集合
含义
- 集合是Java API所提供的一系列类,可以用于动态存放多个对象 (集合只能存对象)
- 集合与数组的不同在于,集合是大小可变的序列,而且元素类型可以不受限定,但只能是引用类型。(集合中不能放基本数据类型,但可以放基本数据类型的包装类)
- 集合类全部支持泛型,是一种数据安全的用法。
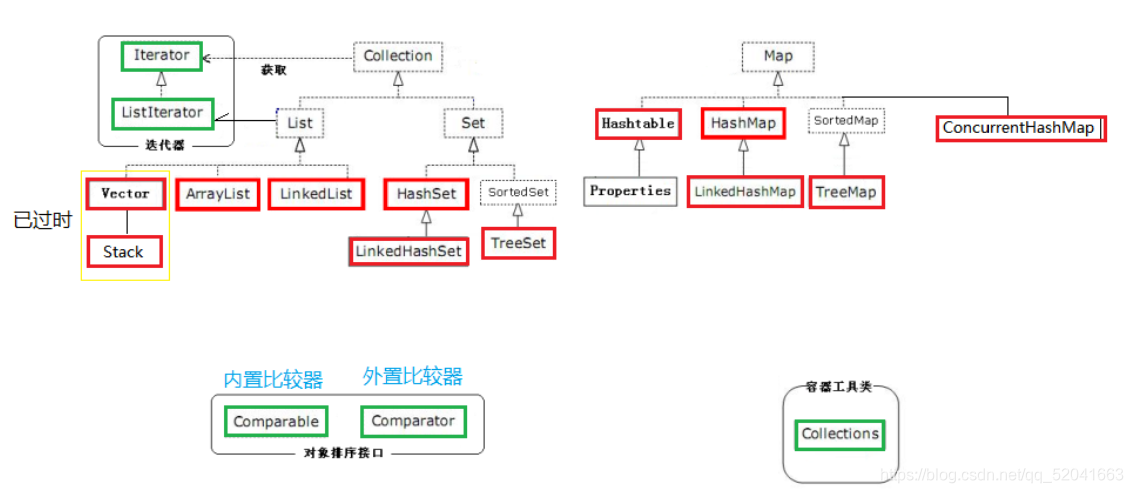
Collection接口
List接口
List中的方法在其实现类中的使用方法都相同
特点:有序且有重复(因为List接口中添加了许多针对下标操作的方法)
实现类:
- ArrayList
- LinkedList
- Vector
- Stack
ArrayList集合
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:使用ArrayList方法 + 泛型 * * 泛型:数据安全的作法,规定集合应该存储什么样的数据类型 */ ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); //添加元素 list.add("张三"); list.add("李四"); list.add("王五"); list.add("韩信"); list.add("张良"); //获取元素的个数 int size = list.size(); System.out.println("获取元素的个数:" + size);//5 //设置指定下标上的元素 list.set(1, "孙尚香"); //获取指定下标上的元素 String elment = list.get(1); System.out.println("获取指定下标上的元素:" + elment);//孙尚香 //在指定下标上插入元素 list.add(1, "黄忠"); ArrayList<String> newList1 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(newList1, "aaa","bbb","ccc","xyz");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 list.addAll(newList1);//将新集合中所有的元素添加到指定集合的末尾 ArrayList<String> newList2 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(newList2, "ddd","eee","fff");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 list.addAll(3, newList2);//将新集合中所有的元素添加到指定集合上指定下标的位置 //清空集合中所有的元素 //list.clear(); System.out.println("判断集合中是否包含某个元素:" + list.contains("bbb"));//true ArrayList<String> newList3 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(newList3, "eee","ddd","fff","ggg");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 System.out.println("判断集合中是否包含某个集合中所有元素:" + list.containsAll(newList3));//false int index = list.indexOf("韩信"); System.out.println("获取元素在集合中的下标:" + index); boolean empty = list.isEmpty();//有元素-false 没有元素-true System.out.println("判断集合中是否没有元素:" + empty);//false //删除 list.remove(3);//依据下标删除元素 list.remove("eee");//依据元素删除元素 //删除 - 去交集 ArrayList<String> newList4 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(newList4, "fff","aaa","bbb","xxx");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 list.removeAll(newList4); //保留交集 ArrayList<String> newList5 = new ArrayList<>(); Collections.addAll(newList5, "111","222","bbb","eee","ccc","yyy");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 list.retainAll(newList5); //替换指定下标上的元素 list.set(2, "亚瑟"); //获取开始下标(包含)到结束下标(不包含)的元素,返回新的集合 List<String> subList = list.subList(1, 3); //将集合转换为数组 Object[] array = subList.toArray(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); System.out.println("-------------"); //遍历 - for for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { System.out.println(list.get(i)); } System.out.println("-------------"); //遍历 - foreach for (String element : list) { System.out.println(element); } System.out.println("-------------"); //遍历 - Iterator迭代器 Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();//获取Iterator迭代器对象 while(it.hasNext()){//判断是否有可迭代的元素 String e = it.next();//返回下一个元素 System.out.println(e); } System.out.println("-------------"); //遍历 - ListIterator迭代器 ListIterator<String> listIterator = list.listIterator();//获取ListIterator迭代器对象 while(listIterator.hasNext()){//判断是否有可迭代的元素 String e = listIterator.next();//返回下一个元素 System.out.println(e); } }
LinkedList集合
调用方法和ArrayList相同,但LinkedList添加了队列模式和栈模式
