目录
a)借助方程或图表。说明DV (Distance Vector)算法的工作原理。答案不应包括任何代码或伪代码。
d)设计你自己的目标序列分配机制。在您的回答中,基于图1中给出的拓扑的示例是首选。
e)根据你在c)和d)中的设计,逐步描述节点在接收DSDV路由更新时会做什么。答案应该涵盖Ad hoc网络中所有可能的场景。

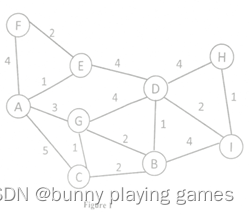
Answer the following questions by applying DSDV(Destination Sequenced Distance Vector)routing algorithm to the Ad Hoc network topology as shown in Figure l below. The solid line indicates the wireless connection between nodes. The number above or right to each line indicates the connection cost for both directions.
将DSDV(Destination Sequenced Distance Vector)路由算法应用于Ad Hoc网络拓扑结构,如图所示,回答以下问题。实线表示节点之间的无线连接。每条线上方或右侧的数字表示两个方向的连接成本。
a) With aid of equations or diagrams. explain the working principle of DV (Distance Vector)
algorithm. Answer should NOT include any codes NOR pseudocode.
a)借助方程或图表。说明DV (Distance Vector)算法的工作原理。答案不应包括任何代码或伪代码。
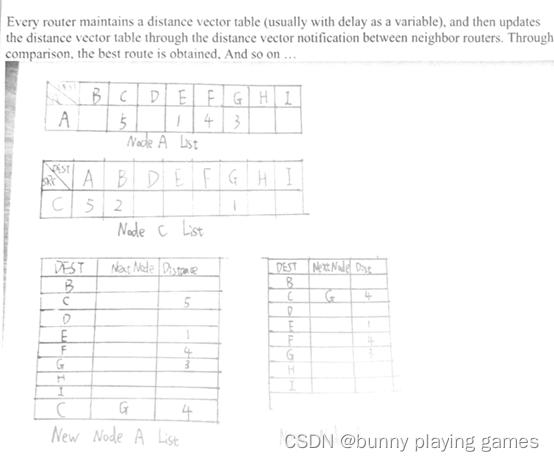
Every router maintains a distance vector table (usually with delay as a variable), and then updates the distance vector table through the distance vector notification between neighbor routers. Through comparison, the best route is obtained. And so on ...
每个路由器都维护一个距离向量表(通常以延迟作为变量),然后通过邻居路由器之间的距离向量通知更新距离向量表。通过比较,得到了最佳路线。等等……

b)With aid of an example, explain the design purpose of destination sequence adopted in DSDV protocol.
b)通过实例说明DSDV协议中采用的目的序列的设计目的。
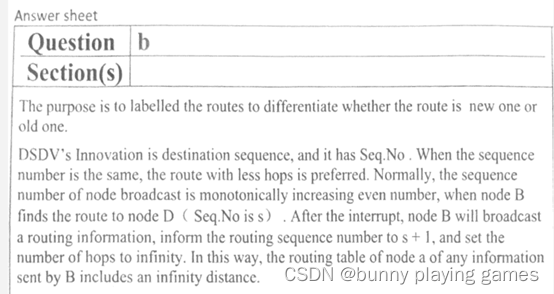
The purpose is to labelled the routes to differentiate whether the route is new one or old one.
DSDV's Innovation is destination sequence, and it has Seq. No . When the sequence number is the same, the route with less hops is preferred. Normally, the sequence number of node broadcast is monotonically increasing even number, when node B finds the route to node D ( Seq. No is s) .After the interrupt, node B will broadcast routing information, inform the routing sequence number to s + 1, and set the number of hops to infinity. In this way, the routing table of node a of any information sent by B includes an infinity distance.
目的是对路由进行标记,区分路由是新路由还是旧路由。
DSDV的创新是目的地序列,它有Seq.NO 当序列号相同时,优先选择跳数少的路由。正常情况下,当节点B找到到节点D (Seq. D)的路由时,节点广播的序列号单调递增为偶数。中断后,节点B广播路由信息,告知路由序列号为s + 1,并设置跳数为无限大。这样,B发送的任何信息在节点a的路由表中都包含一个无穷远的距离。

c) Design your own destination sequence generation/update mechanism. An example based on the topology given in Figure 1 is preferred in your answer.
c)设计自己的目标序列生成/更新机制。在您的回答中,基于图1中给出的拓扑的示例是首选。
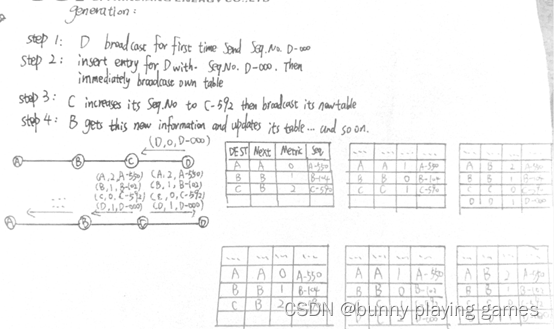

d) Design your own destination sequence distribution mechanism. An example based on the
topology given in Figure 1 is preferred in your answer.
d)设计你自己的目标序列分配机制。在您的回答中,基于图1中给出的拓扑的示例是首选。

