Aliyun
```如果上边命令中访问不了Github,可以使用Gitee的链接:
```shell
sudo curl -fsSL https://gitee.com/tech-shrimp/docker_installer/releases/download/latest/linux.sh| bash -s docker --mirror Aliyun
```然后启动Docker
```shell
sudo systemctl start docker
```2. Docker镜像源添加方法
如因网络问题拉取不到镜像,
可尝试在终端执行 `sudo nano /etc/docker/daemon.json`
输入:
```json
{
"registry-mirrors": [
"https://do.nark.eu.org",
"https://dc.j8.work",
"https://docker.m.daocloud.io",
"https://dockerproxy.com",
"https://docker.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn",
"https://docker.nju.edu.cn"
]
}
```保存退出
然后执行:`sudo systemctl restart docker`
3. 创建并启动Penpot容器
成功拉取 Piwigo 镜像后,我们在Home目录下的docker路径新增该项目目录
```shell
mkdir penpot
```
```shell
cd penpot
```然后在该项目中创建**docker-compose.yml**
```shell
nano docker-compose.yml
```输入下方代码并保存退出:
```yml
version: "3.8"
networks:
penpot:
volumes:
penpot_postgres_v15:
penpot_assets:
# penpot_traefik:
# penpot_minio:
services:
## Traefik service declaration example. Consider using it if you are going to expose
## penpot to the internet or different host than `localhost`.
# traefik:
# image: traefik:v2.9
# networks:
# - penpot
# command:
# - "--api.insecure=true"
# - "--entryPoints.web.address=:80"
# - "--providers.docker=true"
# - "--providers.docker.exposedbydefault=false"
# - "--entryPoints.websecure.address=:443"
# - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.tlschallenge=true"
# - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.email=<EMAIL_ADDRESS>"
# - "--certificatesresolvers.letsencrypt.acme.storage=/traefik/acme.json"
# volumes:
# - "penpot_traefik:/traefik"
# - "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
# ports:
# - "80:80"
# - "443:443"
penpot-frontend:
image: "penpotapp/frontend:latest"
restart: always
ports:
- 9001:80
volumes:
- penpot_assets:/opt/data/assets
depends_on:
- penpot-backend
- penpot-exporter
networks:
- penpot
labels:
- "traefik.enable=true"
## HTTP: example of labels for the case if you are going to expose penpot to the
## internet using only HTTP (without HTTPS) with traefik
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-http.entrypoints=web"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-http.rule=Host(`<DOMAIN_NAME>`)"
# - "traefik.http.services.penpot-http.loadbalancer.server.port=80"
## HTTPS: example of labels for the case if you are going to expose penpot to the
## internet using with HTTPS using traefik
# - "traefik.http.middlewares.http-redirect.redirectscheme.scheme=https"
# - "traefik.http.middlewares.http-redirect.redirectscheme.permanent=true"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-http.entrypoints=web"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-http.rule=Host(`<DOMAIN_NAME>`)"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-http.middlewares=http-redirect"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-https.entrypoints=websecure"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-https.rule=Host(`<DOMAIN_NAME>`)"
# - "traefik.http.services.penpot-https.loadbalancer.server.port=80"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-https.tls=true"
# - "traefik.http.routers.penpot-https.tls.certresolver=letsencrypt"
## Configuration envronment variables for frontend the container. In this case this
## container only needs the `PENPOT_FLAGS`. This environment variable is shared with
## other services but not all flags are relevant to all services.
environment:
## Relevant flags for frontend:
## - demo-users
## - login-with-github
## - login-with-gitlab
## - login-with-google
## - login-with-ldap
## - login-with-oidc
## - login-with-password
## - registration
## - webhooks
##
## You can read more about all available flags on:
## https://help.penpot.app/technical-guide/configuration/#advanced-configuration
- PENPOT_FLAGS=enable-registration enable-login-with-password
penpot-backend:
image: "penpotapp/backend:latest"
restart: always
volumes:
- penpot_assets:/opt/data/assets
depends_on:
- penpot-postgres
- penpot-redis
networks:
- penpot
## Configuration envronment variables for backend the
## container.
environment:
