时间序列数据库IoTDB
一:前置环境准备
JDK1.8+
官网:https://iotdb.apache.org/ & https://iotdb.apache.org/zh/
文档查看地址:https://iotdb.apache.org/zh/UserGuide/latest/QuickStart/QuickStart.html
下载地址:https://iotdb.apache.org/zh/Download/
代码库:https://github.com/apache/iotdb/tree/master
1:windows/mac安装
https://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi/iotdb/1.3.5/apache-iotdb-1.3.5-all-bin.zip
安装之后解压是这样的
然后分别启动服务端和客户端:
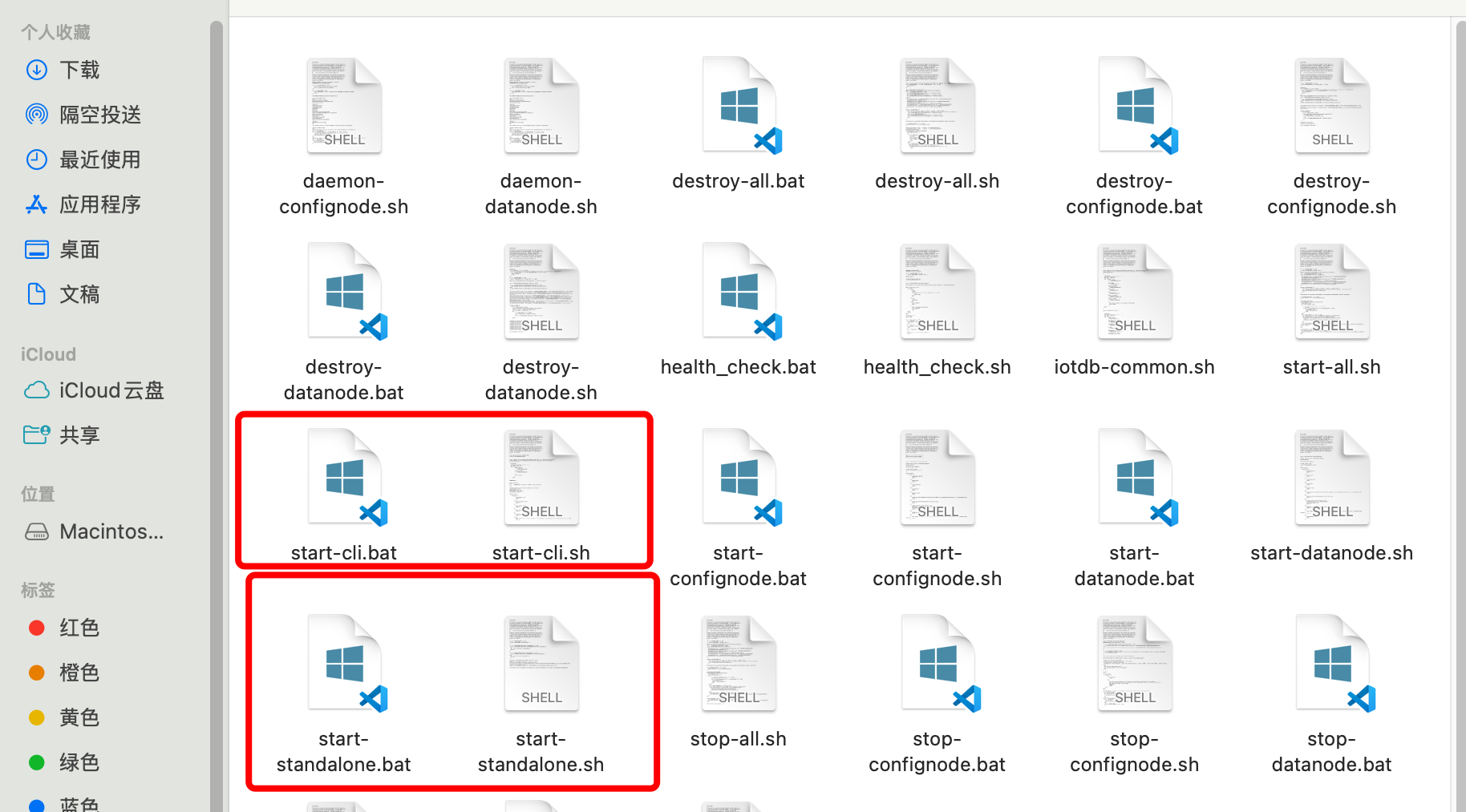
服务端:start-standalone bat
客户端:start-cli.bat -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6667 -u root -pw root
2:快速上手案例
假设现在又如下的终端设备要接入我们的系统平台
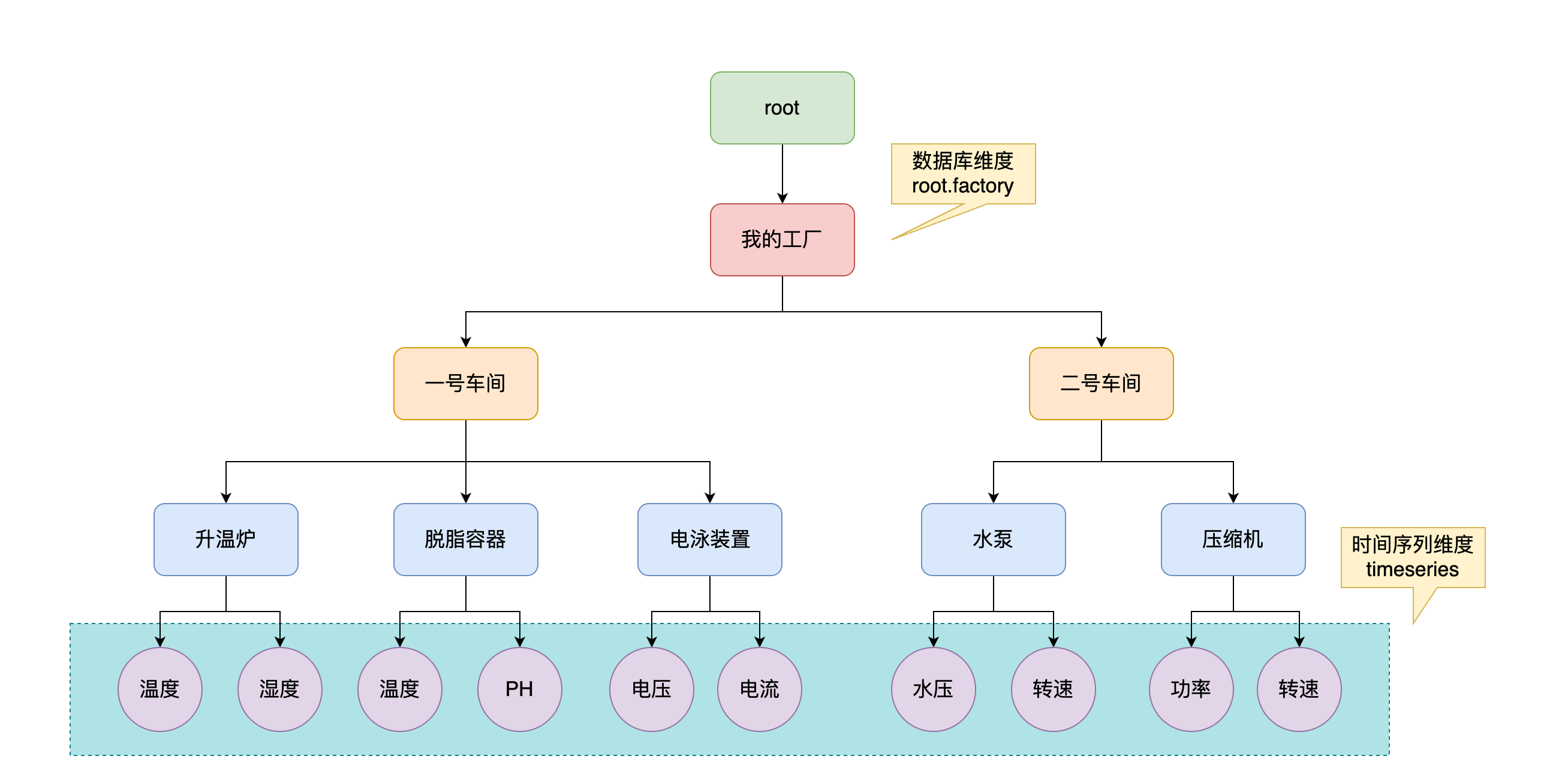
# 创建数据库
create database root.factory;
show databases;
# 创建时间序列
# root -> 我的工厂 -> 一号车间 -> 升温炉 -> 温度 ===> root.factory.chejian1.oven.temp,是double类型的
create timeseries root.factory.chejian1.oven.temp double
# 同理
create timeseries root.factory.chejian1.oven.humidity double
create timeseries root.factory.chejian1.pool.ph double
create timeseries root.factory.chejian1.pool.temp double
# 插入数据
# timestamp可以是时间戳整数,也可以是时间格式
# 可以跟若干个参数分别赋值插入
insert into root.factory.chejian1.oven (timestamp,temp) values(100,15.1);
