目录
1、emmc RPMB 分区简介
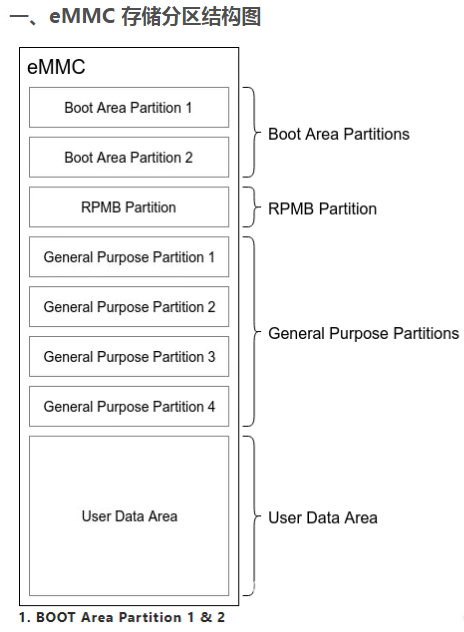
| 分区 | 用途 |
| Boot Area Partitions | 存储引导加载程序,支持安全启动和恢复模式 |
| RPMB Partition | 存储安全关键数据,防止重放攻击 |
| General Purpose Partitions | OEM 自定义数据分区,用于特定功能或镜像存储 |
| User Data Area | 应用程序和用户数据存储 |
RPMB(Replay Protected Memory Block)分区是一种特殊的存储区域,通常用于嵌入式存储设备(如eMMC或UFS),其主要功能是提供一种安全的、不可篡改的存储空间,用于存储敏感数据或运行安全相关的操作。
1、特性
-
防篡改性:RPMB 使用基于硬件的消息认证码(MAC)机制,确保数据在传输和存储过程中未被篡改。
-
回放保护:通过计数器机制,防止旧数据包被重复写入(Replay Attack)。
-
安全访问:只有经过授权的设备和软件可以访问 RPMB 区域。
2、访问机制
-
RPMB 不能像普通存储分区一样直接读取或写入,而是通过专门的命令和协议(如 MMC/JEDEC 标准)与设备通信。
-
每次访问需要通过认证,包括读、写、计数器检查等操作。
3、认证与密钥
-
RPMB 区域基于对称加密技术(如 HMAC),访问权限通过预设的共享密钥控制。
-
密钥通常在设备生产时写入,设备运行时不会暴露给软件层。
4、使用限制
-
容量有限:通常只有几百 KB,适合存储少量关键数据。
-
不可格式化:一旦配置为 RPMB 分区,无法通过普通手段修改或格式化。
2、emmc RPMB 分区验证 - 【mmc 工具】
# 调试设备
# rv1126 & 江波龙emmc
# emmc 原厂硬件分区分包含4块
# 1. boot area partitions
# 2. RPMB partitions
# 3. General purpose partitions
# 4. User Data Area
[root@lemon:/mnt]# ls -lathi /dev/mmcblk0*
2441 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 0 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0
1052 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 32 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0boot0
1051 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 64 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0boot1
158 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 1 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p1
1047 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 10 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p10
1048 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 11 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p11
1049 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 12 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p12
1050 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 13 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p13
159 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 2 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p2
1040 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 3 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p3
1041 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 4 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p4
1042 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 5 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p5
1043 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 6 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p6
1044 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 7 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p7
1045 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 8 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p8
1046 brw-rw---- 1 root root 179, 9 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0p9
2440 crw-rw---- 1 root root 241, 0 Jan 1 1970 /dev/mmcblk0rpmb # rpmb分区# 可借助 mmc 工具查看rv1126平台以支持
# 使用mmc -h 查看 mmc指令手册
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc -h
Usage:
mmc extcsd read <device>
Print extcsd data from <device>.
mmc writeprotect boot get <device>
Print the boot partitions write protect status for <device>.
mmc writeprotect boot set <device>
Set the boot partitions write protect status for <device>.
This sets the eMMC boot partitions to be write-protected until
the next boot.
mmc writeprotect user set <type><start block><blocks><device>
Set the write protect configuration for the specified region
of the user area for <device>.
<type> must be "none|temp|pwron".
"none" - Clear temporary write protection.
"temp" - Set temporary write protection.
"pwron" - Set write protection until the next poweron.
<start block> specifies the first block of the protected area.
<blocks> specifies the size of the protected area in blocks.
NOTE! The area must start and end on Write Protect Group
boundries, Use the "writeprotect user get" command to get the
Write Protect Group size.
mmc writeprotect user get <device>
Print the user areas write protect configuration for <device>.
mmc disable 512B emulation <device>
Set the eMMC data sector size to 4KB by disabling emulation on
<device>.
mmc gp create <-y|-n|-c> <length KiB> <partition> <enh_attr> <ext_attr> <device>
Create general purpose partition for the <device>.
Dry-run only unless -y or -c is passed.
Use -c if more partitioning settings are still to come.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
To set enhanced attribute to general partition being created set
<enh_attr> to 1 else set it to 0.
