文章目录
二叉排序树(Binary Sort Tree),又称为二叉查找树
特点:
若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上的所有结点的值均小于它的根结点的值。同理,右子树是大于根结点的值。它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
注: 若有相同的值,将该结点放在左子结点或右子结点均可(本文放在右子结点)
一、二叉排序树的插入(即二叉树的创建)
(1)步骤
- 若二叉排序树为空树,则新插入的结点为新的根结点。
- 若不为空树,且新结点的值 < 当前结点的值,且当前结点无左结点,则插入新结点(成为当前结点的左结点)。
- 否则,递归当前结点的左结点。
- 若新结点的值 > 当前结点的值,且当前结点无右结点,则插入新结点(成为当前结点的右结点)。
- 否则,递归当前结点的右结点。
(2)实现代码
- Node类的插入函数
public void add(Node node){ //插入结点的方法
if(node != null){
if(node.value < this.value){ //1.若新结点的值 < 当前结点
if(this.left == null){ //1.1当前结点无左结点
this.left = node; //新结点成为当前结点的左结点
}else { //1.2若当前结点有左结点
this.left.add(node); //递归左结点
}
} else if(this.right == null){ //2.若新结点的值>=当前结点,且当前结点无右结点
this.right = node; //2.1新结点成为当前结点的右结点
}else{ //2.2当前结点有右结点
this.right.add(node); //递归右结点
}
}
}
- BinarySortTree类的插入函数
public void add(Node node ){ //二叉排序树插入结点的方法
if(root == null){ //1.若根结点为空
root = node; //1.1把输入的结点放在根结点
}else{ //2.若根结点不为空
root.add(node); //2.1调用Node类中的添加结点的方法
}
}
二、二叉排序树的遍历
和普通二叉树一样,也有前序、中序、后续遍历。这里代码实现了中序遍历。
(1)代码实现
- Node类的中序遍历函数
public void infixOrder(){ //树的中序遍历
if(this.left != null){ //1.若当前结点有左结点
this.left.infixOrder(); //1.1递归该左结点
}
System.out.println(this.value); //2.一直递归到结点无左子结点。并输出这个结点
if(this.right != null){ //3.若当前有右结点
this.right.infixOrder(); //3.1递归该右结点(当右结点无左结点时,该右结点也会被2.1输出)
}
}
- BinarySortTree类的中序遍历函数
public void infixOrder() {
if(this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉排序树为空,不能遍历");
}
}
三、二叉排序树的查找
(1)步骤
二叉排序树可看作一个有序表,它的查找类似与二分查找。
- 若查找的关键字 = 根结点关键字,查找成功。
- 若查找的关键字 < 根结点关键字,递归查找左子树。
- 若查找的关键字 > 根结点关键字,递归查找右子树。
- 若子树为空,则查找失败。
(2)实现代码
- Node类的查找函数
public Node BstSearch(int num){ //结点的查找
if(num == this.value){ //1.若查找的值 = 当前结点的值
return this; //1.1返回当前节点的索引
}else if(num < this.value && this.left != null){ //2.若查找的值 < 当前结点的值
return this.left.BstSearch(num); //2.1递归查找当前结点的左子结点
}else if(num > this.value && this.right != null){ //3.若查找的值 > 当前结点的值
return this.right.BstSearch(num); //3.1递归查找当前结点的右子结点
}
return null; //若没查到,则返回索引null
}
- BinarySortTree类的查找函数
public Node BstSearch(int num){ //树中的结点查找
if(num == root.value){ //1.若要查找的值正好 = 根结点的值
return root; //1.1返回根结点的索引
}else{ //2.若要查找的值 != 根结点的值
return root.BstSearch(num); //2.1递归在树中查找(进入Node类中的查找方法)
}
}
四、二叉排序树的删除
查找要删除结点的父结点
(1)代码实现
- Node类的查找父结点函数
public Node searchParent(int value){
//若要查找的值与当前节点的左子结点的值相等 或 要查找的值与当前结点的右子结点的值相等
if((this.left != null && this.left.value == value)||(this.right != null && this.right.value == value)){
return this; //则当前结点就是父结点
}else if(value < this.value && this.left != null){ //若查找值 < 当前结点的值,且当前结点的左子结点存在
return this.left.searchParent(value); //向左子树递归查找
}else if(value > this.value && this.right != null){ //若查找值 > 当前结点的值,且当前结点的右子结点存在
return this.right.searchParent(value); //向右子树递归查找
}
return null;
}
- BinarySortTree类的查找父结点函数
public Node searchParent(int value){
if(this.root == null){
return null;
}else{
return this.root.searchParent(value);
}
}
第一种删除情况
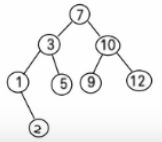
删除叶子结点(例如:2,5,9,12)
