1, JDBC是什么?
- Java DataBase Connectivity ( java语言连接数据库 )
2, JDBC的本质是什么?
- JDBC是sun公司制定的一套接口(interface)
接口都有调用者和实现者。
面向接口调用,面向接口写实现类,这都使属于面向接口编程。
2.1, 为什么要面向接口编程?
- 解耦合:降低程序耦合度,提高程序的扩展力。
多态机制机制就是非常典型的:面向接口编程。
驱动:所有数据库的驱动都是以.jar包的形式存在,jar包中含有多个.class文件,这些class文件就是对JDBC接口的实现。
3, JDBC编程六步
- 1,注册驱动—告诉java程序,即将要连接的是哪个品牌的数据库。
- 2,获取连接—表示JVM的进程和数据库进程之间的通道打开了 ,使用完需要关闭
- 3,获取数据库操作对象—专门执行sql语句的对象
- 4,执行sql语句—(DQL,DML…)
- 5,处理查询结果集—只有当第4步执行的是select语句的时候,才有这第5步处理查询结果集
- 6,释放资源—使用完后一定要关闭资源
4,注册驱动
try{
java.sql.Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printstackTrace();
}
另一种方式
String static jdbcName = "com.mysql.jc.jdbc.Driver";
try{
Class.forName(jdbcName);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
5,获取连接
String static url = "jdbc:mysql://128.2.1.1:3306/bjpowernode";
String static user = "root";
String static password = "333";
Connection conn = null;
try{
//数据库连接对象
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
URL: 统一资源定位符(网络中某个资源的绝对路径)
比如 https://www.baidu.com/ 这就是URL
URL包括哪几部分?
1,协议
2,IP
3,PORT
4,资源名
什么是通信协议,有什么用?
- 通信协议是通信之前就定好的数据传送格式。
数据包具体怎么传数据,格式提前定好的。
6,获取数据库操作对象
Statement stmt = null;
try{
stmt = conn.createStatement();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
7,处理查询结果集
ResultSet rs = null;
try{
String sql = "select empno, ename, sal from emp";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);//专门处理DQL语句
if(rs.next() ){
//以最终查询的列的名字来获得查询结果
String empno = rs.getString("empno");
String sname = rs.getString("ename");
int sal = rs.getInt("sal");
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
注意:最开始时 ,结果集中的光标对象指向第0行.
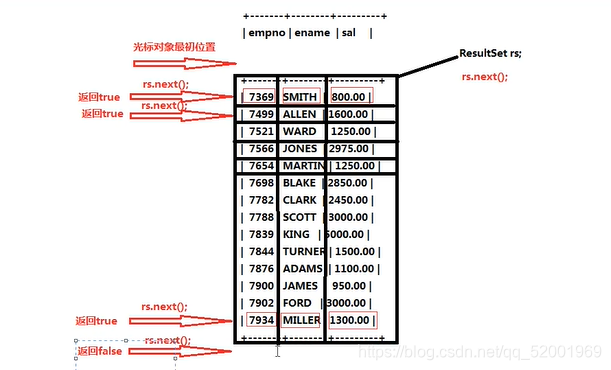
8,执行SQL语句,释放资源
- 为了保证资源一定释放,在finally语句块中关闭资源
并且要遵循从小到大依次关闭,分别对其try…catch
try{
String sql = "insert into dept(deptno, dname, loc) values(50, '人事部', '北京')";
int count = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);//执行DML语句
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try{//先关闭最后的查询结果集资源
if(rs!=null){
rs.close();
}
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
try{//再关闭的数据库操作对象资源
if(stmt != null){
stmt.close();
}
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
try{//再关闭数据库连接对象资源
if(conn != null){
conn.close();
}
}catch(Exception g){
g.printStackTrace();
}
}
9,SQL注入(安全隐患)
- 导致sql注入的根本原因:用户输入的信息中含有sql语句的关键字,并且这些关键字参与sql语句的编译过程,导致sql语句的原意被扭曲,进而达到sql注入。
如下所示的代码执行,便会出现安全隐患!!!
//登录操作,传入Map集合
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Learn_jdbc";
String userName = "root";
String passWord = "123456";
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
String username = userLoginInfo.get("username");//获得用户名
String password = userLoginInfo.get("password");//获得密码
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//注册驱动
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName , passWord );//获得连接
stmt = con.createStatement();//获得数据库操作对象
String sql = "select * from t_user where username = '?' and password = '?'";//获得sql语句对象
res = stmt.executeQuery(sql);//获得结果集
if(res.next() ) {//判断是否找到
return true;
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(res!=null) {//关闭结果集
try {
res.close();
} catch (Exception f) {
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt!=null){
try{//关闭数据库操作
stmt.close();
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(con!=null){
try{//关闭数据库连接
con.close();
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return false;
}
- 如何解决sql注入问题?
只要用户提供的信息不参与sql语句的编译过程,问题就解决了。
即使用户提供的信息中含有sql语句的关键字,但是没有参与编译,不起作用。