To set extended attribute to general partition
set <ext_attr> to 1,2 else set it to 0
mmc enh_area set <-y|-n|-c> <start KiB> <length KiB> <device>
Enable the enhanced user area for the <device>.
Dry-run only unless -y or -c is passed.
Use -c if more partitioning settings are still to come.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
mmc write_reliability set <-y|-n|-c> <partition> <device>
Enable write reliability per partition for the <device>.
Dry-run only unless -y or -c is passed.
Use -c if more partitioning settings are still to come.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
mmc status get <device>
Print the response to STATUS_SEND (CMD13).
mmc bootpart enable <boot_partition> <send_ack> <device>
Enable the boot partition for the <device>.
Disable the boot partition for the <device> if <boot_partition> is set to 0.
To receive acknowledgment of boot from the card set <send_ack>
to 1, else set it to 0.
mmc bootbus set <boot_mode> <reset_boot_bus_conditions> <boot_bus_width> <device>
Set Boot Bus Conditions.
<boot_mode> must be "single_backward|single_hs|dual"
<reset_boot_bus_conditions> must be "x1|retain"
<boot_bus_width> must be "x1|x4|x8"
mmc bkops enable <device>
Enable the eMMC BKOPS feature on <device>.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
mmc hwreset enable <device>
Permanently enable the eMMC H/W Reset feature on <device>.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
mmc hwreset disable <device>
Permanently disable the eMMC H/W Reset feature on <device>.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
mmc sanitize <device>
Send Sanitize command to the <device>.
This will delete the unmapped memory region of the device.
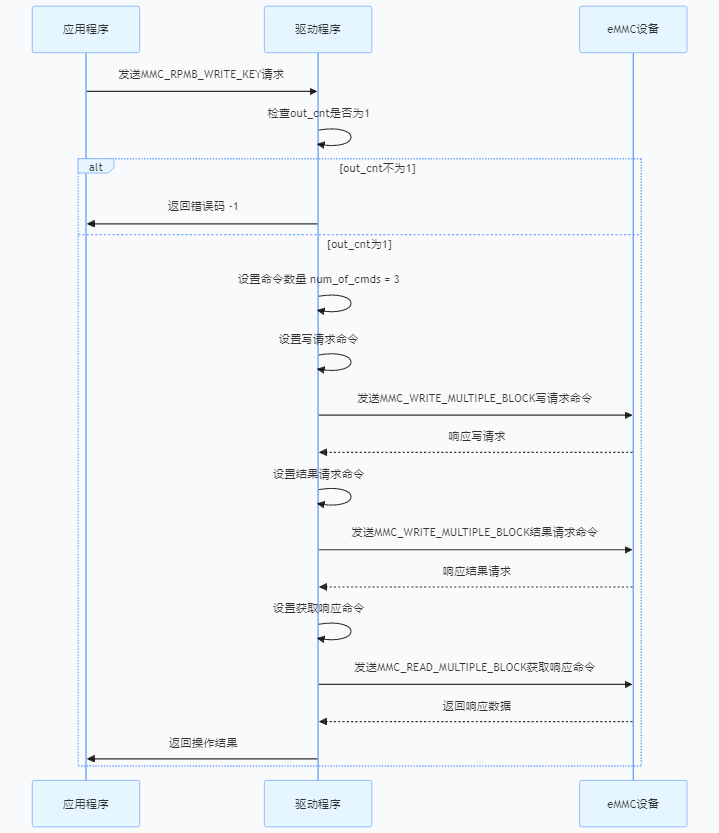
mmc rpmb write-key <rpmb device> <key file>
Program authentication key which is 32 bytes length and stored
in the specified file. Also you can specify '-' instead of
key file path to read the key from stdin.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
Example:
$ echo -n AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHH | \
mmc rpmb write-key /dev/mmcblk0rpmb -
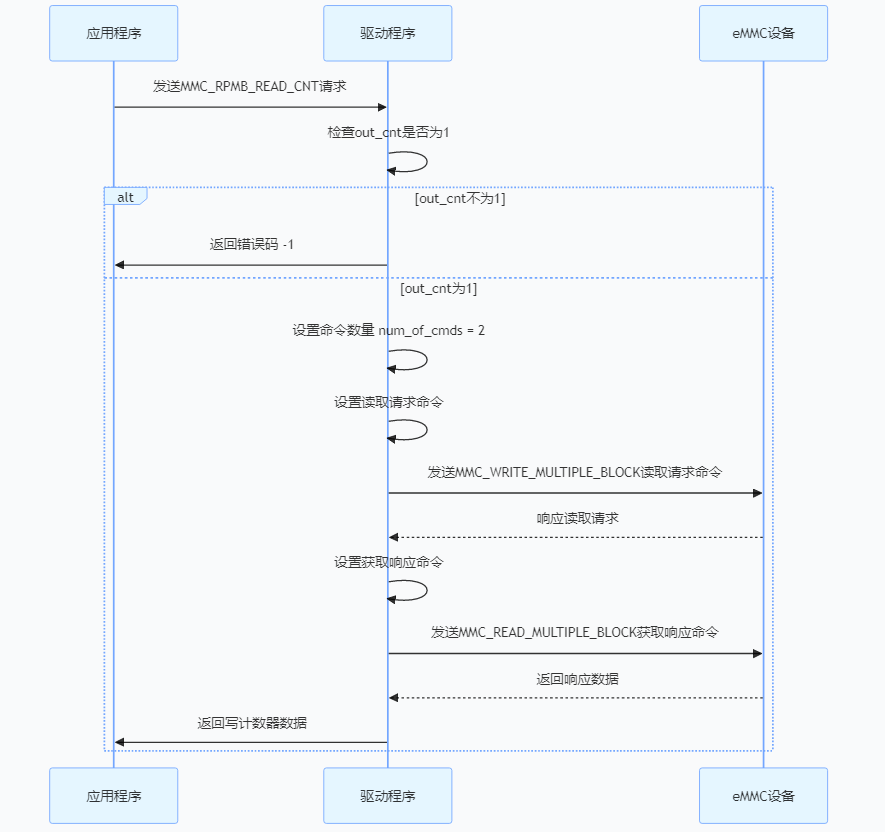
mmc rpmb read-counter <rpmb device>
Counter value for the <rpmb device> will be read to stdout.