insert into root.factory.chejian1.oven (timestamp,temp) values(101,18.2);
insert into root.factory.chejian1.pool (timestamp,ph,temp) values(102,7,35.5);
insert into root.factory.chejian1.pool (timestamp,ph,temp)values(2024-03-012 08:00:00,7,35.5);
# 查询数据
select * from root.factory.chejian1.oven
select ph,temp from root.factory.chejian1.pool
3:集群安装
3.1:集群安装前的介绍
先简单的介绍一下IoTDB的集群架构(3 confignode + 3 datanode)
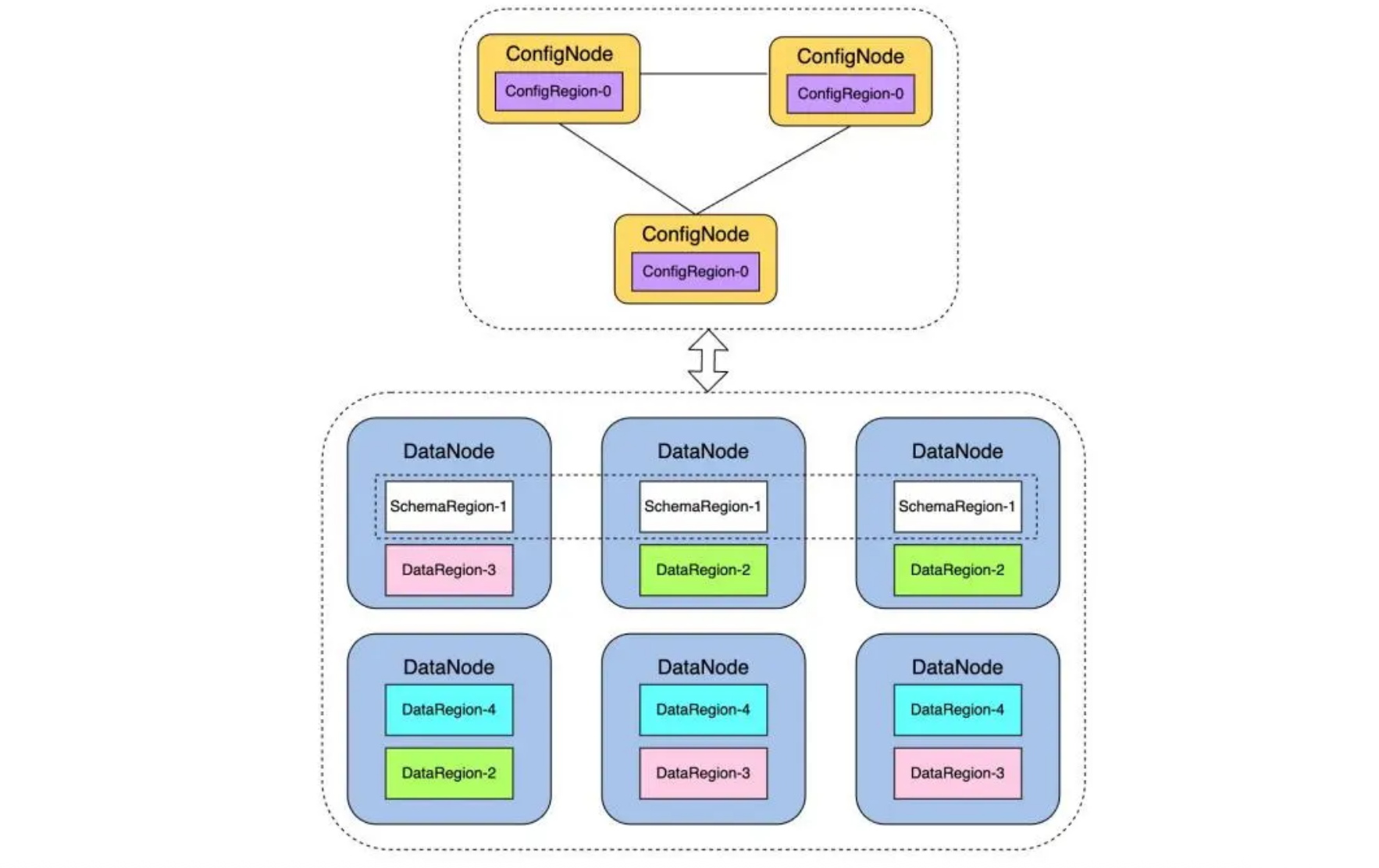
集群分为两种角色:DataNode 和ConfigNode。
- DataNode 进程负责管理时序数据分片 DataRegion 和时序元数据分片 SchemaRegion。
- ConfigNode 进程负责管理分区信息等系统数据分片 ConfigRegion,并作为整个集群的大脑中枢对
DataRegion 和 SchemaRegion 分片进行分配和调度。
为了满足高可用,所有的分片均被冗余存储,并进而通过共识协议来维护多个副本间的一致性(Raft)
元数据 -> 序列的路径,测点的名称和数据类型
通常包括元数据树上该序列的完整路径、测点名称和测点数据类型等信息。
元数据被划分到某个 SchemaRegion 中,并由其专门负责管理时序元数据
数据 -> 采集的时间值
一个测点采集的时间戳和值的序列,随着时间变化的数据
不同设备的数据,按照在不同时间段,划分到不同的 DataRegion 中存储
3.2:安装测试
3.2.1:安装前的准备
准备3台linux主机
| IP地址 | 192.168.1.31 | 192.168.1.32 | 192.168.1.33 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 服务 | ConfigNode | ConfigNode | ConfigNode |
| 服务 | DataNode | DataNode | DataNode |
