题目链接:232.用栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
public:
stack<int> stcIn;
stack<int> stcOut;
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
stcIn.push(x);
}
int pop() {
if(stcOut.empty()){
while(!stcIn.empty()){
stcOut.push(stcIn.top());
stcIn.pop();
}
}
int result = stcOut.top();
stcOut.pop();
return result;
}
int peek() {
int res = this->pop();
stcOut.push(res);
return res;
}
bool empty() {
if(stcIn.empty()&&stcOut.empty()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = new MyQueue();
* obj->push(x);
* int param_2 = obj->pop();
* int param_3 = obj->peek();
* bool param_4 = obj->empty();
*/思路:
在push数据的时候,只要数据放进输入栈就好,但在pop的时候,操作就复杂一些,输出栈如果为空,就把进栈数据全部导入进来(注意是全部导入),再从出栈弹出数据,如果输出栈不为空,则直接从出栈弹出数据就可以了。
最后如何判断队列为空呢?如果进栈和出栈都为空的话,说明模拟的队列为空了。
在代码实现的时候,会发现pop() 和 peek()两个函数功能类似,代码实现上也是类似的,可以思考一下如何把代码抽象一下。
题目链接:225. 用队列实现栈
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que1;
queue<int> que2; // 辅助队列,用来备份
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que1.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que1.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将que1 导入que2,但要留下最后一个元素
que2.push(que1.front());
que1.pop();
}
int result = que1.front(); // 留下的最后一个元素就是要返回的值
que1.pop();
que1 = que2; // 再将que2赋值给que1
while (!que2.empty()) { // 清空que2
que2.pop();
}
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que1.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que1.empty();