mmc rpmb read-block <rpmb device> <address> <blocks count> <output file> [key file]
Blocks of 256 bytes will be read from <rpmb device> to output
file or stdout if '-' is specified. If key is specified - read
data will be verified. Instead of regular path you can specify
'-' to read key from stdin.
Example:
$ echo -n AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHH | \
mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 2 /tmp/block -
or read two blocks without verification
$ mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 2 /tmp/block
mmc rpmb write-block <rpmb device> <address> <256 byte data file> <key file>
Block of 256 bytes will be written from data file to
<rpmb device>. Also you can specify '-' instead of key
file path or data file to read the data from stdin.
Example:
$ (awk 'BEGIN {while (c++<256) printf "a"}' | \
echo -n AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHH) | \
mmc rpmb write-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 - -
mmc cache enable <device>
Enable the eMMC cache feature on <device>.
NOTE! The cache is an optional feature on devices >= eMMC4.5.
mmc cache disable <device>
Disable the eMMC cache feature on <device>.
NOTE! The cache is an optional feature on devices >= eMMC4.5.
mmc csd read <device path>
Print CSD data from <device path>.
The device path should specify the csd file directory.
mmc cid read <device path>
Print CID data from <device path>.
The device path should specify the cid file directory.
mmc scr read <device path>
Print SCR data from <device path>.
The device path should specify the scr file directory.
mmc ffu <image name> <device>
Run Field Firmware Update with <image name> on <device>.
mmc help|--help|-h
Show the help.
mmc <cmd> --help
Show detailed help for a command or subset of commands.
0.1#mmc rpmb --help 可查看手册rpmb相关指令
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb --help
Usage:
mmc rpmb write-key <rpmb device> <key file>
Program authentication key which is 32 bytes length and stored
in the specified file. Also you can specify '-' instead of
key file path to read the key from stdin.
NOTE! This is a one-time programmable (unreversible) change.
Example:
$ echo -n AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHH | \
mmc rpmb write-key /dev/mmcblk0rpmb -
mmc rpmb read-counter <rpmb device>
Counter value for the <rpmb device> will be read to stdout.
mmc rpmb read-block <rpmb device> <address> <blocks count> <output file> [key file]
Blocks of 256 bytes will be read from <rpmb device> to output
file or stdout if '-' is specified. If key is specified - read
data will be verified. Instead of regular path you can specify
'-' to read key from stdin.
Example:
$ echo -n AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHH | \
mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 2 /tmp/block -
or read two blocks without verification
$ mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 2 /tmp/block
mmc rpmb write-block <rpmb device> <address> <256 byte data file> <key file>
Block of 256 bytes will be written from data file to
<rpmb device>. Also you can specify '-' instead of key
file path or data file to read the data from stdin.
