BMP 基本概念
定义与核心特点
BMP(Bitmap,位图)是微软提出的图像文件格式,全称 “设备无关位图(DIB)”,核心特点如下:
- 无压缩:像素数据直接存储,无需解码器即可读取,开发中操作简单;
- 文件较大:无压缩导致文件体积大,不适合网络传输,适合本地开发(如 LCD 显示);
- 设备无关:图像数据与显示设备无关,在不同硬件上显示效果一致;
- 颜色支持全:可支持 1bit(2 色)、4bit(16 色)、8bit(256 色)、16bit(65536 色)、24bit(1678 万色)、32bit(增强真彩色),其中 24bit 是开发中最常用的类型。
与其他图像格式的区别
| 格式 | 压缩方式 | 解码难度 | 文件大小 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMP | 无压缩 | 无(直接读) | 大 | 本地开发、LCD 显示 |
| JPEG | 有损压缩 | 需解码器 | 小 | 照片、网络传输 |
| PNG | 无损压缩 | 需解码器 | 中 | 图标、透明图像、网络传输 |
BMP 内部结构
BMP 文件从开头到结尾依次分为 4 个部分,总结构可表示为:位图文件头(14字节) + 位图信息头(40字节) + 调色板(可选) + 位图数据,其中前两部分固定共 54 字节(需重点记忆)。
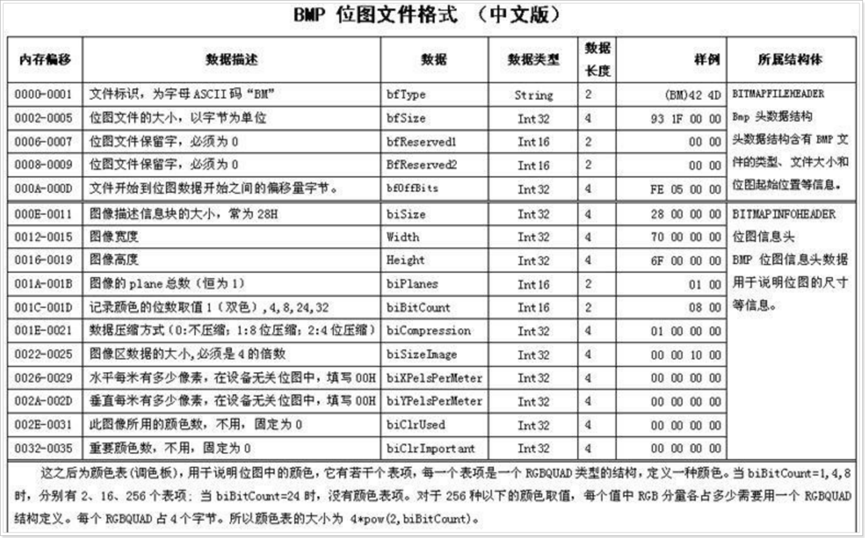
位图文件头(BITMAPFILEHEADER,14 字节)
作用:存储 BMP 文件的基础信息,用于识别文件类型和定位像素数据。结构体定义与字段说明(需注意:编译器默认会对结构体进行 “字节对齐”,需用#pragma pack(1)取消对齐,否则会读错数据):
#pragma pack(1) // 取消结构体字节对齐,确保14字节大小
// 位图文件头结构体(14字节)
typedef struct {
unsigned short bfType; // 2字节:文件标识,必须为0x4D42(即ASCII码“BM”)
unsigned int bfSize; // 4字节:BMP文件总大小(单位:字节)
unsigned short bfReserved1; // 2字节:保留字,必须为0
unsigned short bfReserved2; // 2字节:保留字,必须为0
unsigned int bfOffBits; // 4字节:从文件开头到“位图数据”的偏移量(单位:字节)
} BITMAPFILEHEADER;
#pragma pack() // 恢复默认对齐
字段示例(结合十六进制查看器):
- bfType:0x4D42 → 存储为
42 4D(小端); - bfSize:若文件总大小为 705 字节(0x000002C1)→ 存储为
C1 02 00 00; - bfOffBits:若偏移量为 54 字节(0x00000036)→ 存储为
36 00 00 00(无调色板时,偏移量通常为 54)。
位图信息头(BITMAPINFOHEADER,40 字节)
作用:存储 BMP 图像的技术参数,如分辨率、色深、压缩方式等。结构体定义与字段说明:
#pragma pack(1)// 位图信息头结构体(40字节)
typedef struct {
unsigned int biSize; // 4字节:本结构体大小(固定为40字节,0x28)
int biWidth; // 4字节:图像宽度(单位:像素,正数)
int biHeight; // 4字节:图像高度(单位:像素;正数=从下到上存储,负数=从上到下存储)
unsigned short biPlanes; // 2字节:色彩平面数,必须为1
unsigned short biBitCount; // 2字节:色深(每个像素的bit数),常见1/4/8/24/32
unsigned int biCompression; // 4字节:压缩方式,0=无压缩(开发中常用)
unsigned int biSizeImage; // 4字节:位图数据总大小(单位:字节,=每行字节数×高度)
int biXPelsPerMeter;// 4字节:水平分辨率(像素/米,设备无关时填0)
int biYPelsPerMeter;// 4字节:垂直分辨率(像素/米,设备无关时填0)
unsigned int biClrUsed; // 4字节:实际使用的颜色数(0=使用所有色深对应的颜色)
unsigned int biClrImportant; // 4字节:重要颜色数(0=所有颜色都重要)
} BITMAPINFOHEADER;
#pragma pack()
关键字段注意点:
- biHeight:正数表示像素 “从下到上” 存储(BMP 默认),负数表示 “从上到下”,开发中需根据此值判断是否需要翻转行;
- biBitCount:24bit(真彩色)最常用,无调色板,像素数据直接为 BGR 格式;
- biCompression:必须为 0(无压缩),否则需解码,开发中一般只处理无压缩 BMP。
调色板(可选,RGBQUAD)
作用:为低色深(1/4/8bit)BMP 提供颜色映射,高色深(16/24/32bit)BMP 无调色板。调色板结构(RGBQUAD,4 字节 / 个):
#pragma pack(1)// 调色板颜色项结构体(4字节/个)
typedef struct {
unsigned char rgbBlue; // 1字节:蓝色分量(B)
unsigned char rgbGreen; // 1字节:绿色分量(G)
unsigned char rgbRed; // 1字节:红色分量(R)
unsigned char rgbReserved; // 1字节:保留位,必须为0
} RGBQUAD;
#pragma pack()
调色板数量计算:
- 1bit BMP:2 种颜色 → 2 个 RGBQUAD → 8 字节;
- 4bit BMP:16 种颜色 → 16 个 RGBQUAD → 64 字节;
- 8bit BMP:256 种颜色 → 256 个 RGBQUAD → 1024 字节;
- 24/32bit BMP:无调色板 → 0 字节。
示例:8bit BMP 中,若某调色板项为00 FF 00 00,表示该索引对应的颜色是纯绿色(B=0,G=255,R=0)。
位图数据(核心)
作用:存储每个像素的颜色信息,格式由色深和是否有调色板决定。
数据格式
- 有调色板(1/4/8bit):存储 “颜色索引”,每个索引对应调色板中的一个 RGBQUAD;
- 1bit:每 8 个像素占 1 字节(每个像素 1bit,0/1 对应 2 种颜色);
- 4bit:每 2 个像素占 1 字节(每个像素 4bit,0~15 对应 16 种颜色);
- 8bit:每个像素占 1 字节(0~255 对应 256 种颜色);
- 无调色板(24/32bit):直接存储颜色分量;
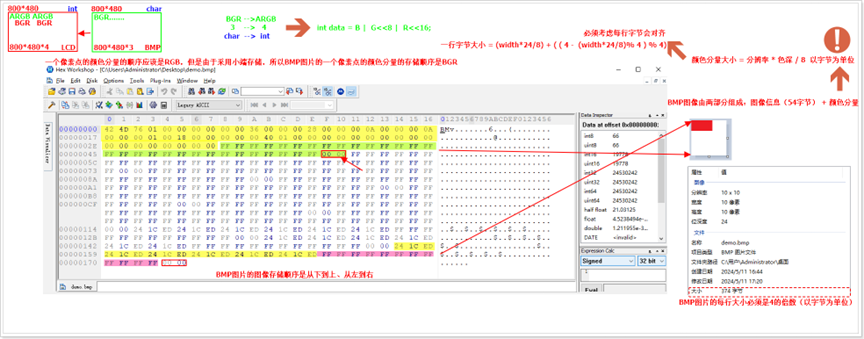
- 24bit:每个像素 3 字节,顺序为B→G→R(重点!BMP 默认 BGR 顺序,非 RGB);
- 32bit:每个像素 4 字节,顺序为B→G→R→A(A 为透明度,0 = 透明,255 = 不透明)。
行对齐规则
CPU 为提高读取效率,要求 BMP 每行的字节数必须是4 的倍数。若自然每行字节数(宽度 × 色深字节数)不是 4 的倍数,需在每行末尾补 “0” 字节,公式如下:
- 色深字节数 = biBitCount / 8(如 24bit=3 字节,8bit=1 字节);
- 自然每行字节数 = 宽度 × 色深字节数;
- 补齐字节数 = (4 - (自然每行字节数 % 4)) % 4;
- 注:要将自然每行字节数 % 4 = 0的情况考虑进去
- 实际每行字节数 = 自然每行字节数 + 补齐字节数。
示例:10×10 的 24bit BMP(宽度 = 10,色深字节数 = 3):
- 自然每行字节数 = 10×3 = 30;
- 补齐字节数 = (4 - 30%4) %4 = (4-2)%4=2;
- 实际每行字节数 = 30+2=32(是 4 的倍数);
- 位图数据总大小 = 32×10=320 字节。
存储顺序
BMP 的像素数据是从下到上、从左到右存储的(biHeight 为正数时),例如 10×10 的图像:
- 第 1 行数据(文件中)对应图像的 “第 10 行”(显示时的最下行);
- 第 10 行数据(文件中)对应图像的 “第 1 行”(显示时的最上行);开发中需将行翻转,才能在 LCD 上正常显示(LCD 通常是从上到下显示)。
BMP 关键技术点
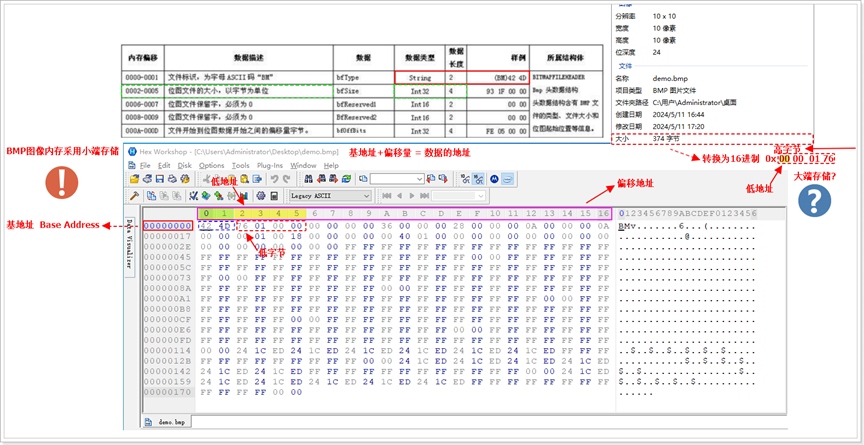
小端存储(必须掌握)
BMP 中多字节数据(如 int32、int16)采用小端字节序存储,即 “低字节存低地址,高字节存高地址”。示例:biWidth=800(十进制)=0x00000320(十六进制):
- 小端存储顺序:20 03 00 00(低字节 20 存低地址,高字节 00 存高地址);
- 读取时:需按小端解析,将字节组合为 0x00000320,即 800 像素。
验证工具:用十六进制查看器(如 Hex Workshop)打开 BMP,查看文件头的 bfSize(偏移 0x02~0x05),若显示 “93 1F 00 00”,则实际值为 0x00001F93=705 字节。