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:队列模式 * * 特点:先进先出 */ LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add("aaa"); list.add("bbb"); list.add("ccc"); list.add("ddd"); //取出顺序与存入顺序相同 while(!list.isEmpty()){ String first = list.removeFirst(); System.out.println(first); } System.out.println("数组中元素的个数为:" + list.size());//0 }public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:LinkedList 栈模式 * * 特点:先进后出 */ LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); list.add("1"); list.add("2"); list.add("3"); list.add("4"); list.add("5"); //取出顺序与存入顺序相反 while(!list.isEmpty()){ //删除最后一个元素,并返回 String element = list.removeLast(); System.out.println(element); } System.out.println("集合中元素的个数:" + list.size());//0 }
Vector集合
Vector调用实现List接口的方法,与上面集合中方法的使用相同,是线程安全的集合。
了解:Vector是元老级别的集合类,在JDK1.0开始。JDK1.2开始才推出集合框架的概念,考虑到当时很多程序员习惯使用Vector,就让Vector多实现了List接口,这样才将其保留下来
知识点:Vector老的方法
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:Vector老的方法,功能和List中的方法一样 */ Vector<String> v = new Vector<>(); //添加 v.addElement("张三"); v.addElement("李四"); v.addElement("王五"); v.addElement("赵六"); //删除 v.removeElement("李四"); //遍历 Enumeration<String> elements = v.elements(); while (elements.hasMoreElements()) { String string = (String) elements.nextElement(); System.out.println(string); } }
Stack集合
Vector的子类
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:Stack * 特点:栈模式 - 先进后出 */ Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); //添加元素 - 将元素压入栈顶 stack.push("1"); stack.push("2"); stack.push("3"); stack.push("4"); stack.push("5"); System.out.println("距离栈顶的位置(从1开始):" + stack.search("2"));//4 //取出顺序与存入顺序相反 while(!stack.empty()){ //获取栈顶第一个元素,并返回 因为不取出元素,所以是死循环 //String element = stack.peek(); //删除栈顶第一个元素,并返回 String element = stack.pop(); System.out.println(element); } System.out.println("栈里元素个数:" + stack.size());//0 }
Set接口
特点:无序且没有重复
实现类:
- HashSet(无序、无重复)
- LinkedHashSet(有序,无重复)
- TreeSet(可对集合中元素排序)
HashSet集合
HashSet方法的使用
public class HashSetTest { public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:使用HashSet方法 * * 特点:去重+无序 */ HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(); //添加元素 set.add("黄忠"); set.add("马超"); set.add("张飞"); set.add("关羽"); set.add("张良"); //获取元素的个数 int size = set.size(); System.out.println("获取元素的个数:" + size);//5 HashSet<String> newSet1 = new HashSet<>(); Collections.addAll(newSet1, "aaa","bbb","ccc","刘备");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 set.addAll(newSet1);//将新集合中所有的元素添加到指定集合的末尾 //清空集合中所有的元素 //set.clear(); System.out.println("判断集合中是否包含某个元素:" + set.contains("张良"));//true HashSet<String> newSet2 = new HashSet<>(); Collections.addAll(newSet2, "eee","ddd","fff","ggg");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 System.out.println("判断集合中是否包含某个集合中所有元素:" + set.containsAll(newSet2));//false boolean empty = set.isEmpty();//有元素-false 没有元素-true System.out.println("判断集合中是否没有元素:" + empty);//false //删除 set.remove("张飞");//依据元素删除元素 //删除 - 去交集 HashSet<String> newSet3 = new HashSet<>(); Collections.addAll(newSet3, "fff","aaa","bbb","xxx");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 set.removeAll(newSet3); //保留交集 HashSet<String> newSet4 = new HashSet<>(); Collections.addAll(newSet4, "周瑜","曹操","张良","诸葛亮","关羽","yyy");//利用集合工具类进行批量添加 set.retainAll(newSet4); //将集合转换为数组 Object[] array = set.toArray(); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array)); System.out.println("-------------"); //遍历 - foreach for (String element : set) { System.out.println(element); } System.out.println("-------------"); //遍历 - Iterator迭代器 Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();//获取Iterator迭代器对象 while(it.hasNext()){//判断是否有可迭代的元素 String e = it.next();//返回下一个元素 System.out.println(e); } } }