每一台主机的占用端口如下:
| 服务 | ConfigNode | DataNode |
|---|---|---|
| 端口 | 10710,10720 | 6667, 10730, 10740, 10750, 10760 |
🚀 在安装之前必须做好如下的工作
- 三台主机都安装了Java8或者Java11(推荐JDK 1.8u291及以上版本)
- 确保三台主机之间网络互通,并且防火墙已开放所有必需的端口,为了测试,可以先都关闭防火墙
- CentOS:
systemctl stop firewalld - Ubuntu:
ufw disable
- CentOS:
- 三台主机时间同步,否则可能导致问题,建议使用NTP服务进行同步
- 从Apache IoTDB官网或镜像站下载最新版本的二进制安装包(例如:
apache-iotdb-1.2.2-all-bin.zip)。将安装包上传到三台服务器的相同目录下,例如/opt/iotdb
3.2.2:安装和配置
以下操作需要在三台服务器上分别执行,注意根据每台服务器的IP修改配置
1️⃣ 解压安装包
# 切换到安装目录
cd /opt/iotdb
# 解压安装包
unzip apache-iotdb-1.2.2-all-bin.zip
# 创建软链接或重命名目录(可选,便于管理)
ln -s apache-iotdb-1.2.2-all-bin/ iotdb-cluster
cd iotdb-cluster
2️⃣ 修改配置文件(核心步骤)
IoTDB集群的配置主要涉及两个文件:confignode-conf.properties 和 datanode-conf.properties。
编辑 conf/confignode-conf.properties 文件:
# 通用内部通信地址(改为当前主机IP)
# 在 .32 和 .33 上分别改为对应的IP
internal_ip=192.168.1.31
# 集群节点通信协议核心端口
internal_port=10710
# ConfigNode 共识协议端口
consensus_port=10720
# 指定集群中所有ConfigNode的地址列表
config_node_cluster=192.168.1.31:10710,192.168.1.32:10710,192.168.1.33:10710
# 数据存储目录(确保目录存在且有写权限)
data_dir=/opt/iotdb/iotdb-cluster/data/confignode