}
};思路:
两个队列来实现栈的思路。
队列是先进先出的规则,把一个队列中的数据导入另一个队列中,数据的顺序并没有变,并没有变成先进后出的顺序。
所以用栈实现队列, 和用队列实现栈的思路还是不一样的,这取决于这两个数据结构的性质。
但是依然还是要用两个队列来模拟栈,只不过没有输入和输出的关系,而是另一个队列完全用来备份的!
如下面动画所示,用两个队列que1和que2实现队列的功能,que2其实完全就是一个备份的作用,把que1最后面的元素以外的元素都备份到que2,然后弹出最后面的元素,再把其他元素从que2导回que1。
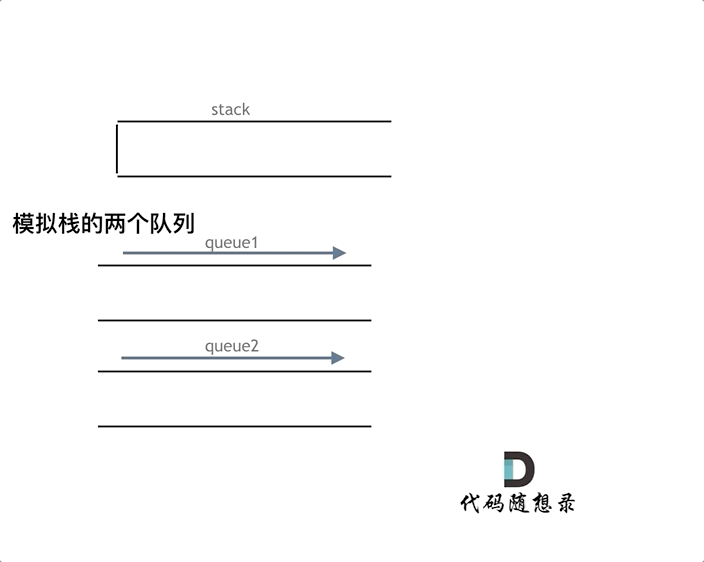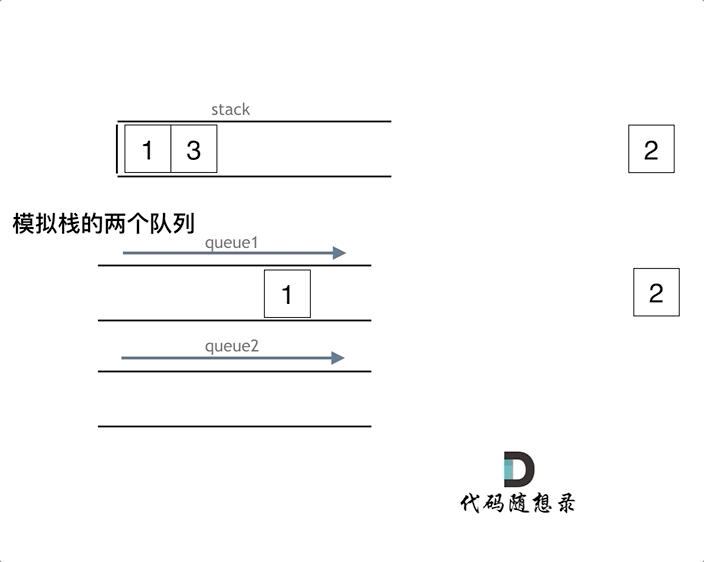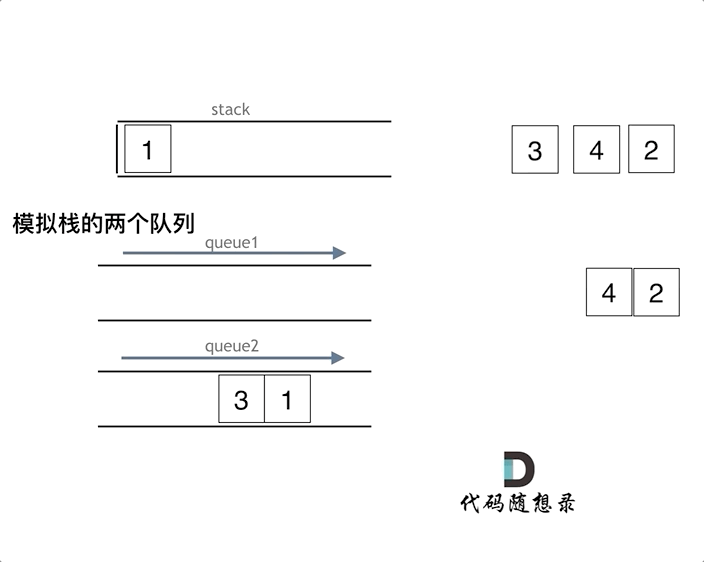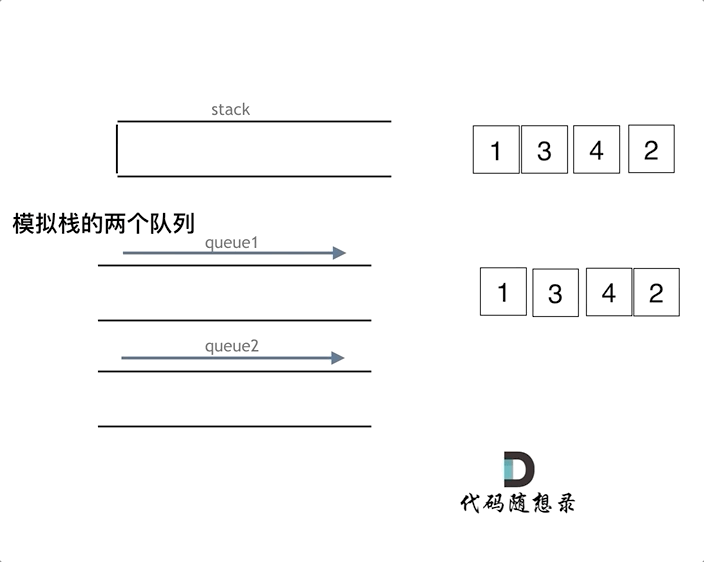
优化(一个队列):
一个队列在模拟栈弹出元素的时候只要将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部,此时再去弹出元素就是栈的顺序了。
class MyStack {
public:
queue<int> que;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
que.push(x);
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int size = que.size();
size--;
while (size--) { // 将队列头部的元素(除了最后一个元素外) 重新添加到队列尾部
que.push(que.front());
que.pop();
}
int result = que.front(); // 此时弹出的元素顺序就是栈的顺序了
que.pop();
return result;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
return que.back();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return que.empty();
}
};




 文章介绍了如何使用栈和队列这两种数据结构来实现队列和栈的功能。在用栈实现队列时,通过两个栈,一个作为输入,一个作为输出,来保持队列的特性。而在用队列实现栈时,利用两个队列的转换达到栈的后进先出效果。此外,还提供了一种优化方案,只用一个队列也能实现栈的功能。
文章介绍了如何使用栈和队列这两种数据结构来实现队列和栈的功能。在用栈实现队列时,通过两个栈,一个作为输入,一个作为输出,来保持队列的特性。而在用队列实现栈时,利用两个队列的转换达到栈的后进先出效果。此外,还提供了一种优化方案,只用一个队列也能实现栈的功能。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