LinkedHashSet集合
特点:去重+有序 (输出的顺序与添加的顺序一致)
方法的使用与 HashSet 相同
TreeSet集合
自然排序
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 知识点:TreeSet排序 * * 需求:创建两个TreeSet对象,分别存Integer、String * * TreeSet:自然排序(根据不同的类型,选择不同排序规则) * * TreeSet存Integer:数字排序 * TreeSet存String:字典排序 */ TreeSet<Integer> set1 = new TreeSet<>(); set1.add(5);//Integer.valueOf(5);自动装箱 set1.add(1);//Integer.valueOf(1); set1.add(4);//Integer.valueOf(4); set1.add(2);//Integer.valueOf(2); set1.add(6);//Integer.valueOf(6); set1.add(3);//Integer.valueOf(3); set1.add(3);//Integer.valueOf(3); for (Integer integer : set1) { System.out.println(integer); } System.out.println("-----"); TreeSet<String> set2 = new TreeSet<>(); set2.add("c"); set2.add("d"); set2.add("a"); set2.add("b"); for (String string : set2) { System.out.println(string); } }
Comparable - 内置比较器
实体类:继承Comparable接口,重写 compareTo方法
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{ private String name; private char sex; private int age; private String classId; private String id; public Student() { } public Student(String classId, String id) { this.classId = classId; this.id = id; } public Student(String name, char sex, int age, String classId, String id) { this.name = name; this.sex = sex; this.age = age; this.classId = classId; this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public char getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(char sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getClassId() { return classId; } public void setClassId(String classId) { this.classId = classId; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this == obj){ return true; } if(obj instanceof Student){ Student stu = (Student) obj; if(this.classId.equals(stu.classId) && this.id.equals(stu.id)){ return true; } } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return name + "\t" + sex + "\t" + age + "\t" + classId + "\t" + id; } //比较规则 //需求:按照年龄排序 @Override public int compareTo(Student o) { return this.age - o.age;//升序 } }测试类
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 需求:创建TreeSet对象,存储Student * * Comparable - 内置比较器 */ TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet<>(); set.add(new Student("aa", '男', 26, "2107", "001")); set.add(new Student("bb", '女', 31, "2107", "002")); set.add(new Student("cc", '男', 29, "2107", "003")); set.add(new Student("dd", '女', 26, "2107", "004")); set.add(new Student("ee", '男', 33, "2107", "005")); set.add(new Student("aaa", '男', 29, "2107", "006")); set.add(new Student("bbb", '女', 34, "2107", "007")); set.add(new Student("ccc", '男', 26, "2107", "008")); set.add(new Student("aaaa", '男', 29, "2107", "009")); set.add(new Student("bbbb", '女', 25, "2108", "001")); set.add(new Student("cccc", '男', 27, "2108", "002")); set.add(new Student("dddd", '女', 24, "2108", "003")); set.add(new Student("eeee", '男', 24, "2108", "004")); set.add(new Student("ffff", '女', 29, "2108", "005")); set.add(new Student("hhhh", '男', 29, "2108", "006")); for (Student stu : set) { System.out.println(stu); } }
Comparator - 外置比较器
创建匿名内部类实现Comparator接口,重写compare方法