像素颜色转换(BMP→LCD)
LCD 通常使用 32bit ARGB 格式(A = 透明度,R = 红,G = 绿,B = 蓝),而 24bit BMP 是 32bit BGR 格式(无 A),需进行格式转换:
- 24bit BMP 像素:B(1 字节)、G(1 字节)、R(1 字节);
- 32bit LCD 颜色:A(1 字节,设为 0x00 = 不透明)、R(1 字节)、G(1 字节)、B(1 字节);
- 转换公式:
lcd_color = (R << 16) | (G << 8) | (B << 0) | (0x00 << 24);
示例:BMP 像素为 B=0x00、G=0x00、R=0xFF(纯红):
- 转换后 LCD 颜色 = (0xFF<<16) | (0x00<<8) | (0x00<<0) = 0x00FF0000(ARGB)。
行翻转处理(BMP→LCD)
由于 BMP 是 “从下到上” 存储,LCD 是 “从上到下” 显示,需将 BMP 的行数据翻转:
- 假设 BMP 高度为 H,读取 BMP 的第 i 行数据(0≤i<H),对应 LCD 的第(H-1 -i)行;
- 示例:BMP 第 0 行(文件中)→ LCD 第 9 行(H=10 时),BMP 第 9 行→ LCD 第 0 行。
BMP 实战代码
读取 BMP 的宽、高、文件大小(命令行传参)
功能:通过命令行传入 BMP 文件路径,输出图像的宽度、高度、文件总大小。代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 取消结构体对齐,确保读取14字节和40字节
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct {
unsigned short bfType; // 2字节:文件标识("BM")
unsigned int bfSize; // 4字节:文件总大小(字节)
unsigned short bfReserved1; // 2字节:保留字(0)
unsigned short bfReserved2; // 2字节:保留字(0)
unsigned int bfOffBits; // 4字节:位图数据偏移量(字节)
} BITMAPFILEHEADER;
typedef struct {
unsigned int biSize; // 4字节:结构体大小(40)
int biWidth; // 4字节:宽度(像素)
int biHeight; // 4字节:高度(像素)
unsigned short biPlanes; // 2字节:色彩平面数(1)
unsigned short biBitCount; // 2字节:色深(bit)
unsigned int biCompression; // 4字节:压缩方式(0=无压缩)
unsigned int biSizeImage; // 4字节:位图数据大小(字节)
int biXPelsPerMeter;// 4字节:水平分辨率(0)
int biYPelsPerMeter;// 4字节:垂直分辨率(0)
unsigned int biClrUsed; // 4字节:使用颜色数(0)
unsigned int biClrImportant; // 4字节:重要颜色数(0)
} BITMAPINFOHEADER;
#pragma pack()
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
// 检查命令行参数(需传入BMP文件路径)
if (argc != 2) {
printf("用法:%s <BMP文件路径>\n", argv[0]);
printf("示例:%s test.bmp\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// 打开BMP文件(只读模式)
/**
* @brief open函数:打开文件
* @param argv[1] 命令行传入的BMP文件路径(如"test.bmp")
* @param O_RDONLY 打开模式:只读
* @return 成功返回文件描述符(非负整数);失败返回-1
*/
int bmp_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (bmp_fd == -1) {
perror("open BMP文件失败"); // 打印错误原因(如文件不存在)
exit(1);
}
// 读取位图文件头(14字节)
BITMAPFILEHEADER file_header;