要想用户信息不参与sql语句的编译,那么必须使用java.sql.PreparedStatement。
PreparedStatement接口继承了java.sql.Statement。
PreparedStatement是属于预编译的数据库操作对象。
PreparedStatement的原理是:预先对sql语句的框架进行编译,然后再给sql语句传"值"。
将上述代码改为:
//登录操作,传入Map集合
private static boolean login(Map<String, String> userLoginInfo) {
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Learn_jdbc";
String userName = "root";
String passWord = "123456";
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try{
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");//注册驱动
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName , passWord );//获得连接
stmt = con.createStatement();//获得数据库操作对象
String username = userLoginInfo.get("username");//获得用户名
String password = userLoginInfo.get("password");//获得密码
String sql = "select * from t_user where username = '?' and password = '?'";//获得sql语句对象
res = stmt.executeQuery(sql);//获得结果集
if(res.next() ) {//判断是否找到
return true;
}
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(res!=null) {//关闭结果集
try {
res.close();
} catch (Exception f) {
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(stmt!=null){
try{//关闭数据库操作
stmt.close();
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(con!=null){
try{//关闭数据库连接
con.close();
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return false;
}
10,对比 PreparedStatement与Statement
- Statement存在SQL注入问题,而PreparedStatement不存在SQL注入问题.
- Statement是编译一次执行一次,而PreparedStatement是执行一次,可执行N次,效率更高.
- PreparedStatement 会在编译阶段做类型的安全检查.
若业务方面必须要求SQL注入的时候,必须使用Statement, 因此两者都有各自的用处。
11,JDBC事务机制
- 单机事务,只需要记住以下三行代码和基本应用即可。
- con.setAutoCommit(false);//开启事务
- con.commit();//提交事务
- con.rollback();//回滚事务
public class JDBCtest4 {
public static void main(String args[]){
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/Learn_jdbc";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
String jdbc = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
Connection con = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
try{
//注册驱动
Class.forName(jdbc);
//获得连接
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
con.setAutoCommit(false);
//获得sql语句对象
String sql = "update t_user set username = ?, password = ? where id = ?";
//获得数据库操作对象
ps = con.prepareStatement(sql);
ps.setString(1, "小里");
ps.setString(2, "333");
ps.setInt(3, 1);
//获得操作影响结果
int count = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
String s = null;
s.toString();
ps.setString(1, "小王");
ps.setString(2, "444");
ps.setInt(3, 2);
//获得操作影响结果
count = ps.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(count);
con.commit();
}catch(Exception e){
//回滚事务
if(con!=null){
try{
con.rollback() ;
}catch(SQLException e1){
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}finally{
if(ps!=null){
try{//关闭数据库操作
ps.close();
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(con!=null){
try{//关闭数据库连接
con.close();
}catch(Exception f){
f.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
注:集群式事务在此不作讨论。





 本文详细介绍了Java JDBC的基本概念,包括它作为Sun公司制定的数据库连接接口,以及面向接口编程的优势。讲解了JDBC编程的六步流程,强调了资源释放的重要性。同时,针对SQL注入问题,对比了Statement和PreparedStatement的区别,指出PreparedStatement能有效防止SQL注入并提高效率。此外,还探讨了JDBC事务管理,通过设置自动提交、提交和回滚事务来确保数据一致性。
本文详细介绍了Java JDBC的基本概念,包括它作为Sun公司制定的数据库连接接口,以及面向接口编程的优势。讲解了JDBC编程的六步流程,强调了资源释放的重要性。同时,针对SQL注入问题,对比了Statement和PreparedStatement的区别,指出PreparedStatement能有效防止SQL注入并提高效率。此外,还探讨了JDBC事务管理,通过设置自动提交、提交和回滚事务来确保数据一致性。
















 1761
1761

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