## Relevant flags for backend:
## - demo-users
## - email-verification
## - log-emails
## - log-invitation-tokens
## - login-with-github
## - login-with-gitlab
## - login-with-google
## - login-with-ldap
## - login-with-oidc
## - login-with-password
## - registration
## - secure-session-cookies
## - smtp
## - smtp-debug
## - telemetry
## - webhooks
## - prepl-server
##
## You can read more about all available flags and other
## environment variables for the backend here:
## https://help.penpot.app/technical-guide/configuration/#advanced-configuration
- PENPOT_FLAGS=enable-registration disable-secure-session-cookies
## Penpot SECRET KEY. It serves as a master key from which other keys for subsystems
## (eg http sessions, or invitations) are derived.
##
## If you leve it commented, all created sessions and invitations will
## become invalid on container restart.
##
## If you going to uncomment this, we recommend use here a trully randomly generated
## 512 bits base64 encoded string. You can generate one with:
##
## python3 -c "import secrets; print(secrets.token_urlsafe(64))"
# - PENPOT_SECRET_KEY=my-insecure-key
## The PREPL host. Mainly used for external programatic access to penpot backend
## (example: admin). By default it listen on `localhost` but if you are going to use
## the `admin`, you will need to uncomment this and set the host to `0.0.0.0`.