/**
* @brief read函数:从文件读取数据
* @param bmp_fd BMP文件描述符
* @param &file_header 存储读取数据的缓冲区(文件头结构体)
* @param sizeof(file_header) 读取的字节数(14)
* @return 成功返回读取的字节数(14);失败返回-1
*/
int ret = read(bmp_fd, &file_header, sizeof(file_header));
if (ret != sizeof(file_header)) {
perror("read 文件头失败");
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
// 验证是否为BMP文件(bfType必须为0x4D42,即"BM")
if (file_header.bfType != 0x4D42) {
printf("错误:%s 不是BMP文件\n", argv[1]);
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
// 读取位图信息头(40字节)
BITMAPINFOHEADER info_header;
ret = read(bmp_fd, &info_header, sizeof(info_header));
if (ret != sizeof(info_header)) {
perror("read 信息头失败");
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
// 输出BMP关键信息
printf("BMP文件路径:%s\n", argv[1]);
printf("文件总大小:%u 字节\n", file_header.bfSize);
printf("图像宽度:%d 像素\n", info_header.biWidth);
printf("图像高度:%d 像素\n", abs(info_header.biHeight)); // 取绝对值,忽略存储方向
printf("色深:%d bit\n", info_header.biBitCount);
printf("压缩方式:%s(%u)\n", info_header.biCompression == 0 ? "无压缩" : "有压缩", info_header.biCompression);
// 关闭文件,释放资源
close(bmp_fd);
return 0;
}
编译与运行:
gcc bmp_info.c -o bmp_info
./bmp_info test.bmp
运行结果:
BMP文件路径:test.bmp
文件总大小:xxx 字节
图像宽度:xxx 像素
图像高度:xxx 像素
色深:24 bit
压缩方式:无压缩(0)
在 LCD 上显示 24bit 无压缩 BMP
功能:打开 24bit 无压缩 BMP,在 800×480 的 LCD 上显示(需确保 BMP 分辨率与 LCD 一致)。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <linux/fb.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct {
unsigned short bfType; // 2字节:"BM"
unsigned int bfSize; // 4字节:文件总大小
unsigned short bfReserved1; // 2字节:0
unsigned short bfReserved2; // 2字节:0
unsigned int bfOffBits; // 4字节:位图数据偏移量
} BITMAPFILEHEADER;
typedef struct {
unsigned int biSize; // 4字节:40
int biWidth; // 4字节:宽度
int biHeight; // 4字节:高度
unsigned short biPlanes; // 2字节:1
unsigned short biBitCount; // 2字节:色深(24)
unsigned int biCompression; // 4字节:0(无压缩)
unsigned int biSizeImage; // 4字节:位图数据大小
int biXPelsPerMeter;// 4字节:0
int biYPelsPerMeter;// 4字节:0
unsigned int biClrUsed; // 4字节:0
unsigned int biClrImportant; // 4字节:0