Example:
$ (awk 'BEGIN {while (c++<256) printf "a"}' | \
echo -n AAAABBBBCCCCDDDDEEEEFFFFGGGGHHHH) | \
mmc rpmb write-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 - -
0.1# 执行指令
[root@lemon:~]# mmc rpmb read-counter /dev/mmcblk0rpmb
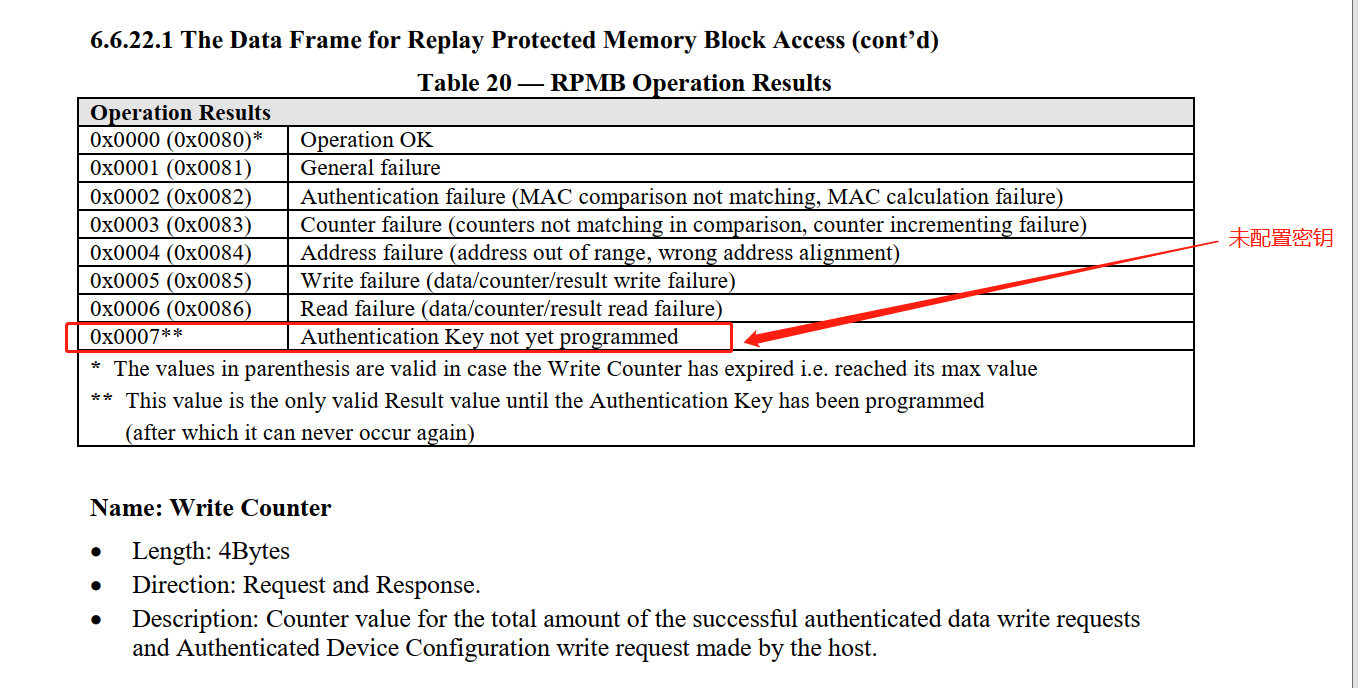
RPMB operation failed, retcode 0x0007错误代码 0x0007 表示 RPMB 操作失败,通常是由于 密钥未编程 或 认证失败。
1、错误原因分析
1.1、错误码解析
-
0x0001:身份验证失败(Invalid MAC)
-
0x0002:计数器不匹配
-
0x0004:写操作失败
-
0x0007 = 0x0001 | 0x0002 | 0x0004 → 综合错误(通常是密钥问题)
1.2、根因分析
-
RPMB 密钥(RPMB_KEY)未正确编程到 eMMC
-
使用的密钥与 eMMC 中存储的密钥不匹配
2、解决方案步骤
2.1、确认 RPMB 密钥状态
# 检查是否已编程密钥(返回0表示未编程)
# 如果返回 0x0007,说明密钥未编程或无效
mmc rpmb read-counter /dev/mmcblk0rpmb2.2、生成 RPMB 密钥
# 生成随机密钥(32字节)
# if=/dev/random:从 Linux 的加密安全随机数生成器读取数据
# bs=32:块大小为 32 字节(RPMB 密钥的固定长度)
# count=1:生成 1 个块(即 32 字节)
# 输出:生成二进制文件 rpmb_key.bin
dd if=/dev/random of=rpmb_key.bin bs=32 count=1生成密钥
MD5:F7CC32EA67F06DB0A5D4D55E9BAD6215
2.3、设置密钥
# 注意:密钥一旦编程,无法读取或修改!
# 编程密钥到 eMMC(只能执行一次!)
# mmc rpmb write-key <rpmb device> <key file>
# Usage: mmc rpmb write-key </path/to/mmcblkXrpmb> </path/to/key>
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb write-key /dev/mmcblk0rpmb rpmb_key.bin
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# 2.4、验证密钥
# 读取计数器(应返回当前计数器值,而非错误)
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb read-counter /dev/mmcblk0rpmb
Counter value: 0x000000002.5、 执行 RPMB 数据读写
2.5.1、写入数据
# 待写入文件生成
# 写入文件必须是256字节否则会写入失败
# eg:
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb write-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x00 dat_rpmb.dat rpmb_key.bin
Data must be 256 bytes length, but we read only 5, exit
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]#
# 生成256大小的文件
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# { printf '1137'; dd if=/dev/zero bs=1 count=252 2>/dev/null | tr '\0' 'a'; } > dat_rpmb.dat
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# ls -lath
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4.0K Apr 21 06:49 .
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 256 Apr 21 06:49 dat_rpmb.dat
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 32 Apr 21 06:12 rpmb_key.bin
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4.0K Apr 21 06:10 ..