# 其他保持默认即可
在192.168.1.32和192.168.1.33上重复此步骤,仅将 internal_ip 改为各自的IP地址。
编辑 conf/datanode-conf.properties 文件:
# 通用内部通信地址(改为当前主机IP)
# 在 .32 和 .33 上分别改为对应的IP
internal_ip=192.168.1.31
# DataNode 核心端口
internal_port=10730
# DataNode 共识协议端口
consensus_port=10740
# DataNode 和数据模式同步端口
schema_region_consensus_port=10750
data_region_consensus_port=10760
# DataNode 对外提供服务的RPC端口(客户端连接使用)
rpc_port=6667
# MPP数据交换端口
mpp_data_exchange_port=10770
# 指定集群中所有ConfigNode的地址列表(与ConfigNode配置中的一致)
config_node_cluster=192.168.1.31:10710,192.168.1.32:10710,192.168.1.33:10710
# 数据存储目录(确保目录存在且有写权限)
data_dir=/opt/iotdb/iotdb-cluster/data/datanode
# 其他保持默认即可
同样,在另外两台主机上修改此文件时,只更改 internal_ip 为各自的IP。
3️⃣ 设置环境变量
编辑 ~/.bashrc 或 /etc/profile 文件,添加IoTDB的启动脚本路径到 PATH 中。
# 在最后追加这两行
export IOTDB_HOME=/opt/iotdb/iotdb-cluster
export PATH=$PATH:$IOTDB_HOME/sbin
执行 source ~/.bashrc 使其生效。
3.2.3:启动集群
⚠️ 启动顺序非常重要:必须先启动所有ConfigNode,然后再启动DataNode。
在三台服务器上分别执行:
# 进入IoTDB目录
cd /opt/iotdb/iotdb-cluster
# 启动ConfigNode服务
sbin/start-confignode.sh
# 检查启动是否成功,查看日志输出
tail -f logs/log_confignode.log
看到日志中包含“ConfigNode has started.”等字样即表示启动成功。等待三个ConfigNode都启动完毕并完成互相发现。