} BITMAPINFOHEADER;
#pragma pack()
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc != 2) {
printf("用法:%s <24bit BMP文件路径>\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
// -------------------------- 处理BMP文件 --------------------------
int bmp_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (bmp_fd == -1) { perror("open BMP失败"); exit(1); }
// 读文件头
BITMAPFILEHEADER file_hdr;
if (read(bmp_fd, &file_hdr, sizeof(file_hdr)) != sizeof(file_hdr)) {
perror("read 文件头失败");
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
if (file_hdr.bfType != 0x4D42) {
printf("不是BMP文件\n");
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
// 读取位图信息头(40字节),并校验读取是否完整
BITMAPINFOHEADER info_hdr;
if (read(bmp_fd, &info_hdr, sizeof(info_hdr)) != sizeof(info_hdr)) {
perror("read 信息头失败");
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
//判断是否为24bit无压缩
if (info_hdr.biBitCount != 24 || info_hdr.biCompression != 0) {
printf("仅支持24bit无压缩BMP\n");
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
// 计算BMP每行参数(对齐处理)
int bmp_width = info_hdr.biWidth; // BMP宽度
int bmp_height = abs(info_hdr.biHeight); // BMP高度(取绝对值)
int bmp_pixel_bytes = 3; // 24bit=3字节/像素
int bmp_line_bytes = bmp_width * bmp_pixel_bytes; // 自然每行字节数
int bmp_pad_bytes = (4 - (bmp_line_bytes % 4)) % 4; // 补齐字节数
int bmp_line_total = bmp_line_bytes + bmp_pad_bytes; // 实际每行字节数
// 定位到位图数据(跳过文件头、信息头、调色板)
lseek(bmp_fd, file_hdr.bfOffBits, SEEK_SET);
// -------------------------- 处理LCD设备 --------------------------
// 打开LCD设备
int lcd_fd = open("/dev/fb0", O_RDWR);
if (lcd_fd == -1) { perror("open LCD失败"); close(bmp_fd); exit(1); }
// 获取LCD参数(宽、高、色深)
struct fb_var_screeninfo lcd_var;
if (ioctl(lcd_fd, FBIOGET_VSCREENINFO, &lcd_var) == -1) {
perror("ioctl 获取LCD参数失败");
close(lcd_fd);
close(bmp_fd);
exit(1);
}
int lcd_width = lcd_var.xres; // LCD宽度(如800)
int lcd_height = lcd_var.yres; // LCD高度(如480)
int lcd_pixel_bytes = lcd_var.bits_per_pixel / 8; // LCD字节/像素(32bit=4)
// 内存映射LCD(直接操作内存控制LCD)
size_t lcd_map_len = lcd_width * lcd_height * lcd_pixel_bytes;