# - PENPOT_PREPL_HOST=0.0.0.0
## Public URI. If you are going to expose this instance to the internet and use it
## under different domain than 'localhost', you will need to adjust it to the final
## domain.
##
## Consider using traefik and set the 'disable-secure-session-cookies' if you are
## not going to serve penpot under HTTPS.
- PENPOT_PUBLIC_URI=http://localhost:9001
## Database connection parameters. Don't touch them unless you are using custom
## postgresql connection parameters.
- PENPOT_DATABASE_URI=postgresql://penpot-postgres/penpot
- PENPOT_DATABASE_USERNAME=penpot
- PENPOT_DATABASE_PASSWORD=penpot
## Redis is used for the websockets notifications. Don't touch unless the redis
## container has different parameters or different name.
- PENPOT_REDIS_URI=redis://penpot-redis/0
## Default configuration for assets storage: using filesystem based with all files
## stored in a docker volume.
- PENPOT_ASSETS_STORAGE_BACKEND=assets-fs
- PENPOT_STORAGE_ASSETS_FS_DIRECTORY=/opt/data/assets
## Also can be configured to to use a S3 compatible storage
## service like MiniIO. Look below for minio service setup.
# - AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<KEY_ID>
# - AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY=<ACCESS_KEY>
# - PENPOT_ASSETS_STORAGE_BACKEND=assets-s3
# - PENPOT_STORAGE_ASSETS_S3_ENDPOINT=http://penpot-minio:9000
# - PENPOT_STORAGE_ASSETS_S3_BUCKET=<BUKET_NAME>