在三台服务器上分别执行:
# 启动DataNode服务
sbin/start-datanode.sh
# 检查启动是否成功,查看日志输出
tail -f logs/log_datanode.log
看到日志中包含“DataNode has started.”等字样,并且显示“Successfully connected to ConfigNode”即表示启动成功,并已加入集群。
3.2.4:验证集群的状态
在任意一台服务器上,使用命令行客户端连接本机的DataNode:
# 连接客户端 -h 后可以是三台主机中任意一台的IP
sbin/start-cli.sh -h 192.168.1.31 -p 6667 -u root -pw root
# 连接成功后,执行集群状态查看命令
IoTDB> show cluster;
如果集群搭建成功,这个命令将返回一个包含 3个DataNode 和 3个ConfigNode 的详细信息列表。
3.2.5:停止集群
停止顺序与启动顺序相反:先停所有DataNode,再停所有ConfigNode。
在三台服务器上分别执行:
# 停止DataNode
sbin/stop-datanode.sh
# 停止ConfigNode
sbin/stop-confignode.sh
二:基本概念
1:存储组database
存储组是数据库的顶层命名空间,是用于隔离不同业务或设备的数据的逻辑单元。
一个设备(实体)的所有数据必须属于同一个存储组。
你可以把它想象成文件系统中的“盘符”(如C盘、D盘),或者关系型数据库中的“数据库”(Database)。
- 数据隔离:不同存储组的数据在物理存储、内存缓存、刷盘策略上都是隔离的,互不影响。
- 资源管理:可以针对不同的存储组独立设置权限、配置TTL(生存时间)、数据压缩方式等。
对于一个工厂,可以为不同车间设置存储组:root.factory1, root.factory2。
2:设备device
设备是产生时序数据的实体,是时序数据归属的逻辑单元。
它在存储组之下,相当于关系型数据库中的“一张表”。一个设备是其下所有时序的父节点。
在IoTDB中,设备是用从根节点到设备节点的路径唯一标识的
实例:root.factory1.water_tank 可以表示一个具体的水箱设备。
3:测点/时间序列timeseries
这是IoTDB中最基本的数据单元。
一个时间序列由“设备路径 + 测量名称(传感器)”唯一确定,它代表了一个特定传感器在特定设备上随时间变化而产生的数据点序列。
🚀 组成部分如下:
- 路径:完整路径如