unsigned int *lcd_mem = (unsigned int *)mmap(
NULL, // 让系统分配地址
lcd_map_len, // 映射长度
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, // 读写权限
MAP_SHARED, // 共享映射(修改同步到硬件)
lcd_fd, // LCD文件描述符
0 // 偏移量0
);
if (lcd_mem == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap LCD失败");
close(lcd_fd);
close(bmp_fd); exit(1);
}
// -------------------------- BMP→LCD显示 --------------------------
// 分配缓冲区存储BMP一行数据
unsigned char *bmp_line_buf = (unsigned char *)malloc(bmp_line_total);
if (bmp_line_buf == NULL) { perror("malloc 失败"); goto end; }
// 读取BMP每行数据,转换后写入LCD(行翻转处理)
for (int y = 0; y < bmp_height; y++) {
// 读取BMP一行数据(包含补齐字节)
read(bmp_fd, bmp_line_buf, bmp_line_total);
// 计算LCD行号(BMP从下到上→LCD从上到下)
int lcd_y = bmp_height - 1 - y;
if (lcd_y >= lcd_height) break; // 超出LCD高度,跳过
// 遍历每行每个像素,转换BGR→ARGB,写入LCD
for (int x = 0; x < bmp_width; x++) {
if (x >= lcd_width) break; // 超出LCD宽度,跳过
// 提取BMP像素的B、G、R分量(BGR顺序)
unsigned char B = bmp_line_buf[x * 3 + 0];
unsigned char G = bmp_line_buf[x * 3 + 1];
unsigned char R = bmp_line_buf[x * 3 + 2];
// 转换为LCD的ARGB格式(A=0x00不透明)
unsigned int lcd_color = (R << 16) | (G << 8) | B | (0x00 << 24);
// 写入LCD内存(LCD行号×LCD宽度 + LCD列号)
lcd_mem[lcd_y * lcd_width + x] = lcd_color;
}
}
// 等待按键退出(保持显示)
printf("按任意键退出...\n");
getchar();
// -------------------------- 释放资源 --------------------------
end:
free(bmp_line_buf);
munmap(lcd_mem, lcd_map_len); // 解除LCD映射
close(lcd_fd);
close(bmp_fd);
return 0;
}
等比例缩小 BMP 为 1/2(生成新文件)
功能:将任意尺寸 24bit 无压缩 BMP 等比例缩小为原来的 1/2(宽、高各减半),新文件路径通过命令行传递。核心思路:
- 读取原 BMP 的文件头、信息头;
- 计算新 BMP 的宽(原宽 / 2)、高(原高 / 2),修改新文件头和信息头;
- 读取原 BMP 的像素数据,每隔一个像素取一个(如原 (x,y)→新 (x/2,y/2));
- 处理新 BMP 的行对齐,写入新文件。
代码框架(关键部分):
// 新BMP参数计算
int new_width = bmp_width / 2; // 新宽度=原宽度/2
int new_height = bmp_height / 2; // 新高度=原高度/2
int new_line_bytes = new_width * 3; // 新自然每行字节数
int new_pad_bytes = (4 - (new_line_bytes % 4)) % 4; // 新补齐字节数
int new_line_total = new_line_bytes + new_pad_bytes; // 新实际每行字节数
int new_data_size = new_line_total * new_height; // 新位图数据大小