(1)算法思路
- 先找到要删除的结点target。
- 找到target的父节点parent。
- 确定target是parent的左子结点还是右子结点。
- 若是左子结点,则parent.left = null;若是右子结点,则parent.right = null。
(2)代码实现
Node parent = searchParent(value); //在二叉树中找到要删除结点的父结点
if (target.left == null && target.right == null) { //4.若要删除的结点是叶子结点
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) { //4.1若要删除的结点是父结点的左子结点
parent.left = null; //4.2将父结点的左子结点置空即可删除
}else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) { //4.3若要删除的结点是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = null; //4.4将父结点的右子结点置空即可删除
}
}
第二种删除情况
删除只有一棵子树(只有左子树或右子树)的结点(例如:1)

(1)算法思路
- 先找到要删除的结点target。
- 找到target的父结点parent。
- 确定target的子结点是左子结点还是右子结点。
- 确定target是parent的左子结点还是右子结点。
- 若target有左子结点
5.1 若target是parent的左子结点,则parent.left = target.left。
5.2 若target是parent的右子结点,则parent.right = target.left。 - 若target是parent的右子结点
6.1 若target是parent的左子结点,则parent.left = target.right。
6.2 若taret是parent的右子结点,则parent.right = target.right。
(2)代码实现
if(target.left != null){ //6.1若删除的结点只有左子树
if (parent.left.value == value) { //6.11且target是父结点的的左子结点
parent.left = target.left; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
}else { //6.12若target是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = target.left; //把要删除结点的右子树连在它的父结点上
}
}else{ //6.2.若删除的结点只有右子树
if (parent.left.value == value) //6.21且target是父结点的的左子结点
parent.left = target.right; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
else { //6.22若target是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = target.right; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
}
}
第三种删除情况
删除有两棵子树的结点(例如:7,3,10)

(1)算法思路
- 先找到要删除的结点target。
- 找到target的父结点parent。
- 从target的右子树找到最小结点。
- 用一个临时变量,将最小结点的值保存
- 删除该最小结点
(2)解析
该算法思路的意思就是,从被删除结点的右子树中找到一个值最小的结点A(A的值为a),把A放在被删除结点的位置上,A原先的位置被清除。
(3)代码实现
- 删除target(要删除的结点)的右子树中的最小值结点
//返回以node为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值,这是target就指向了最小结点,删除这个最小结点
public int deleteTreeMin(Node node){ //该函数仅在被删除的结点左右子树都存在的情况下使用
Node target = node;
while(target.left != null){
target = target.left;
}
deleteNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
- 删除target结点
if(target.left != null && target.right != null) { //5.删除有两棵子树的结点
int min = deleteTreeMin(target.right);
target.value = min;
}
删除算法的代码(包含以上三种情况)
public int deleteTreeMin(Node node){ //该函数仅在被删除的结点左右子树都存在的情况下使用
Node target = node;
while(target.left != null){
target = target.left;
}
deleteNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
public boolean deleteNode(int value) {
if (this.root == null) { //1.若二叉树为空,则删除结点失败
return false;
} else {
Node target = BstSearch(value); //若二叉树不为空,先在二叉树中找到要删除的结点
if (target == null) { //2.若在二叉树中没找到结点,则删除失败
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { //3.若整个二叉树只有一个根结点
root = null; //3.1则将这个根结点置空,返回删除成功
return true;
}
Node parent = searchParent(value); //在二叉树中找到要删除结点的父结点
if (target.left == null && target.right == null) { //4.若要删除的结点是叶子结点
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) { //4.1若要删除的结点是父结点的左子结点
parent.left = null; //4.2将父结点的左子结点置空即可删除