root.factory1.water_tank.temperature - 时间戳:数据点产生的时间。
- 值:数据点的数值
- 数据类型:值的数据类型(如 FLOAT, DOUBLE, INT32, BOOLEAN, TEXT等)
🚀 实例:设备 root.factory1.water_tank 有两个传感器(即两个时间序列):
root.factory1.water_tank.temperature(温度,FLOAT类型)root.factory1.water_tank.status(状态,BOOLEAN类型)
4:物理量/测量measurement
也称为传感器(Sensor),它是设备的一个感知单元,是时间序列的名称部分。
它定义了被监测的物理量是什么(如 temperature, speed, pressure)。
设备 + 测量 = 时间序列
5:模板schema template
一种用于模式预定义和复用的机制。
对于一个特定类型的设备(如所有型号相同的风机),其拥有的传感器(测量)集合是固定的。模板就是用来定义这个集合的
- 避免重复定义:一次性定义好某类设备的模式,然后可以批量应用到多个实体设备上。
- 保证模式一致:确保同类型设备拥有相同的传感器结构,便于管理和查询。
- 高效注册:新设备挂载模板后,其下的所有时间序列会被自动创建,无需手动逐个创建。
例如定义一个 wind_turbine_template 模板,包含 speed, angle, temperature, power 四个测量。所有风机设备都可以挂载这个模板。
6:节点node
IoTDB中的元数据节点形成了一个树形结构。存储组、设备、测量都是树上的节点。
- 内部节点: 路径中的非叶子节点,如
root,factory1,water_tank。 - 叶子节点: 路径的最后一层,即存储实际数据的测量,如
temperature。
例如路径 root.factory1.water_tank.temperature 包含了4个节点
一个路径中由 ‘.’ 分割的部分叫做路径结点名(nodeName)。例如:root.a.b.c为一个层级为 4 的路径。
通配符*和***在路径中表示一层。**在路径中表示是(*)+,即为一层或多层*
7:对应关系
8:基本概念中的SQL命令
8.1:存储组相关
-- 设置一个存储组
SET STORAGE GROUP TO root.factory1;
-- 设置另一个存储组
SET STORAGE GROUP TO root.factory2;
-- 查看存储组