int new_file_size = 54 + new_data_size; // 新文件总大小(无调色板,54字节头)
// 构造新文件头
BITMAPFILEHEADER new_file_hdr;
new_file_hdr.bfType = 0x4D42;
new_file_hdr.bfSize = new_file_size;
new_file_hdr.bfReserved1 = 0;
new_file_hdr.bfReserved2 = 0;
new_file_hdr.bfOffBits = 54; // 无调色板,偏移54
// 构造新信息头
BITMAPINFOHEADER new_info_hdr;
new_info_hdr.biSize = 40;
new_info_hdr.biWidth = new_width;
new_info_hdr.biHeight = -new_height; // 设为负数,从上到下存储(无需翻转)
new_info_hdr.biPlanes = 1;
new_info_hdr.biBitCount = 24;
new_info_hdr.biCompression = 0;
new_info_hdr.biSizeImage = new_data_size;
new_info_hdr.biXPelsPerMeter = 0;
new_info_hdr.biYPelsPerMeter = 0;
new_info_hdr.biClrUsed = 0;
new_info_hdr.biClrImportant = 0;
// 读取原BMP数据,缩小后写入新文件
unsigned char *old_line = malloc(bmp_line_total);
unsigned char *new_line = malloc(new_line_total);
int new_fd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644); // 新建文件
write(new_fd, &new_file_hdr, sizeof(new_file_hdr)); // 写新文件头
write(new_fd, &new_info_hdr, sizeof(new_info_hdr)); // 写新信息头
for (int y = 0; y < new_height; y++) {
// 读取原BMP的2行(缩小1/2,取偶数行)
lseek(bmp_fd, file_hdr.bfOffBits + (y*2) * bmp_line_total, SEEK_SET);
read(bmp_fd, old_line, bmp_line_total);
// 提取原BMP的偶数列像素,组成新行
for (int x = 0; x < new_width; x++) {
int old_x = x * 2; // 取原BMP的偶数列
new_line[x*3 + 0] = old_line[old_x*3 + 0]; // B
new_line[x*3 + 1] = old_line[old_x*3 + 1]; // G
new_line[x*3 + 2] = old_line[old_x*3 + 2]; // R
}
// 补0字节(对齐)
memset(new_line + new_line_bytes, 0, new_pad_bytes);
// 写入新BMP的一行
write(new_fd, new_line, new_line_total);
}
注意事项
- 结构体对齐问题:编译器默认会对结构体进行 “字节对齐”(如 int 按 4 字节对齐),导致 14 字节的文件头被扩展为 16 字节,必须用
#pragma pack(1)取消对齐,否则读取数据错误; - biHeight 正负问题:biHeight 为正数时 BMP 从下到上存储,为负数时从上到下存储,开发中需用
abs(biHeight)获取高度,根据正负判断是否需要行翻转; - LCD 与 BMP 分辨率不一致:若 BMP 分辨率小于 LCD,可指定显示位置(如居中);若大于 LCD,需进行缩放(如双线性插值),避免显示不全;
- 调色板 BMP 处理:对于 8bit 以下 BMP,需先读取调色板,再根据像素索引查找对应的 BGR 颜色,再转换为 LCD 格式;
- 权限问题:操作
/dev/fb0需 root 权限,运行 LCD 相关程序时需用sudo ./xxx。
























 1200
1200

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








