homework2 - TDD实践
一.“迭代”章节的练习
1. 修改测试代码,以便调用者可以指定字符重复的次数,然后修复代码
- 修改Repeat函数
将原有的iteraction.go中的Repeat的函数定义进行更改。使它可以接收两个参数,一个为用于重复的基础字符串character,另一个为重复次数time;package iteraction // Repeat is a function that repeat character at time times // character, the string to repeat; // time, the time that character repeat func Repeat(character string, time int) string { var repeated string for i := 0; i < time; i++ { repeated = repeated + character } return repeated } - 完善iteraction_test函数
为了让TestRepeat函数可以接收用户输入的重复次数,我们import了flag库
调用结果:func TestRepeat(t *testing.T) { // 利用flag.Args获取go test --args后的所有参数,并以string类型分片存于arglist中 arglist := flag.Args() var time int var e error if len(arglist) == 0 { // 如果没有参数,那么默认参数为5 time = 5 } else { if len(arglist) > 1 { // 如果参数超过1,那么只用第一个 fmt.Println("only the frist arg is useful") } time, e = strconv.Atoi(arglist[0]) if e != nil { // 当输入的参数不为数字,那么报错 t.Errorf("the first arg is not a num") } } // 调用Repeat; repeated := Repeat("a", time) expected := "aaaaa" if repeated != expected { t.Errorf("expected '%q' but got '%q'", expected, repeated) } }
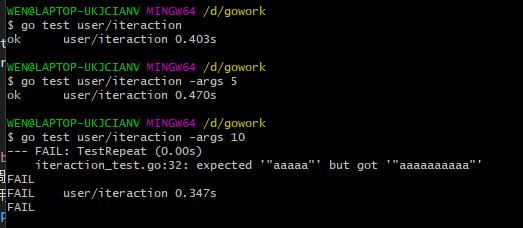
可以看见,当没有任何传入参数的时候,time设置为默认值5,输出和预期字符串相同的字符串,输出ok;当调用-args后面跟着5的时候,我们的test输出“aaaaa”,和预期的字符串相同输出ok;而当调用后面跟着10的时候,我们的test报FAIL,且输出为“aaaaaaaaaa”;
2. ExampleRepeat 实现
在itreaction_test.go文件中加入ExampleRepeat函数的实现
func ExampleRepeat() {
out := Repeat("z", 3)
fmt.Println(out)
// Output: zzz
}
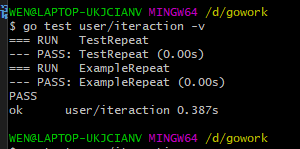
测试结果:
3. string包测试
本人认为较为重要的几个函数:
- Compare;
- Split;
- Contain;
以下为各个函数的测试函数,均位于iteraction_test.go中 - Compare;
func TestCompare(t *testing.T) { a, b := "hello", "hello" same := strings.Compare(a, b) if same != 0 { t.Error("fail: a and b should be the same") } } - Split;
func TestSplit(t *testing.T) { a, b := "aaaabaaaa", "b" s := strings.Split(a, b) if len(s) != 2 || s[0] != "aaaa" { t.Error("fail: a and b must be split by b and become two part") } } - Contain;
func TestContain(t *testing.T) { a, b := "hello, world", "hello" contain := strings.Contains(a, b) if contain == false { t.Error("fail: a should contain b") } }
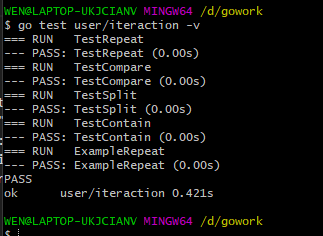
测试结果:
二.快排算法go语言实现
先写测试
qicksort_test.go:
package qicksort
import (
"testing"
)
func TestQicksort(t *testing.T) {
a := []int{0, 5, 1, 6, 8, 9, 2, 3, 7, 4}
b := Qicksort(a)
for i, v := range b {
if v != i {
t.Error("b is ", b, " not sorted")
break
}
}
}
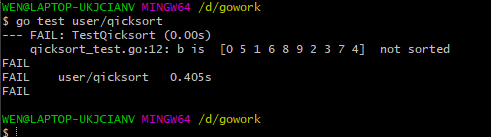
尝试运行
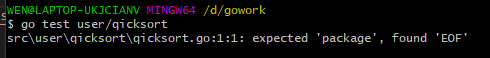
go test user/qicksort
运行结果:
使用最少的代码让程序运行起来
qicksort.go:
package qicksort
// Qicksort is a function to sort int array a
func Qicksort(a []int) []int {
return a
}
运行结果:
将代码补充完整,使其通过测试
qicksort.go:
package qicksort
func qicksort(a []int, low, high int) {
// 当low >= high的时候,说明已经拍好序了,直接返回;
if low >= high {
return
}
// 遍历low->high的所有节点,根据a[low]将他们分为两部分:
// low->mid-1: 小于a[low]的所有值;
// mid+1->high: 大于a[low]的所有值;
mid := low
for i := low; i <= high; i++ {
if a[low] > a[i] {
mid++
temp := a[mid]
a[mid] = a[i]
a[i] = temp
}
}
temp := a[low]
a[low] = a[mid]
a[mid] = temp
// 对所有小于a[low]的值进行qicksort
qicksort(a, low, mid-1)
// 对所有大于a[low]的值进行qicksort
qicksort(a, mid+1, high)
}
// Qicksort is a function to sort int array a
func Qicksort(a []int) []int {
high := 9
low := 0
qicksort(a, low, high)
return a
}
输出结果
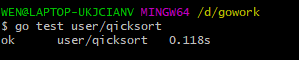
重构
在qicksort函数中,我们多次用到了数值的交换:
temp := a[mid]
a[mid] = a[i]
a[i] = temp
因此,我们可以将它独立出来成为一个函数;
func swap(a, b int) (int, int) {
return b, a
}
在之前的版本中Qicksort只能接受一个大小为10的int数组,我们改动Qicksort中的high的赋值语句,使得high = len(a) - 1,那么我们的Qicksort能够接受任意长度大于等于0的int数组,并对它们进行排序。
重构后的qicksort.go如下:
package qicksort
func swap(a, b int) (int, int) {
return b, a
}
func qicksort(a []int, low, high int) {
// 当low >= high的时候,说明已经拍好序了,直接返回;
if low >= high {
return
}
// 遍历low->high的所有节点,根据a[low]将他们分为两部分:
// low->mid-1: 小于a[low]的所有值;
// mid+1->high: 大于a[low]的所有值;
mid := low
for i := low; i <= high; i++ {
if a[low] > a[i] {
mid++
a[mid], a[i] = swap(a[mid], a[i])
// temp := a[mid]
// a[mid] = a[i]
// a[i] = temp
}
}
a[low], a[mid] = swap(a[low], a[mid])
// temp := a[low]
// a[low] = a[mid]
// a[mid] = temp
// 对所有小于a[low]的值进行qicksort
qicksort(a, low, mid-1)
// 对所有大于a[low]的值进行qicksort
qicksort(a, mid+1, high)
}
// Qicksort is a function to sort int array a
func Qicksort(a []int) []int {
high := len(a) - 1 // 传来的a的数组大小-1即为数组上限;
low := 0
qicksort(a, low, high)
return a
}
输出结果:

基准测试
基准测试函数(qicksort_test.go):
func BenchmarkQicksort(b *testing.B) {
a := []int{0, 5, 1, 6, 8, 9, 2, 3, 7, 4}
for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
Qicksort(a)
}
}
输出结果:
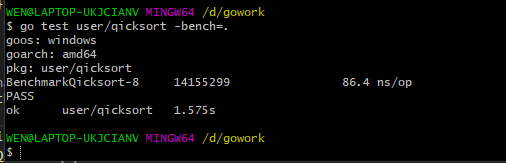
- 14155299:说明Qicksort函数在我的计算机中运行了14155299次;
- 86.4ns :说明每个Qicksort函数的运行时长平均为86.4ns;




 本文介绍了Go语言中使用TDD(测试驱动开发)方法改进`Repeat`函数,允许指定字符重复次数,并实现了测试用例。接着展示了如何编写ExampleRepeat示例,以及对`strings`包中的`Compare`, `Split`, `Contains`函数进行测试。此外,还实现了快速排序算法,从初始的空实现逐步完善并通过测试,最后进行了代码重构,提高效率。并提供了基准测试以评估排序函数的性能。
本文介绍了Go语言中使用TDD(测试驱动开发)方法改进`Repeat`函数,允许指定字符重复次数,并实现了测试用例。接着展示了如何编写ExampleRepeat示例,以及对`strings`包中的`Compare`, `Split`, `Contains`函数进行测试。此外,还实现了快速排序算法,从初始的空实现逐步完善并通过测试,最后进行了代码重构,提高效率。并提供了基准测试以评估排序函数的性能。
















 508
508

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