## Telemetry. When enabled, a periodical process will send anonymous data about this
## instance. Telemetry data will enable us to learn on how the application is used,
## based on real scenarios. If you want to help us, please leave it enabled. You can
## audit what data we send with the code available on github
- PENPOT_TELEMETRY_ENABLED=true
## Example SMTP/Email configuration. By default, emails are sent to the mailcatch
## service, but for production usage is recommended to setup a real SMTP
## provider. Emails are used to confirm user registrations & invitations. Look below
## how mailcatch service is configured.
- PENPOT_SMTP_DEFAULT_FROM=no-reply@example.com
- PENPOT_SMTP_DEFAULT_REPLY_TO=no-reply@example.com
- PENPOT_SMTP_HOST=penpot-mailcatch
- PENPOT_SMTP_PORT=1025
- PENPOT_SMTP_USERNAME=
- PENPOT_SMTP_PASSWORD=
- PENPOT_SMTP_TLS=false
- PENPOT_SMTP_SSL=false
penpot-exporter:
image: "penpotapp/exporter:latest"
restart: always
networks:
- penpot
environment:
# Don't touch it; this uses internal docker network to
# communicate with the frontend.
- PENPOT_PUBLIC_URI=http://penpot-frontend
## Redis is used for the websockets notifications.
- PENPOT_REDIS_URI=redis://penpot-redis/0
penpot-postgres:
image: "postgres:15"
restart: always
stop_signal: SIGINT
volumes:
- penpot_postgres_v15:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- penpot
environment:
- POSTGRES_INITDB_ARGS=--data-checksums