}else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) { //4.3若要删除的结点是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = null; //4.4将父结点的右子结点置空即可删除
}
}else if(target.left != null && target.right != null) { //5.删除有两棵子树的结点
int min = deleteTreeMin(target.right);
target.value = min;
}
else { //6.删除只有一棵子树的结点
if(target.left != null){ //6.1若删除的结点只有左子树
if (parent.left.value == value) { //6.11且target是父结点的的左子结点
parent.left = target.left; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
}else { //6.12若target是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = target.left; //把要删除结点的右子树连在它的父结点上
}
}else{ //6.2.若删除的结点只有右子树
if (parent.left.value == value) //6.21且target是父结点的的左子结点
parent.left = target.right; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
else { //6.22若target是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = target.right; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
五、二叉排序树代码汇总
(1)结点Node类
class Node{ //建立结点
int value;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(int value){
this.value = value;
}
public void add(Node node){ //添加结点的方法
if(node != null){
if(node.value < this.value){ //1.若新结点的值比当前结点小
if(this.left == null){ //1.1当前结点无左结点
this.left = node; //新结点成为当前结点的左结点
}else { //1.2若当前结点有左结点
this.left.add(node); //递归左结点
}
} else if(this.right == null){ //2.若新结点的值>=当前结点,且当前结点无右结点
this.right = node; //2.1新结点成为当前结点的右结点
}else{ //2.2当前结点有右结点
this.right.add(node); //递归右结点
}
}
}
public void infixOrder(){ //树的中序遍历
if(this.left != null){ //1.若当前结点有左结点
this.left.infixOrder(); //1.1递归该左结点
}
System.out.println(this.value); //2.一直递归到结点无左子结点。并输出这个结点
if(this.right != null){ //3.若当前有右结点
this.right.infixOrder(); //3.1递归该右结点(当右结点无左结点时,该右结点也会被2.1输出)
}
}
public Node BstSearch(int num){ //结点的查找
if(num == this.value){ //1.若查找的值 = 当前结点的值
return this; //1.1返回当前节点的索引
}else if(num < this.value && this.left != null){ //2.若查找的值 < 当前结点的值
return this.left.BstSearch(num); //2.1递归查找当前结点的左子结点
}else if(num > this.value && this.right != null){ //3.若查找的值 > 当前结点的值
return this.right.BstSearch(num); //3.1递归查找当前结点的右子结点
}
return null; //若没查到,则返回索引null
}
public Node searchParent(int value){
//若要查找的值与当前节点的左子结点的值相等 或 要查找的值与当前结点的右子结点的值相等
if((this.left != null && this.left.value == value)||(this.right != null && this.right.value == value)){
return this; //则当前结点就是父结点
}else if(value < this.value && this.left != null){ //若查找值 < 当前结点的值,且当前结点的左子结点存在
return this.left.searchParent(value); //向左子树递归查找
}else if(value > this.value && this.right != null){ //若查找值 > 当前结点的值,且当前结点的右子结点存在
return this.right.searchParent(value); //向右子树递归查找
}
return null;
}
}
(2)二叉排序树BinarySortTree类
static class BinarySortTree { //创建二叉排序树
private Node root; //根结点
public void add(Node node) { //二叉排序树添加结点的方法
if (root == null) { //1.若根结点为空
root = node; //1.1把输入的结点放在根结点
} else { //2.若根结点不为空
root.add(node); //2.1调用Node类中的添加结点的方法
}
}
public void infixOrder() {
if (this.root != null) {
this.root.infixOrder();
} else {
System.out.println("二叉排序树为空,不能遍历");
}
}