SHOW STORAGE GROUP;
-- 删除存储组(会删除其下所有数据!)
DELETE STORAGE GROUP root.factory1;
-- 删除多个
DELETE STORAGE GROUP root.factory1, root.factory2;
8.2:时间序列操作
-- 创建一条时间序列并指定数据类型
CREATE TIMESERIES root.factory1.water_tank.temperature
WITH DATATYPE=FLOAT, ENCODING=GORILLA;
-- 创建一条布尔型时间序列
CREATE TIMESERIES root.factory1.water_tank.status
WITH DATATYPE=BOOLEAN, ENCODING=PLAIN;
-- 查看所有时间序列
SHOW TIMESERIES;
-- 查看特定路径下的时间序列
SHOW TIMESERIES root.factory1.water_tank.*;
-- 删除时间序列
DELETE TIMESERIES root.factory1.water_tank.temperature;
8.3:设备和数据的操作
🎉 插入数据 (IoTDB会自动创建不存在的设备和时间序列,但推荐先创建模式)
-- 向设备 water_tank 插入一条数据,时间戳可自动生成或指定
INSERT INTO root.factory1.water_tank(timestamp, temperature, status)
VALUES (NOW(), 27.5, true);
-- 指定时间戳
INSERT INTO root.factory1.water_tank(timestamp, temperature, status)
VALUES (1717593169000, 27.5, true);
-- 也可以省略timestamp关键字,直接按顺序写
INSERT INTO root.factory1.water_tank(time, temperature, status)
VALUES (1717593169000, 27.5, true);
-- 查询某个设备下所有传感器的最新数据
SELECT * FROM root.factory1.water_tank;
-- 查询特定传感器,最近10条数据
SELECT temperature FROM root.factory1.water_tank
ORDER BY TIME DESC
LIMIT 10;
-- 带时间条件的查询