Distribution:
It through broadcasting to distribute. There are 2 ways:
1. Broadcast now:
When a new node enters, the link breaks or the metric changes, it immediately broadcasts the routing information to the neighbor nodes
2. Full (partial) update
1 Full update: send all routing information to neighbor nodes
2 Partial update: only changed route entries are sent
发行:
它通过广播进行发行。
有两种方法:
1立即广播:
当新节点进入时。链路中断或度量值发生变化,立即将路由信息广播给邻居节点
2全更新(部分更新)
1全更新:将所有路由信息发送到邻居节点。
2部分更新:只发送变化的路由表项
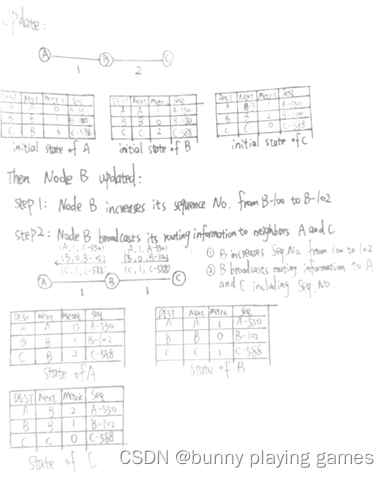
e) Based on your design in c) and d), describe step-by-step what nodes will do while receiving a DSDV route updates. Answers should cover all possible scenarios in Ad hoc Networks.
e)根据你在c)和d)中的设计,逐步描述节点在接收DSDV路由更新时会做什么。答案应该涵盖Ad hoc网络中所有可能的场景。

Scenario 1: Intermediate Node, IN moves
Its last node will initiate a local query. For example, if the distance from destination is 3, the local query will start from this node and look for at most 3.If it finds the destination, it will take the new path. If it can't find the destination, it will let the last node initiate a local query. The mechanism is similar. Until half of the nodes LQ are not found, it will start from the beginning
Scenario 2: DEST moves
The last node will send a route notification, which means that the road is blocked. Then the last node initiates a local query, and if it can't find it, it will send RN to the last node, and then go to LQ until it can't find it half way back
Scenario 3:SRC Moves
The second node sends down RN, which means that we have no use of the moved source to start a new BQ directly
场景1:中间节点,IN
移动它的最后一个节点将发起本地查询。例如,如果到目的地的距离为3,则本地查询将从该节点开始,最多查找3。如果它找到了目的地,它将采用新的路径。如果它找不到目的地,它将让最后一个节点发起一个本地查询。机制是相似的。直到有一半的节点LQ没有找到,它将从最开始
场景2:DEST移动
最后一个节点将发送一个路由通知,这意味着道路被阻塞。然后最后一个节点发起一个本地查询,如果它找不到它,它会把RN发送给最后一个节点,然后再去LQ,直到它在中途找不到它。
场景3:SRC移动
第二个节点向下发送RN,这意味着我们没有使用移动的源来直接启动一个新的BQ

f)Discuss the advantages and disadvantages in your destination sequence generation/update
mechanism design.
f)讨论目标序列生成/更新机制设计的优点和缺点。
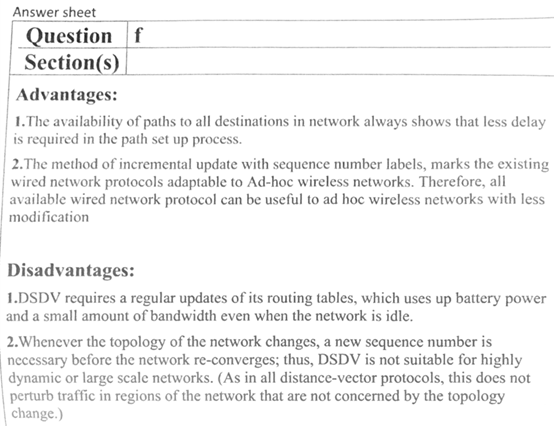
Advantages:
1.The availability of paths to all destinations in network always shows that less delay is required in the path set up process.
2.The method of incremental update with sequence number labels, marks the existing wired network protocols adaptable to Ad-hoc wireless networks. Therefore, all available wired network protocol can be useful to ad hoc wireless networks with less modification
Disadvantages:
1.DSDV requires a regular updates of its routing tables, which uses up battery power and a small amount of bandwidth even when the network is idle.
2.Whenever the topology of the network changes, a new sequence number is necessary before the network re-converges; thus, DSDV is not suitable for highly dynamic or large scale networks. (As in all distance-vector protocols, this does not perturb traffic in regions of the network that are not concerned by the topology change.)
优点:
1.网络中所有目的地的路径可用性总是表明在路径设置过程中需要更少的延迟。
2.增量更新的方法带有序列号标签,标志着现有的有线网络协议适用于Ad-hoc无线网络。因此,所有现有的有线网络协议都可以用于自组织无线网络
缺点:
1.DSDV需要定期更新路由表,即使在网络空闲时也会消耗电池电量和少量带宽。
2.每当网络的拓扑结构发生变化时,在网络重新收敛之前需要一个新的序列号;因此,DSDV不适合高动态或大规模的网络。(与所有距离矢量协议一样,这不会影响网络中不受拓扑变化影响的区域的流量。)





 本文探讨了DSDV路由算法在Ad Hoc网络中的应用,详细解释了DV算法的基本原理,介绍了DSDV中目的地序列的设计目的,并提出了自定义的目标序列生成与更新机制。此外,还讨论了该机制的优点和局限。
本文探讨了DSDV路由算法在Ad Hoc网络中的应用,详细解释了DV算法的基本原理,介绍了DSDV中目的地序列的设计目的,并提出了自定义的目标序列生成与更新机制。此外,还讨论了该机制的优点和局限。

















 8461
8461

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