- POSTGRES_DB=penpot
- POSTGRES_USER=penpot
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=penpot
penpot-redis:
image: redis:7
restart: always
networks:
- penpot
## A mailcatch service, used as temporal SMTP server. You can access via HTTP to the
## port 1080 for read all emails the penpot platform has sent. Should be only used as a
## temporal solution meanwhile you don't have a real SMTP provider configured.
penpot-mailcatch:
image: sj26/mailcatcher:latest
restart: always
expose:
- '1025'
ports:
- "1080:1080"
networks:
- penpot
## Example configuration of MiniIO (S3 compatible object storage service); If you don't
## have preference, then just use filesystem, this is here just for the completeness.
# minio:
# image: "minio/minio:latest"
# command: minio server /mnt/data --console-address ":9001"
# restart: always
#
# volumes:
# - "penpot_minio:/mnt/data"
#
# environment:
# - MINIO_ROOT_USER=minioadmin
# - MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD=minioadmin
#
# ports:
# - 9000:9000
# - 9001:9001
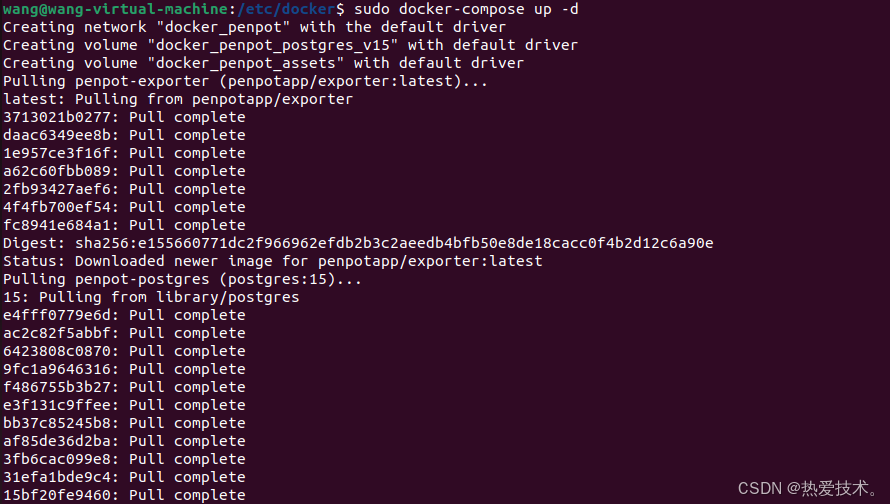
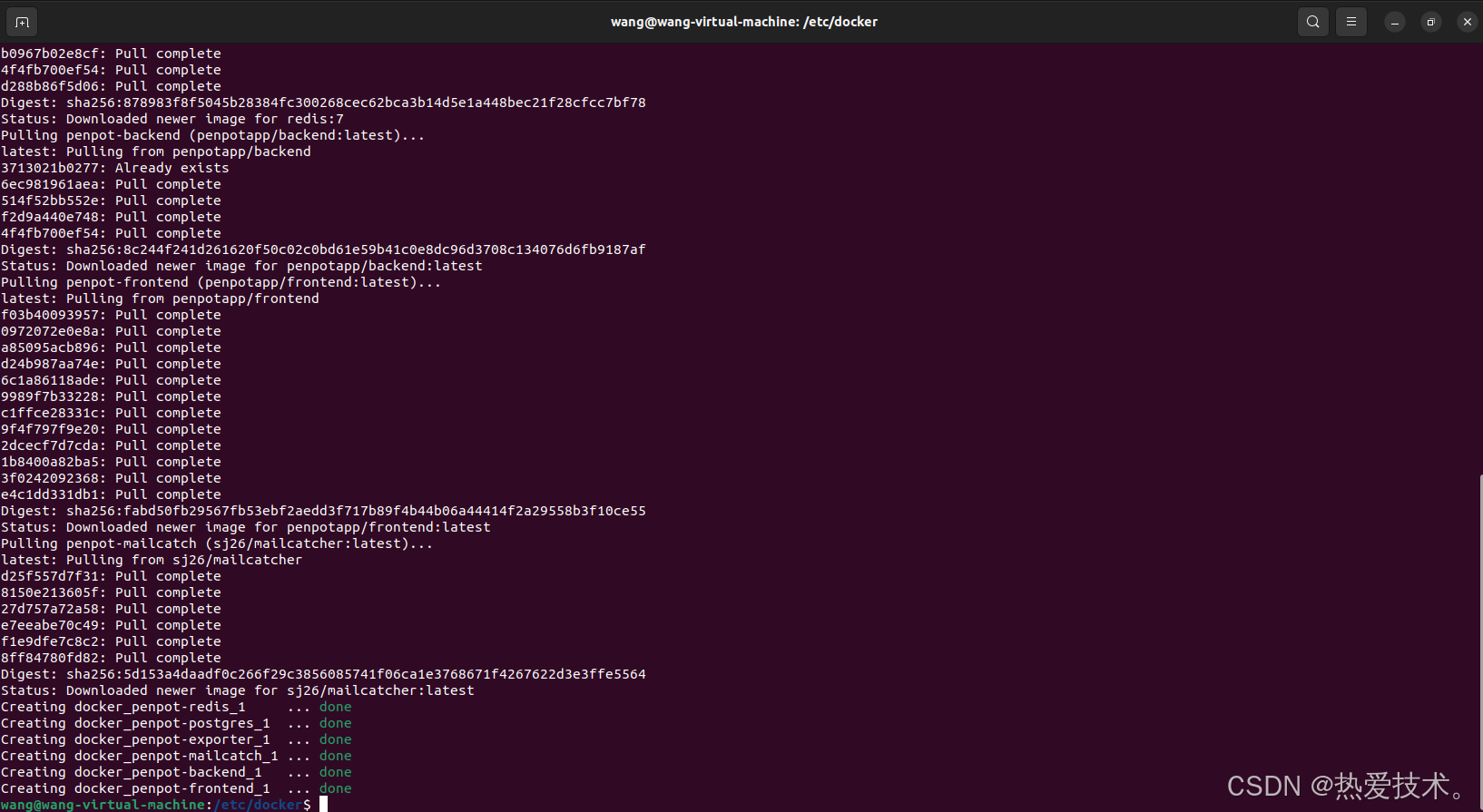
```然后执行下方命令启动容器运行镜像:
```shell
sudo docker compose up -d
```
如需停止可以执行:
```shell
sudo docker-compose down
```
3. 本地使用Penpot进行创作
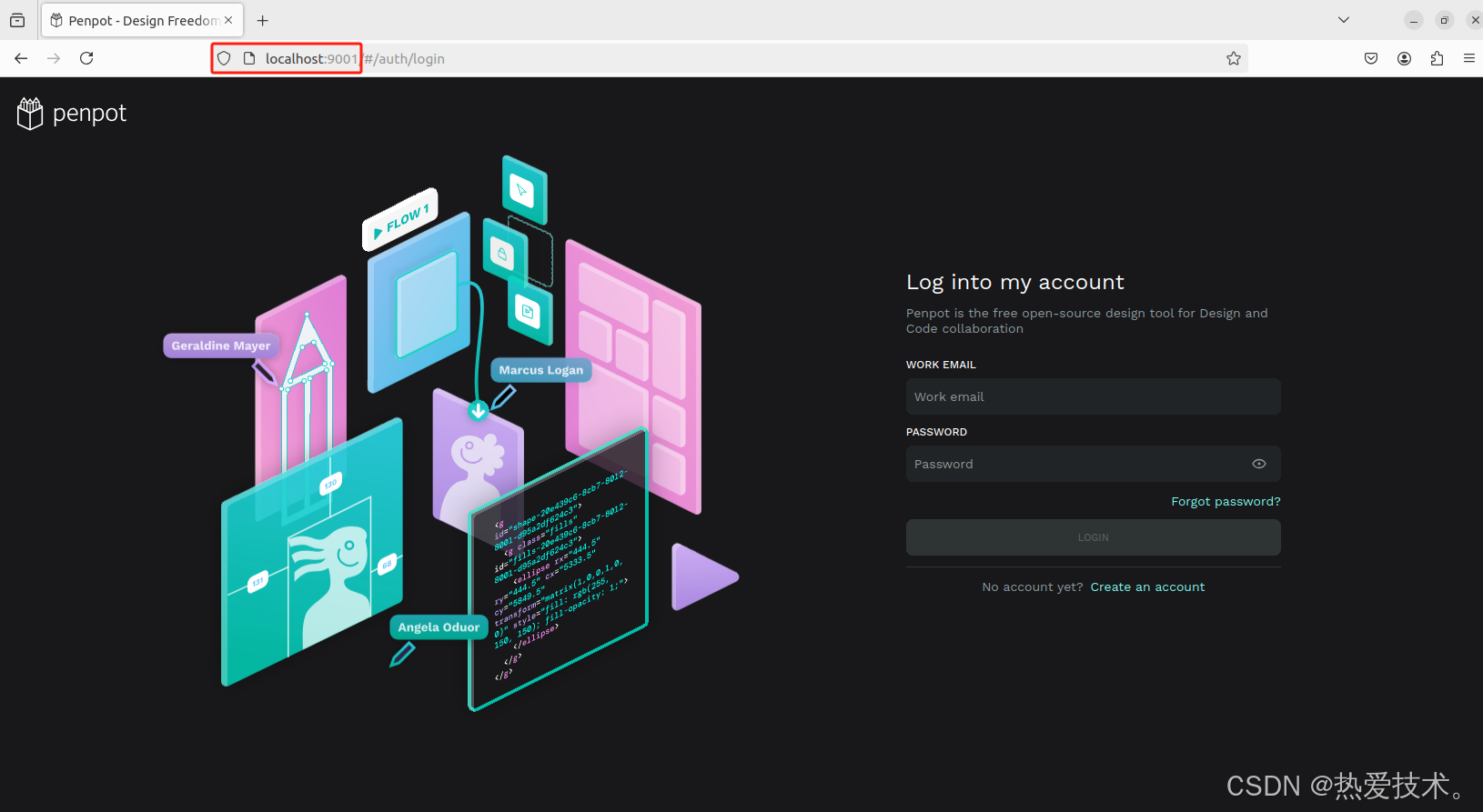
接下来我们就可以通过任意浏览器进行访问测试,打开一个浏览器输入localhost:9001,可以看到进入到了Penpot的登录界面,注册一个用户名和密码。
选择使用用途
