C语言和C++中,指针有两个const,一个修饰指向,一个修饰自身
const p 修饰指向
const int p; // 修饰内容(指向)
int const* p; // 修饰内容(指向)
int* const p; // 修饰地址(自身)
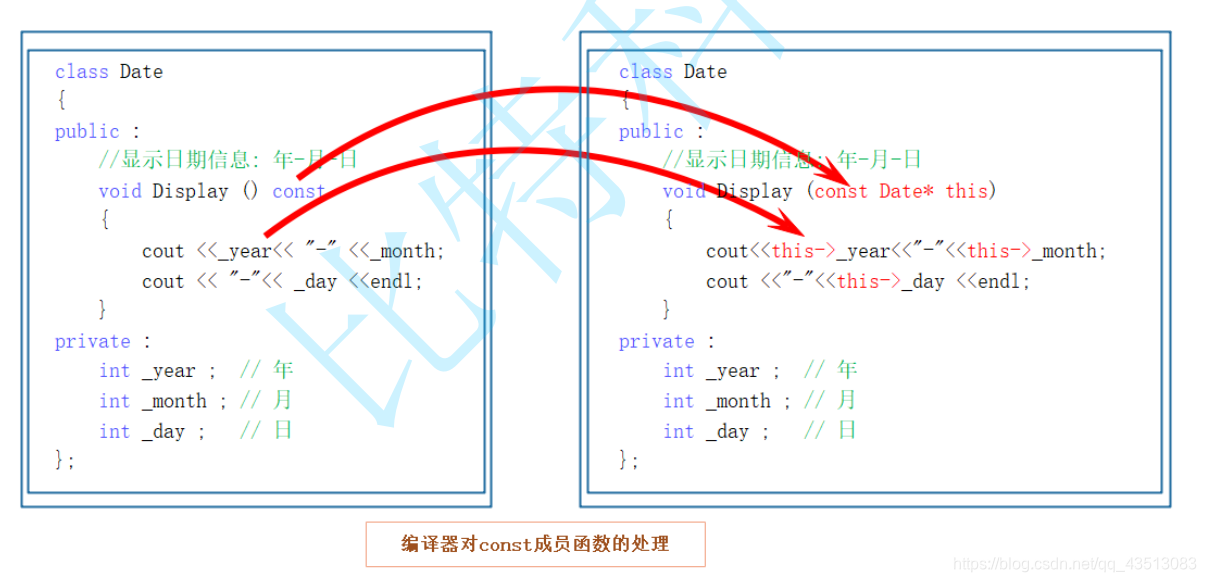
const修饰类成员函数,实际修饰该成员函数隐含的指针(修饰this指针),表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改
const成员函数不能修改成员变量(修饰限制this指针)当前对象中的内容不允许修改
普通类型对象内部可以调用const类型成员函数,const类型成员函数内部不能调用普通类型成员函数
取地址及const取地址操作符重载:
class Date
{
public :
Date* operator&()
{
return this ;
}
const Date* operator&()const
{
return this ;
}
private :
int _year ; // 年
int _month ; // 月
int _day ; // 日
};
class Date {
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1); //全缺省函数构造
Date(const Date& d); //拷贝构造
Date& operator=(const Date& d); //赋值运算符的重载
Date operator+(int days);
int operator+(const Date& d);
Date& operator++(); //前置++ 运算符重载
Date operator++(int); //后置++
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
bool operator>(const Date& d)const;
};
通过代码实例明确const的使用规则和适用范围:
//这两个函数形成重载(参数列表不一样)
void PrintDate()
void PrintDate()const {
void PrintDate1() {
PrintDate2();
}
void PrintDate2()const {
cout << _day << endl;
//只读函数,不可修改
//_day=1; 错
//普通类型对象内部可以调用const类型成员函数,const类型成员函数内部不能调用普通类型成员函数
//PrintDate1();
}
const常用于拷贝构造:Date(const Date& d);





















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