[root@CHCNAV:/mnt/test_rpmb]#
[root@CHCNAV:/mnt/test_rpmb]# cat dat_rpmb.dat
1137aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]#
# 写入数据
# Usage: mmc rpmb write-block </path/to/mmcblkXrpmb> <address> </path/to/input_file> </path/to/key>
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb write-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x00 dat_rpmb.dat rpmb_key.bin
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# 2.5.2、读取数据
# 创建空文件接收数据
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# touch output.dat
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# ls -lath
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4.0K Apr 21 06:57 .
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Apr 21 06:57 output.dat
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 256 Apr 21 06:49 dat_rpmb.dat
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 32 Apr 21 06:12 rpmb_key.bin
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4.0K Apr 21 06:10 ..
# 读取数据
# Usage: mmc rpmb read-block </path/to/mmcblkXrpmb> <address> <blocks count> </path/to/output_file> [/path/to/key]
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x00 1 output.dat rpmb_key.bin
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# ls
dat_rpmb.dat output.dat rpmb_key.bin
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# cat output.dat
1137aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]#
# 输出到终端控制台
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x00 1 - rpmb_key.bin
1137aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]#
# 支持非验证读取
# Usage : or read two blocks without verification
$ mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x02 1 /tmp/block
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb read-block /dev/mmcblk0rpmb 0x00 1 -
1137aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# 2.6、 再次读取 RPMB 计数器
# 计数器值+1
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc rpmb read-counter /dev/mmcblk0rpmb
Counter value: 0x00000001
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# 3、常见问题排查
问题 解决方法
密钥未编程 执行 mmc rpmb key 编程密钥
密钥不匹配 使用正确的 rpmb_key.bin 文件
eMMC 不支持 RPMB 检查 `mmc extcsd read grep RPMB_MULT`
权限不足 使用 sudo 或以 root 用户操作
4、关键注意事项
4.1、密钥安全
-
备份 rpmb_key.bin 到安全位置,丢失后无法恢复!
4.2、单次编程
-
每个 eMMC 的 RPMB 密钥只能编程一次。
4.3、分区支持非认证读取
-
rpmb分区必须认证写入,即需要密钥写入
-
rpmb分区支持认证/非认证读取,即无需密钥也可读取数据,只是无法修改
3、emmc RPMB分区使用
3.1、emmc RPMB 数据协议
【图1】【RPMB读写数据帧】RPMB区操作需使用特定数据帧格式传递
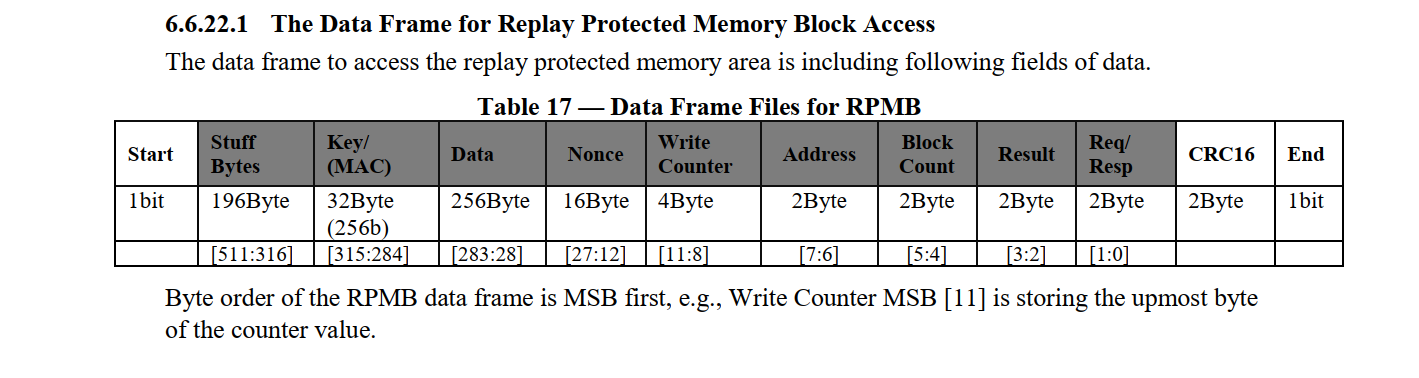
| 数据段 | 含义 | 描述 |
| stuff | 预留填充字段 | |