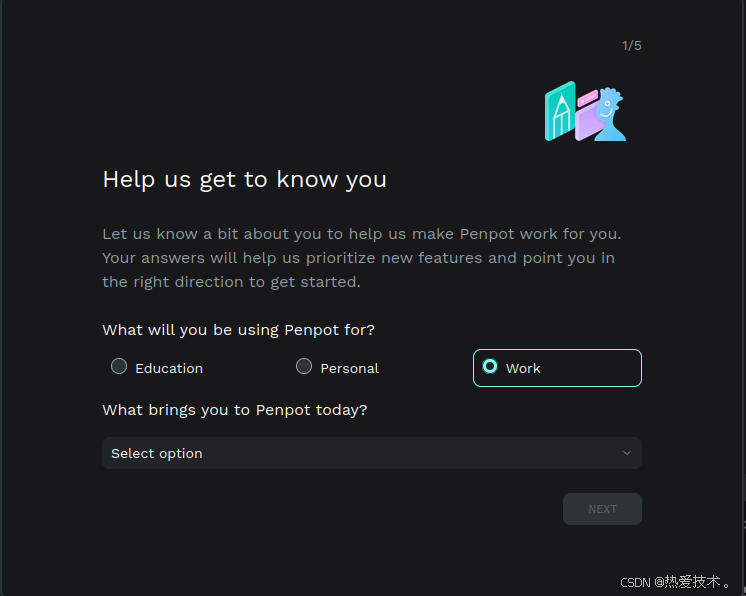
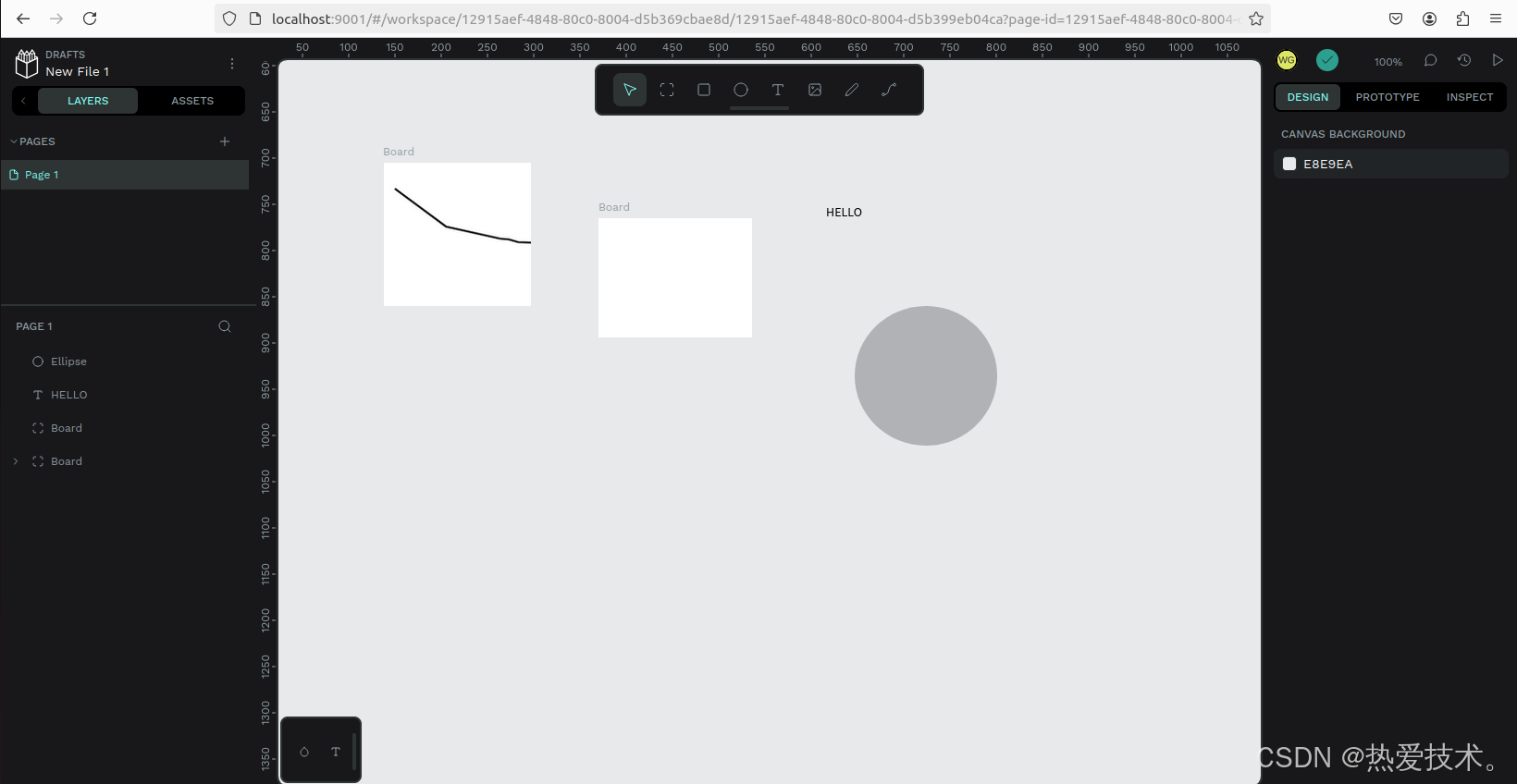
然后进入到设计界面,可以自由创作了!
画板跟同类设计软件的画布功能差不多,并具有固定的边缘。你可以根据你的需要,选择一个特定的屏幕或打印用的尺寸。
1. 创建画板:点击工具栏中 “移动” 箭头正下方的第一个方形图标。点击并拖动箭头来创建一个自定义尺寸的画板。你也可以在 “设计属性” 边栏选择包揽设备最常用分辨率和标准打印尺寸的预设模板。
2. 选择和移动画板:点击画板的名称或没有图层的区域。当边框变成绿色时,代表着你选择成功了。一旦选择了,按住 “Shift” 键,然后点击并拖动画板来移动它。
3. 设置画板为缩略图:选择一个画板并点击右键。在菜单上,选择 “设置为缩略图”。选定的画板将作为文件缩略图显示在仪表板的卡片上。
目前我们在本机部署了 Penpot ,如果想团队协作多人使用,或者在异地其他设备使用的话就需要结合Cpolar内网穿透实现公网访问,免去了复杂得本地部署过程,只需要一个公网地址直接就可以进入到Penpot中。
接下来教大家如何安装Cpolar并且将 Penpot 实现公网访问。
4. 公网远程访问本地Penpot
### 4.1 内网穿透工具安装
下面是安装cpolar步骤:
> Cpolar官网地址: [https://www.cpolar.com](https://www.cpolar.com/)
使用一键脚本安装命令
```
curl https://get.cpolar.sh | sudo sh
```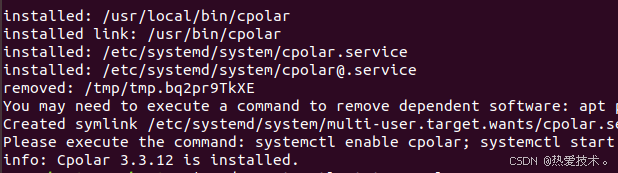
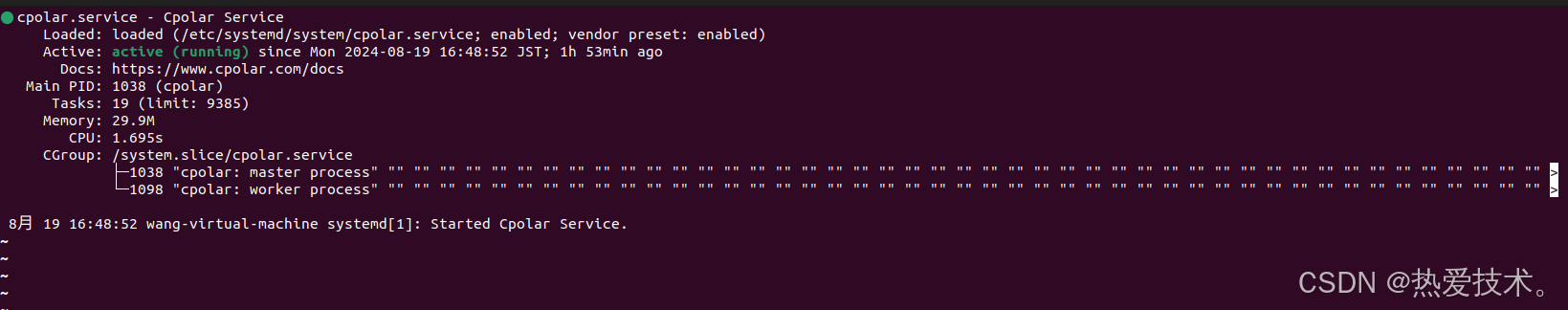
安装完成后,执行下方命令查看cpolar服务状态:(如图所示即为正常启动)
```
sudo systemctl status cpolar
```
Cpolar安装和成功启动服务后,在浏览器上输入ubuntu主机IP加9200端口即:【[http://localhost:9200](http://localhost:9200/)】访问Cpolar管理界面,使用Cpolar官网注册的账号登录,登录后即可看到cpolar web 配置界面,接下来在web 界面配置即可:
### 4.2 创建远程连接公网地址
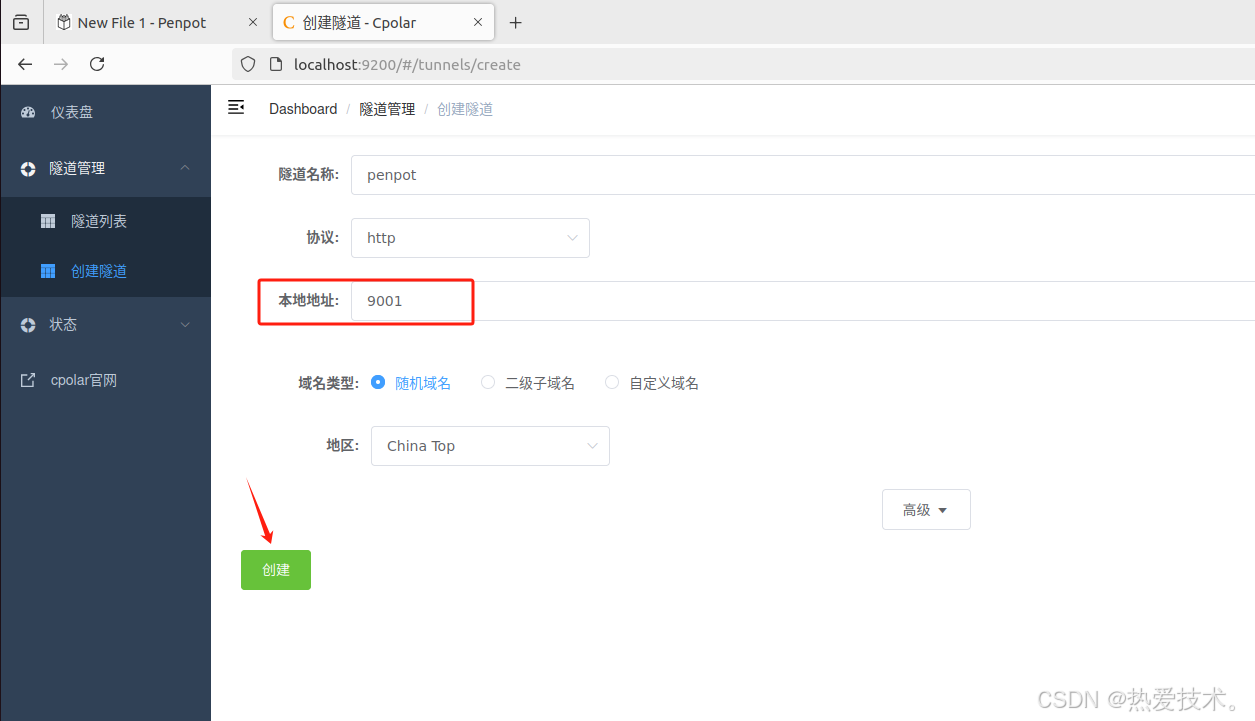
登录cpolar web UI管理界面后,点击左侧仪表盘的隧道管理——创建隧道:
- 隧道名称:可自定义,本例使用了: Penpot 注意不要与已有的隧道名称重复
- 协议:http
- 本地地址:9001
- 域名类型:随机域名
- 地区:选择China Top
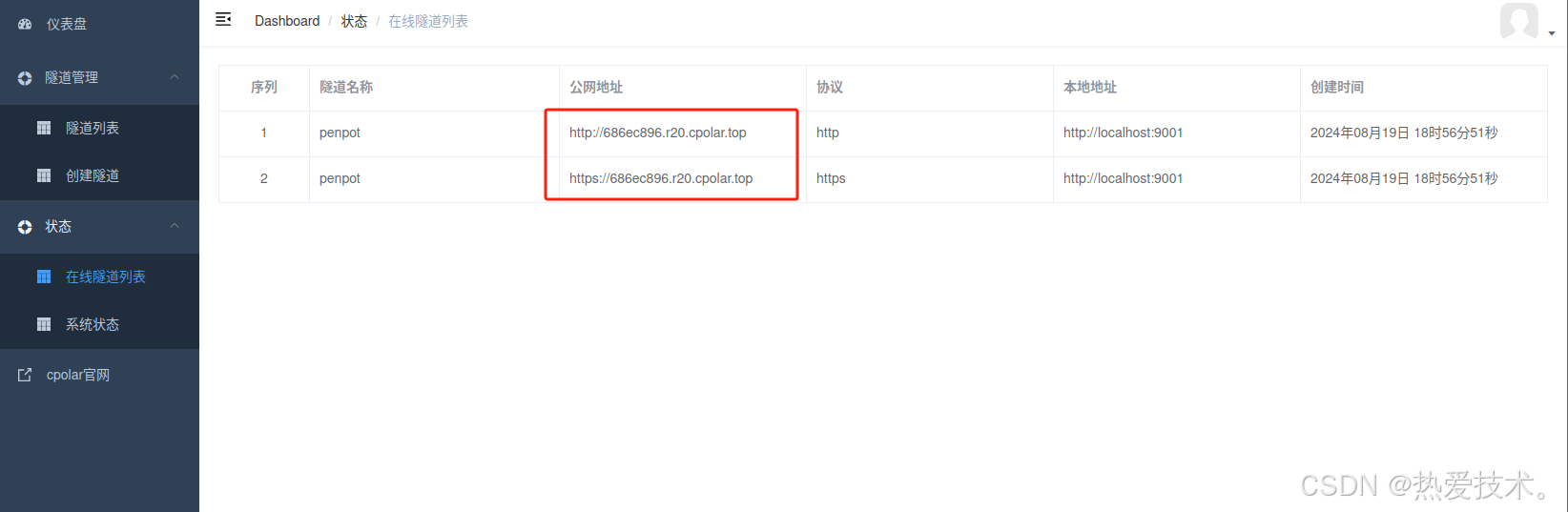
创建成功后,打开左侧在线隧道列表,可以看到刚刚通过创建隧道生成了两个公网地址,接下来就可以在其他电脑(异地)上,使用任意一个地址在浏览器中访问即可。
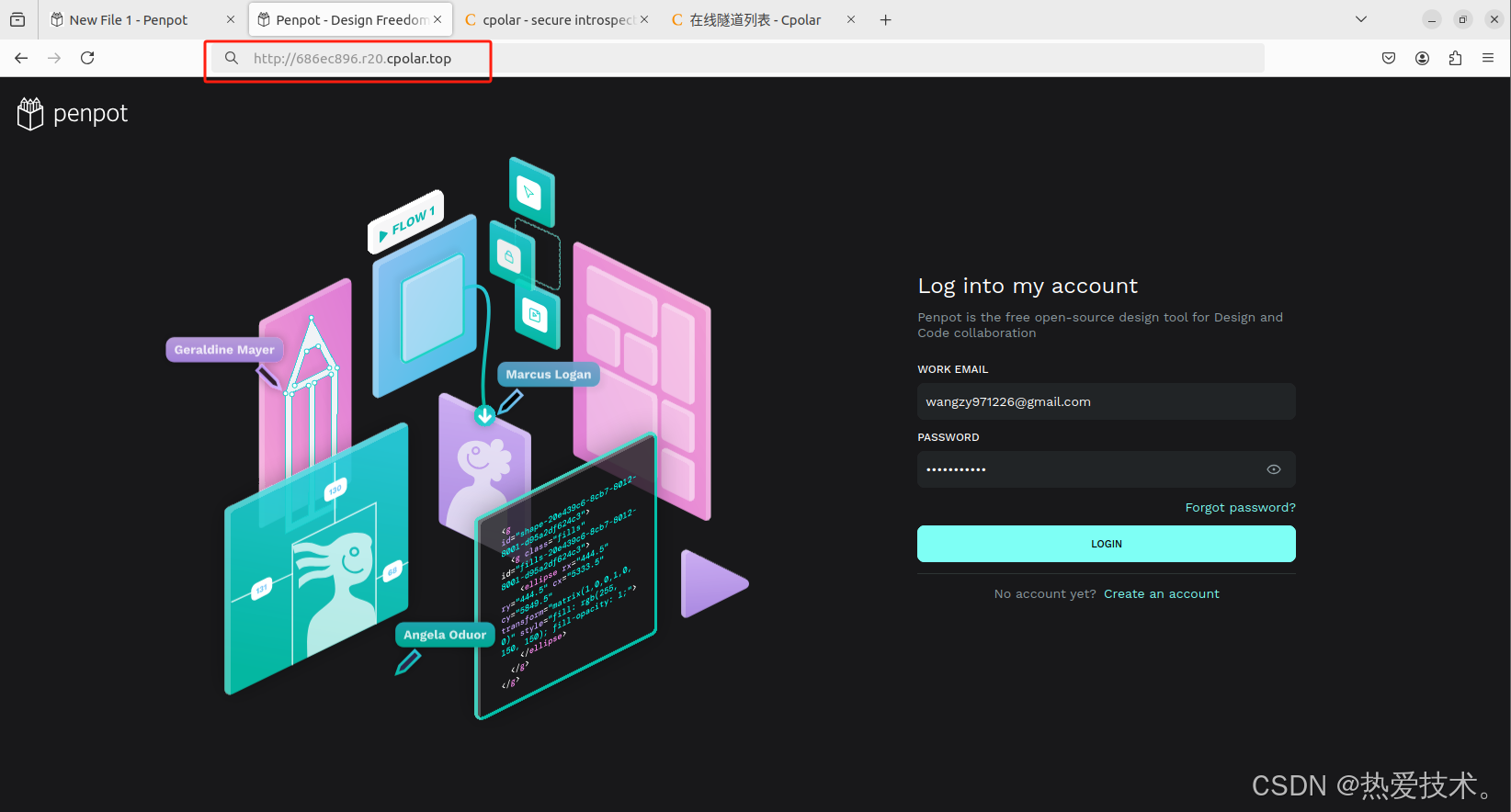
如下图所示,成功实现使用公网地址异地远程访问本地部署的Penpot设计创作平台!