public static void main(String[] args) { /** * 需求:创建TreeSet对象,存储Student,按照名字长度排序,长度一致按照年龄排序 * * Comparator - 外置比较器 */ TreeSet<Student> set = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() { @Override public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) { if(o1.equals(o2)){ return 0; } if(o1.getName().length() != o2.getName().length()){ return o1.getName().length() - o2.getName().length(); } if(o1.getAge() != o2.getAge()){ return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); } return 1; } }); set.add(new Student("aa", '男', 26, "2107", "001")); set.add(new Student("bb", '女', 31, "2107", "002")); set.add(new Student("cccc", '男', 27, "2108", "002")); set.add(new Student("dddd", '女', 24, "2108", "003")); set.add(new Student("eeee", '男', 24, "2108", "004")); set.add(new Student("cc", '男', 29, "2107", "003")); set.add(new Student("aaa", '男', 29, "2107", "006")); set.add(new Student("bbb", '女', 34, "2107", "007")); set.add(new Student("dd", '女', 26, "2107", "004")); set.add(new Student("ccc", '男', 26, "2107", "008")); set.add(new Student("aaaa", '男', 29, "2107", "009")); set.add(new Student("bbbb", '女', 25, "2108", "001")); set.add(new Student("ee", '男', 33, "2107", "005")); set.add(new Student("ffff", '女', 29, "2108", "005")); set.add(new Student("hhhh", '男', 29, "2108", "006")); for (Student stu : set) { System.out.println(stu); } }
泛型
含义:数据安全的做法
泛型限定:
? 表示什么类型都可以
? extends A 表示元素必须是A类或A的子类
? super A 表示元素必须是A类或A的父类
迭代器
含义:遍历集合中的元素
分类:Iterator 和 ListIterator
Iterator 和 ListIterator 区别
- Iterator :Collection接口下所有的实现类都可以获取的迭代器,可以在遍历时删除元素: iterator.remove();
- ListIterator :List接口下所有的实现类可以获取的迭代器,可以在遍历时删除、替换、添加元素,也可以指定下标开始遍历,还可以倒序遍历
public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); //向ArrayList 中添加元素("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd") list.add("aaa"); list.add("bbb"); list.add("ccc"); list.add("ddd"); //遍历到bbb时,替换该元素 ListIterator<String> it = list.listIterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String next = it.next(); if (next.equals("bbb")) { it.set("xxx"); } } //遍历到bbb时,添加元素 ListIterator<String> it = list.listIterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { String next = it.next(); if (next.equals("bbb")) { it.add("xyz"); } } //从bbb开始遍历(指定下标开始遍历) ListIterator<String> it = list.listIterator(1); while (it.hasNext()) { String next = it.next(); System.out.println(next); } //倒序输出 ListIterator<String> it = list.listIterator(list.size()); while (it.hasPrevious()) { String previous = it.previous(); System.out.println(previous); } }
比较器接口
作用:排序时使用
分类:
内置比较器:Comparable - compareTo()
外置比较器:Comparator - compare()
使用场景:
内置比较器:对象要想存入TreeSet、TreeMap中,对象所属的类必须要实现内置比较器,重写 compareTo 方法
外置比较器:当内置比较的规则不满足现在的需求,但又不能改动内置比较器规则时,实现Comparator 接口,重写 compare 方法
优先级别:外置比较器 > 内置比较器





 本文详细介绍了Java集合框架中的ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector、Stack、HashSet、LinkedHashSet和TreeSet等类的特性与使用方法,包括增删改查、遍历、排序和比较器。还探讨了泛型、迭代器和比较器在集合操作中的应用,以及内在的Comparable和Comparator接口的实现。此外,文章通过实例展示了如何在实际编程中安全有效地操作集合数据。
本文详细介绍了Java集合框架中的ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector、Stack、HashSet、LinkedHashSet和TreeSet等类的特性与使用方法,包括增删改查、遍历、排序和比较器。还探讨了泛型、迭代器和比较器在集合操作中的应用,以及内在的Comparable和Comparator接口的实现。此外,文章通过实例展示了如何在实际编程中安全有效地操作集合数据。
















 2590
2590

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