| MAC | 使用sha256算法: HMAC(Key + Data + ... + Req/Resp) | 认证密钥(Authentication Key): 一次性可编程认证密钥寄存器。此寄存器不能被主机覆盖、擦除或读取。在设备生产过程中写入,当计算MAC时,eMMC重播保护内存块引擎用来验证访问 |
| Data | 用户数据 | |
| Nonce | 随机数 | |
| Write Counter | 写计数器 | 主机写认证数据成功次数和写认证设备配置次数之和的计数器值。eMMC生产后的初始值为0x000000000。值将由eMMC重播保护内存块引擎与成功的编程访问。无法重置该值。当计数器达到其最大值0x FFFF FFFF后,它将不再增加(防止溢出),数组帧中操作结果(result)的位[7]值将被永久设置为1,表示计数器过期 |
| Address | 读写数据的起始地址 | 此地址非emmc物理地址 为RPMB区的逻辑地址 |
| Block Count | 读写数据块的数量 | 要求读取/编程的块数(半扇区,256B)。此值等于CMD23参数中的计数值 |
| Result | 指令操作结果 | 具体含义见下图【图3】 |
| Req/Resp | 指令类型 | 具体含义见下图【图2】 |
【图2】【指令类型】定义(请求【host -> emmc】 / 应答【emmc -> host】)操作指令id
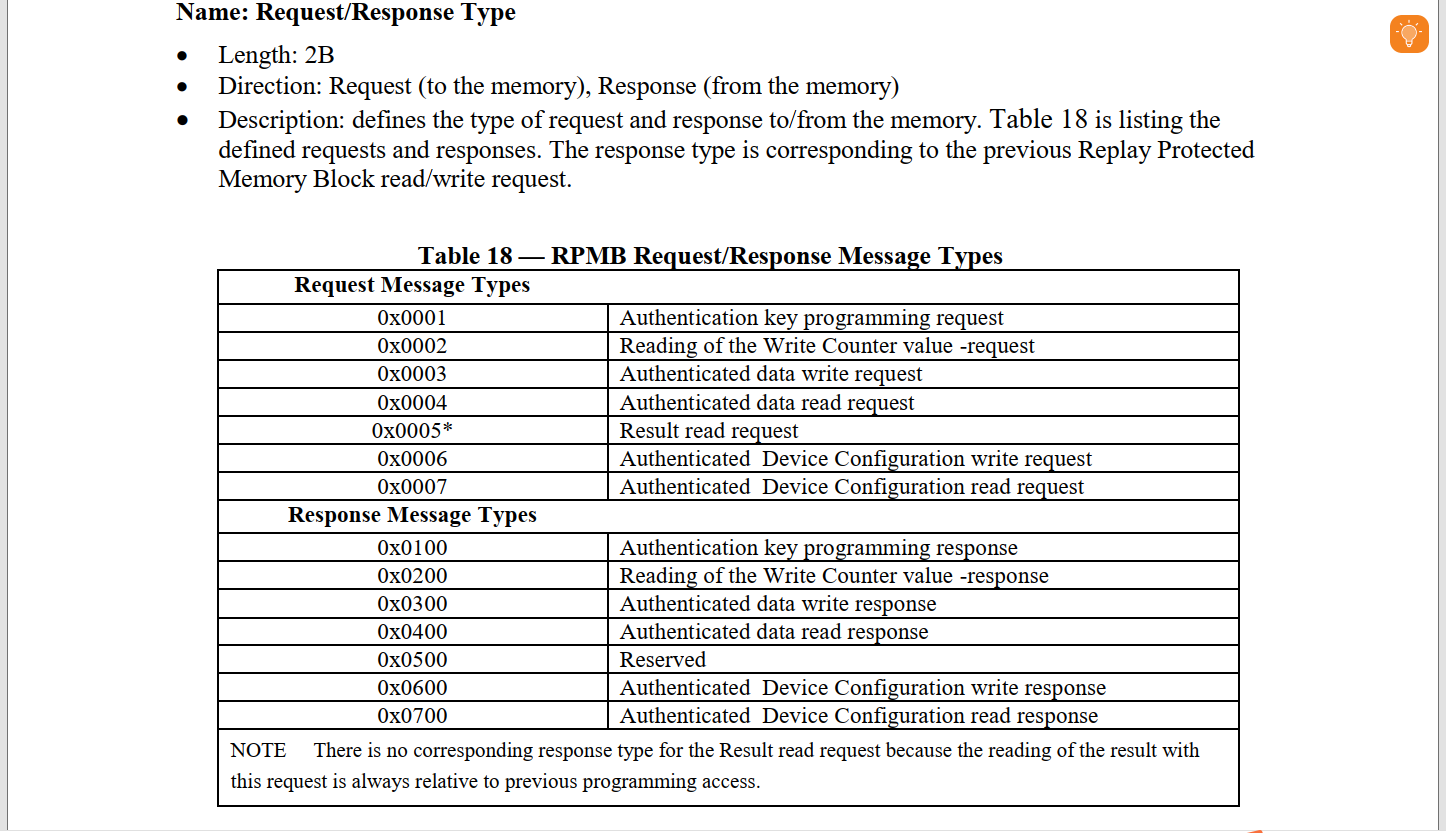
【图3】【指令操作结果】可通过读取写计数器的结果,判断密钥状态
【图4】【RPMB区大小】可通过读取EXT_CSD值确认
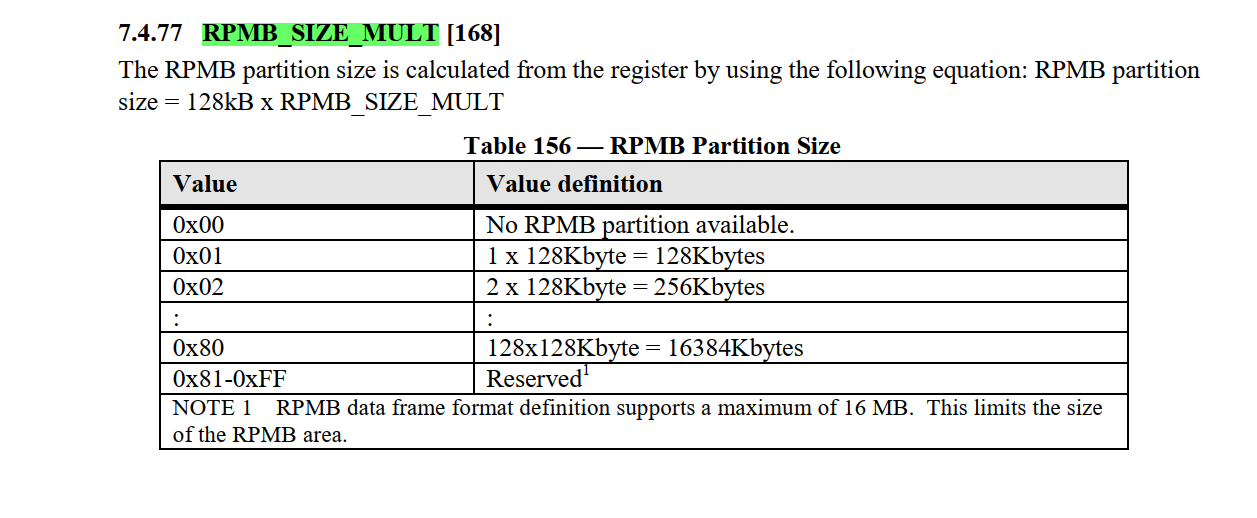
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# mmc extcsd read /dev/mmcblk0rpmb |grep RPMB
R/W Replay Protected Memory Block (RPMB)
RPMB Size [RPMB_SIZE_MULT]: 0x20
[root@lemon:/mnt/test_rpmb]# 调试设备RPMB区 size = 0x20 * 128KB = 4MB
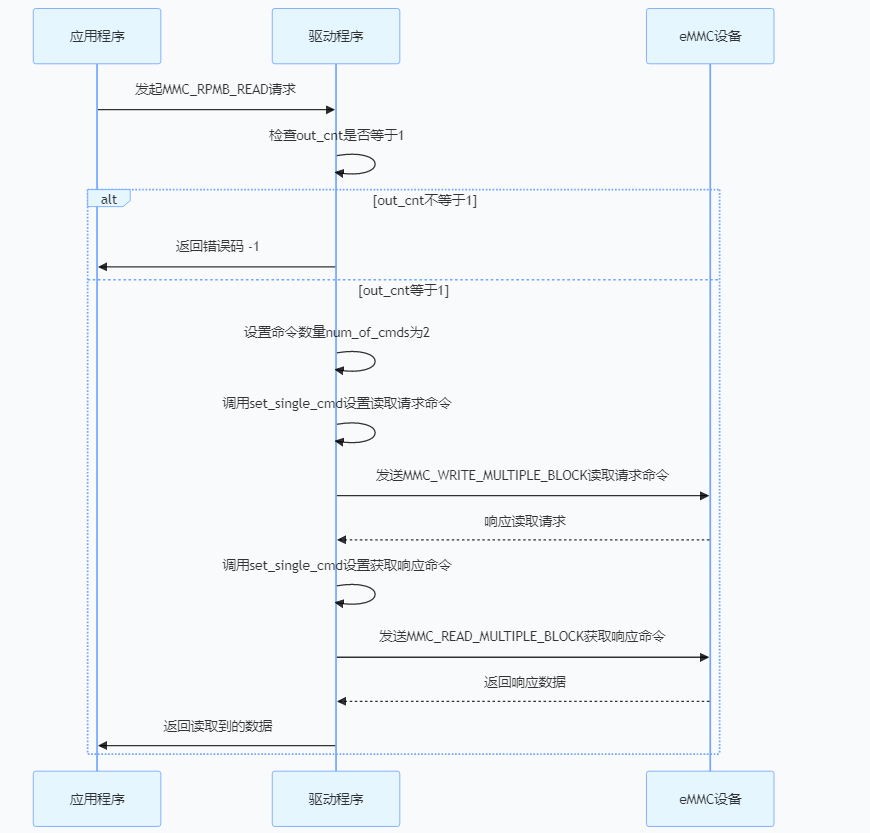
3.2、相关命令
| 命令 | 指令枚举 | 用途 | 关键参数 | rpmb用途 |
| CMD18 | MMC_READ_MULTIPLE_BLOCK | 多块读取 | blocks = 帧数 | 1、读数据帧 2、读指令应答 |
| CMD23 | 设置多块读写块数 | / | / | |
| CMD25 | MMC_WRITE_MULTIPLE_BLOCK | 多块写入 | (1<<31)| 1 1、高位1,标记为RPMB命令 2、低位1,标记为写入(0表示读取) | 1、写数据帧 2、写指令配置 |
注:(以下问题结论来源于网上资料,本人也不是很清楚,欢迎大佬解答🎤🎤🎤)
🔍【奇怪知识+1】为什么RPMB不需要CMD23?