**小结**
为了方便演示,我们在上边的操作过程中使用了cpolar生成的HTTP公网地址隧道,其公网地址是随机生成的。
这种随机地址的优势在于建立速度快,可以立即使用。然而,它的缺点是网址是随机生成,这个地址在24小时内会发生随机变化,更适合于临时使用。
如果有长期远程访问本地 Penpot设计创作平台或者其他本地部署的服务的需求,但又不想每天重新配置公网地址,还想地址好看又好记,那我推荐大家选择使用固定的二级子域名方式来远程访问。
5. 固定Penpot公网地址
由于以上使用cpolar所创建的隧道使用的是随机公网地址,24小时内会随机变化,不利于长期远程访问。因此我们可以为其配置二级子域名,该地址为固定地址,不会随机变化【ps:cpolar.cn已备案】
> 注意需要将cpolar套餐升级至基础套餐或以上,且每个套餐对应的带宽不一样。【cpolar.cn已备案】
登录cpolar官网,点击左侧的预留,选择保留二级子域名,地区选择china vip top,然后设置一个二级子域名名称,填写备注信息,点击保留。
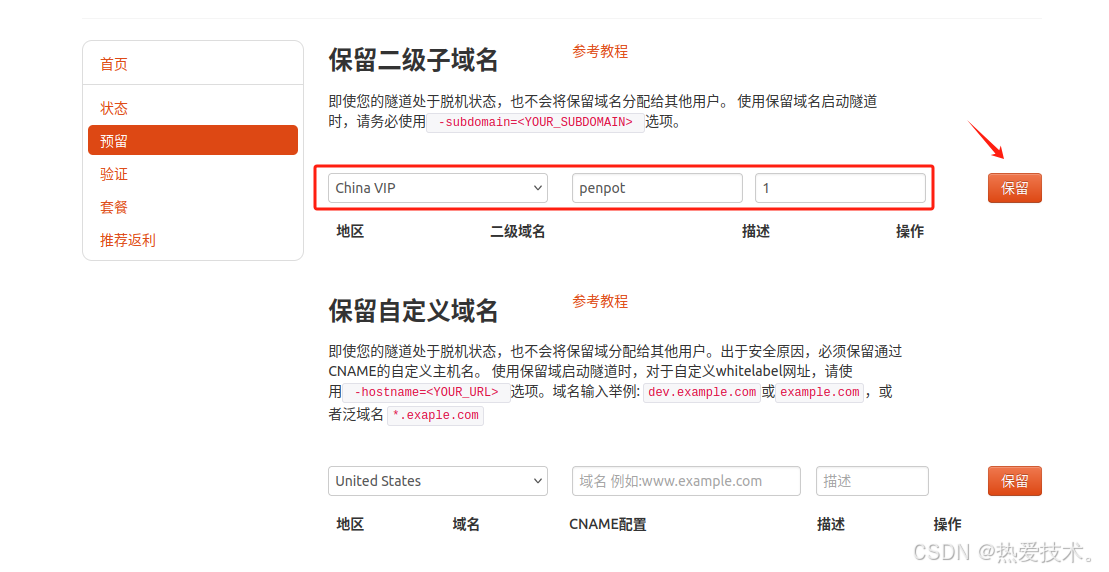
保留成功后复制保留的二级子域名地址:
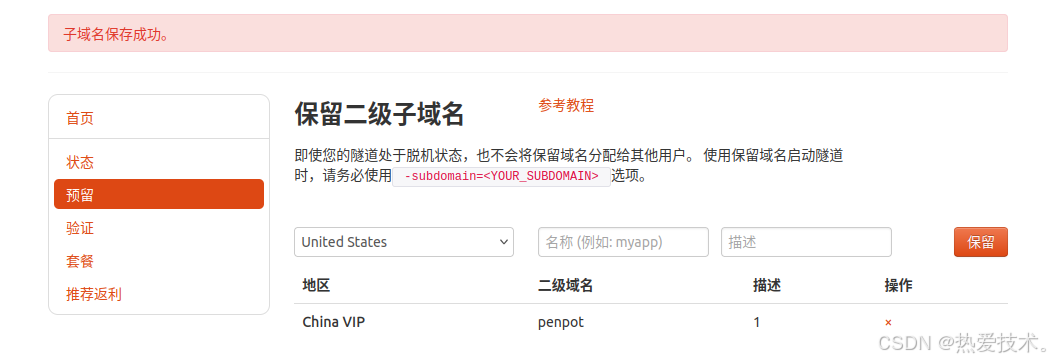
登录cpolar web UI管理界面,点击左侧仪表盘的隧道管理——隧道列表,找到所要配置的隧道,点击右侧的`编辑`。