public Node BstSearch(int num) { //树中的结点查找
if (num == root.value) { //1.若要查找的值正好 = 根结点的值
return root; //1.1返回根结点的索引
} else { //2.若要查找的值 != 根结点的值
return root.BstSearch(num); //2.1递归在树中查找(进入Node类中的查找方法)
}
}
public Node searchParent(int value) {
if (this.root == null) {
return null;
} else {
return this.root.searchParent(value);
}
}
//返回以node为根结点的二叉排序树的最小结点的值,这是target就指向了最小结点,删除这个最小结点
public int deleteTreeMin(Node node){ //该函数仅在被删除的结点左右子树都存在的情况下使用
Node target = node;
while(target.left != null){
target = target.left;
}
deleteNode(target.value);
return target.value;
}
public boolean deleteNode(int value) {
if (this.root == null) { //1.若二叉树为空,则删除结点失败
return false;
} else {
Node target = BstSearch(value); //若二叉树不为空,先在二叉树中找到要删除的结点
if (target == null) { //2.若在二叉树中没找到结点,则删除失败
return false;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) { //3.若整个二叉树只有一个根结点
root = null; //3.1则将这个根结点置空,返回删除成功
return true;
}
Node parent = searchParent(value); //在二叉树中找到要删除结点的父结点
if (target.left == null && target.right == null) { //4.若要删除的结点是叶子结点
if (parent.left != null && parent.left.value == value) { //4.1若要删除的结点是父结点的左子结点
parent.left = null; //4.2将父结点的左子结点置空即可删除
}else if (parent.right != null && parent.right.value == value) { //4.3若要删除的结点是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = null; //4.4将父结点的右子结点置空即可删除
}
}else if(target.left != null && target.right != null) { //5.删除有两棵子树的结点
int min = deleteTreeMin(target.right);
target.value = min;
}
else { //6.删除只有一棵子树的结点
if(target.left != null){ //6.1若删除的结点只有左子树
if (parent.left.value == value) { //6.11且target是父结点的的左子结点
parent.left = target.left; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
}else { //6.12若target是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = target.left; //把要删除结点的右子树连在它的父结点上
}
}else{ //6.2.若删除的结点只有右子树
if (parent.left.value == value) //6.21且target是父结点的的左子结点
parent.left = target.right; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
else { //6.22若target是父结点的右子结点
parent.right = target.right; //把要删除结点的左子树连在它的父结点上
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
(3)主函数
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = new int[]{7, 3, 10, 12, 5, 1, 9, 2,7};
BinarySortTree BST = new BinarySortTree();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i) {
BST.add(new Node(arr[i]));
}
System.out.println("中序遍历二叉排序树~");
BST.infixOrder();
System.out.println("二叉排序树的查找~");
System.out.println(BST.BstSearch(10).value);
System.out.println("二叉排序树的查找结点的父结点~");
// System.out.println(BST.searchParent(2).value);
System.out.println("二叉排序树的删除~");
BST.deleteNode(7);
}
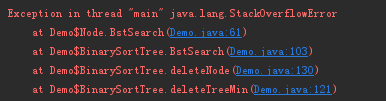
六、存在问题
- 被删除的结点可能不存在父结点。
- 若二叉排序树中有重复元素,则删除会报错。
以上两种情况都会报错。





 本文详细介绍了二叉排序树的概念、特性,并分别阐述了插入、中序遍历、查找、删除操作的步骤和实现代码。在删除操作中,讨论了删除叶子节点、只有一个子节点和有两个子节点的情况。同时,文章指出了删除操作可能遇到的问题,如节点无父节点和重复元素的情况。
本文详细介绍了二叉排序树的概念、特性,并分别阐述了插入、中序遍历、查找、删除操作的步骤和实现代码。在删除操作中,讨论了删除叶子节点、只有一个子节点和有两个子节点的情况。同时,文章指出了删除操作可能遇到的问题,如节点无父节点和重复元素的情况。
















 3263
3263

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