🕵️♂️ 民间科学家推测:
-
协议规定:RPMB 操作通过固定的多命令序列实现原子性。
-
硬件支持:eMMC 控制器在 RPMB 模式下自动管理块计数。
3.3、rpmb读写流程
3.3.1、密钥烧录
3.3.2、写数据计数器读取
3.3.3、数据写入
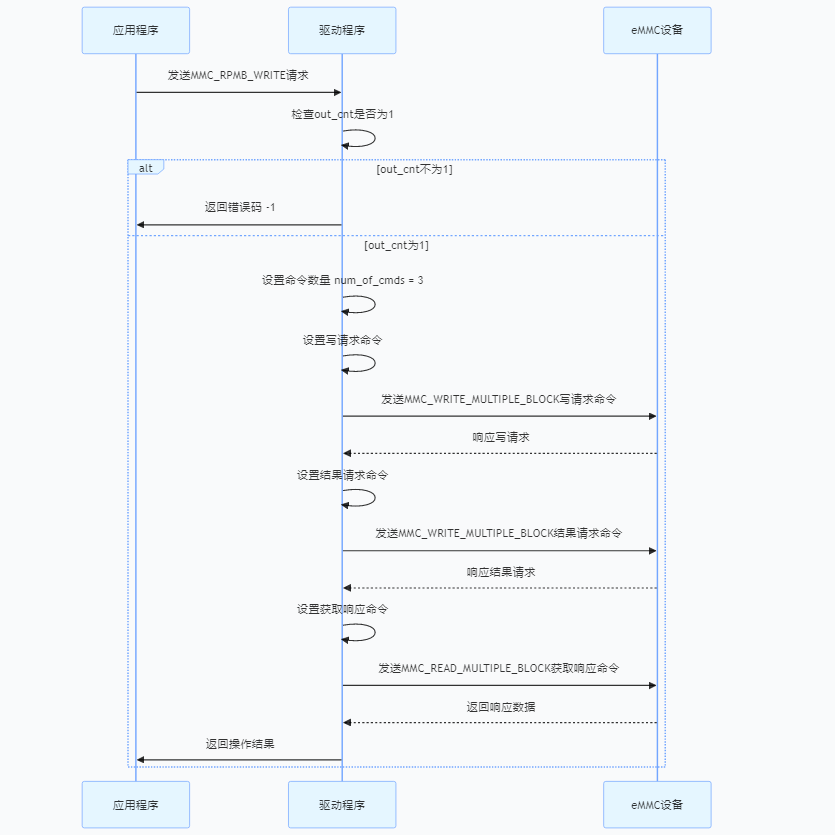
3.3.4、数据读取
3.4、读写组件实现
基于 mmc-utils 二次开发,封装 eMMC RPMB(Replay Protected Memory Block) 安全存储区操作接口,提供 密钥认证、防重放攻击、数据签名校验 等核心功能,适用于嵌入式安全存储场景。
3.4.1、核心特性
✅ 标准化接口:兼容 JEDEC eMMC 规范,提供读写、计数等基础操作
✅ 安全算法集成:内置 HMAC-SHA256 签名验证,保障数据完整性
✅ 易用封装:简化 RPMB 开发流程,降低嵌入式安全存储集成门槛
3.4.2、项目链接
📌 遵循 GPL-2.0,衍生自大佬的 mmc-utils,完整代码已开源,📦 开箱即用,欢迎 Star & Fork 👉 项目地址
适用场景:嵌入式设备安全、可信存储等。
🎯 写在最后
📌 本文性质
"这是一篇来自嵌入式摸鱼工程师的工作笔记📒,记录了和RPMB斗智斗勇的血泪史💦"
🙏 求指教
"欢迎各位大佬拍砖🧱(轻点打脸)"
"发现错误?您将获得【首席捉虫官】荣誉证书🐛(虚拟版)"
💌 交流方式
"评论区已铺好红毯👑,期待您的:"
-
"👏 点赞暴击"
-
"💡 神评论"
-
"🤔 灵魂提问"
✨ 特别声明
"本文内容最终解释权归咖啡因☕和熬夜🌙共同所有"
✨ 友情提示
点赞👍 + 收藏⭐ = 获得「下次更新优先踹你通知」特权!
开源万岁:代码可以白嫖,但记得留下你的 Star🌟!
(不然下次更新可能要等 10 年⏳…开玩笑的,但真的会伤心💔)
🤪 终极警告:
"转载不留名?小心你的 eMMC 寿命-1%!"
(虽然技术上做不到,但玄学警告⚠️)























 1097
1097

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