修改隧道信息,将保留成功的二级子域名配置到隧道中
- 域名类型:选择二级子域名
- Sub Domain:填写保留成功的二级子域名
- 地区: China VIP
点击`更新`
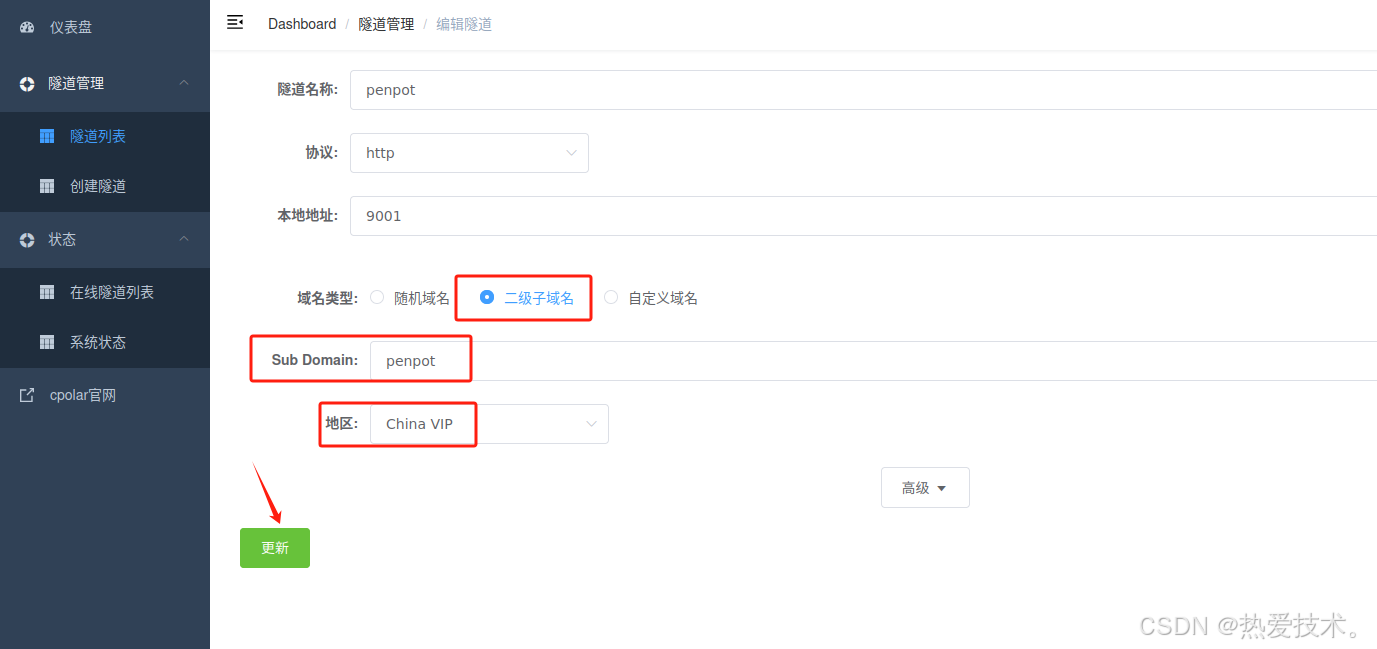
更新完成后,打开在线隧道列表,此时可以看到随机的公网地址已经发生变化,地址名称也变成了保留和固定的二级子域名名称。
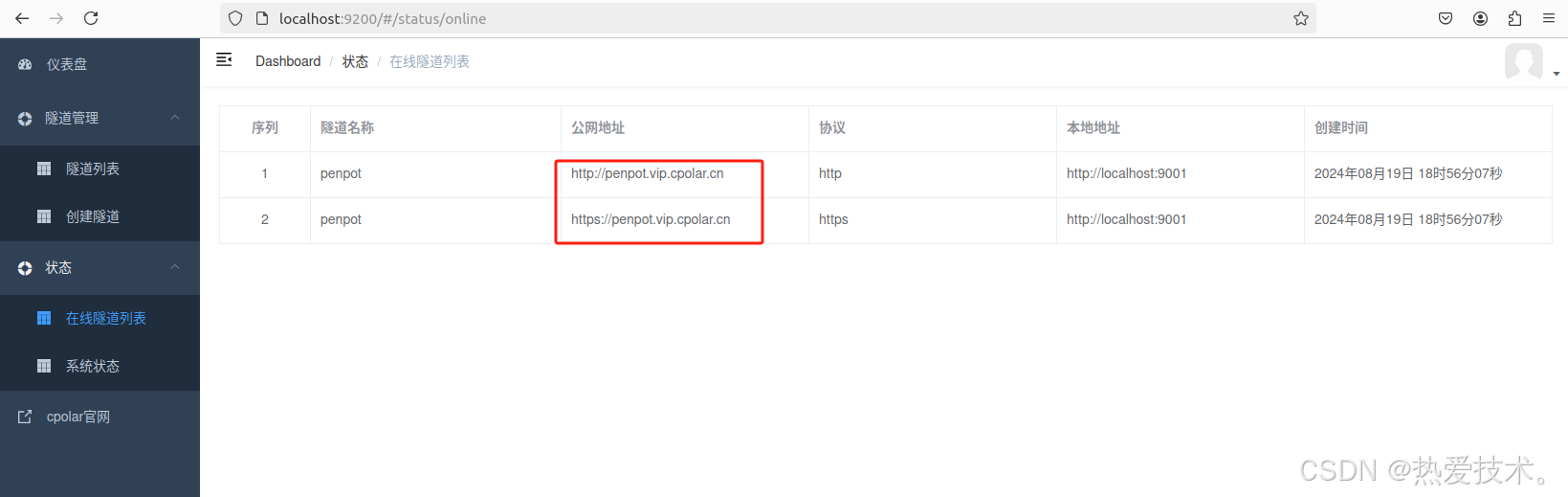
最后,我们使用固定的公网地址访问 Penpot 界面可以看到访问成功,一个永久不会变化的远程访问方式即设置好了。
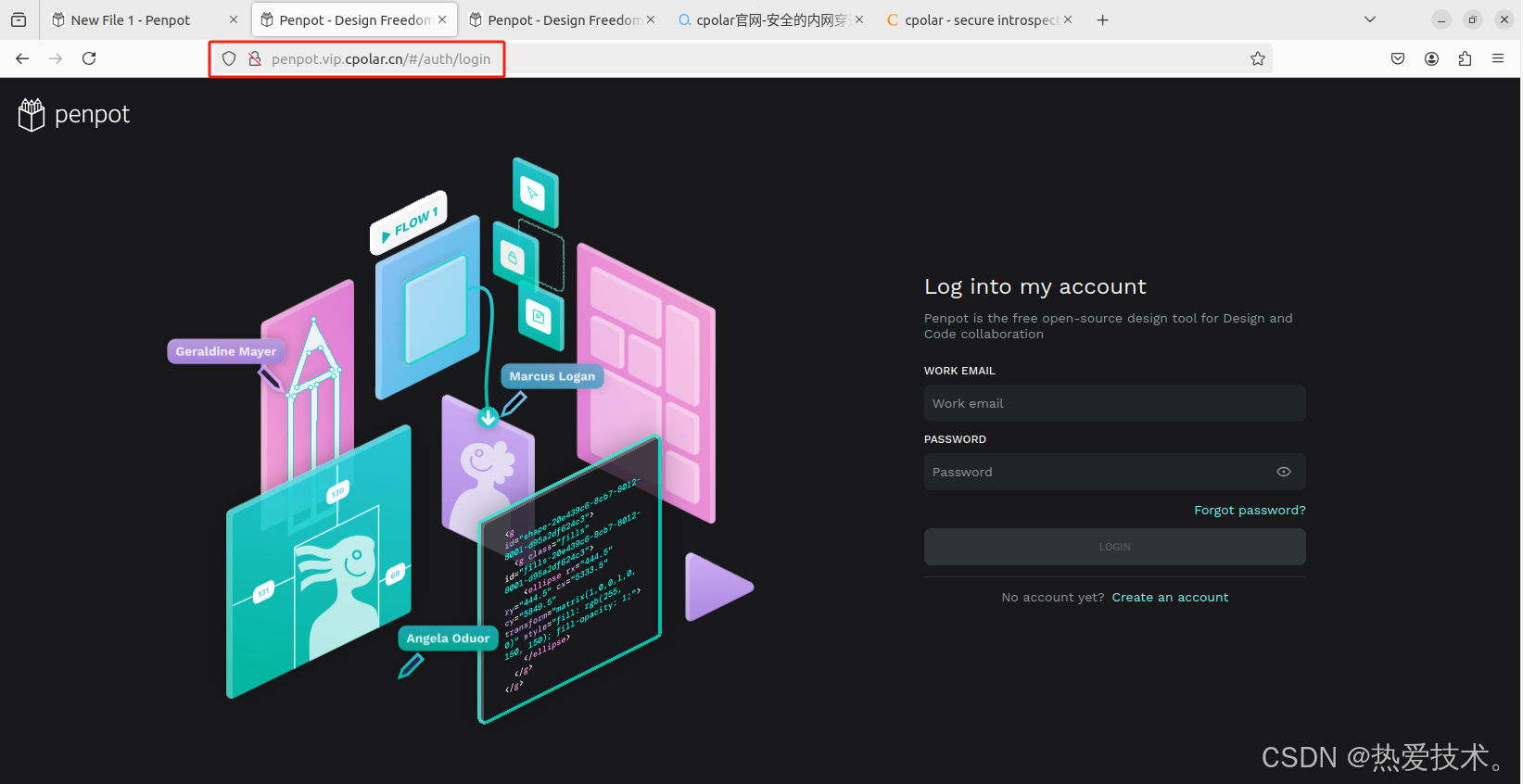
接下来就可以随时随地进行异地公网来使用Penpot创作平台了,把固定的公网地址分享给身边的人,方便团队协作,同时也大大提高了工作效率!自己用的话,无需云服务器,还可以实现异地其他设备登录!以上就是如何在本地安装Penpot的全部过程。
**这套组合让我们的跨国项目交付周期缩短40%,而服务器成本仅为商业方案的1/5——开源工具的力量正在于此。**
本篇文章知识点来源[cpolar官网][https://www.cpolar.com]























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