SELECT status, temperature FROM root.factory1.water_tank
WHERE time > 1717593169000;
8.4:模板操作
-- 1. 创建模板(定义具有相同属性设备的表模板)
CREATE SCHEMA TEMPLATE wind_turbine_template(
speed FLOAT ENCODING=GORILLA,
angle INT32 ENCODING=PLAIN,
temperature FLOAT ENCODING=GORILLA,
power DOUBLE ENCODING=GORILLA
)
-- 2. 将模板挂载到某个设备路径下(该路径下的所有设备都将拥有模板中的序列)
SET SCHEMA TEMPLATE wind_turbine_template TO root.factory1.wind_turbine
-- 3. 激活模板(在挂载后,插入数据前必须激活)
ACTIVATE SCHEMA TEMPLATE wind_turbine_template ON root.factory1.wind_turbine.d001
-- 查看模板
SHOW SCHEMA TEMPLATES;
SHOW NODES IN SCHEMA TEMPLATE wind_turbine_template;
三:数据类型和编码介绍
1:基本数据类型
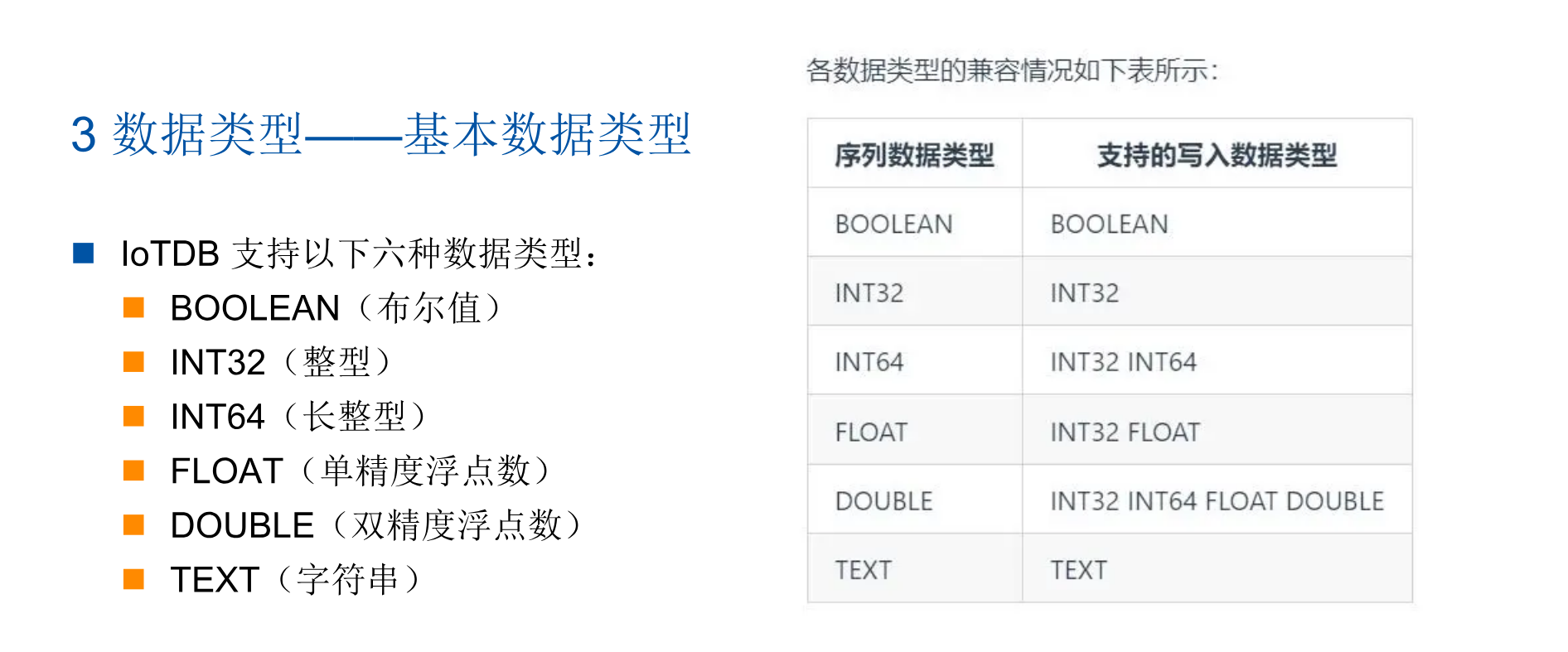
2:时间戳数据类型

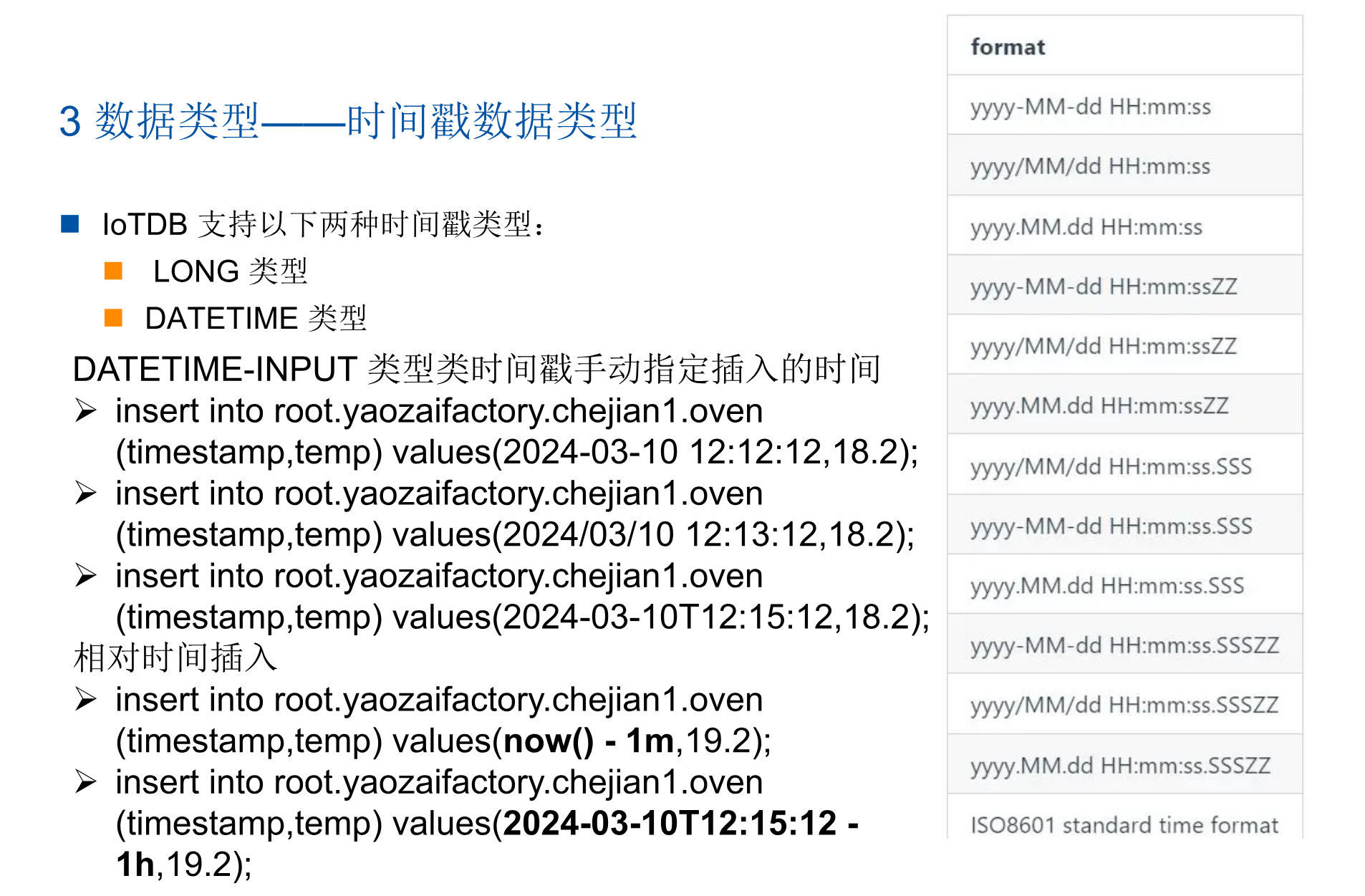
3:数据的编码
什么是编码?
- 数据编码指的是将原始数据转换为一种特定的格式或语言
- 编码提高数据的存储效率,需要在数据写入的过程中对数据进行编码,从而减少磁盘空间的使用量。
- 我们使用的时候,只需要根据数据的变化趋势和数据类型,进行选择想要的编码方式
- 我的理解:通过简单的数据格式描述复杂的原始数据
编码举例,差分编码:一个序列,需要进行传输 :1, 2, 3, 2, 1
- 第一个数字是1,没有前一个数字,所以我们传输1。
- 第二个数字是2,与前一个数字1相比,差异是1,所以我们传输1。
- 第三个数字是3,与前一个数字2相比,差异是1,所以我们传输1。
- 第四个数字是2,与前一个数字3相比,差异是-1,所以在传输时我们考虑符号,传输-1
- 第五个数字是1,与前一个数字2相比,差异是-1,所以在传输时我们考虑符号,传输-1
我们写入的时候,经过计算,序列将是:1, 1, 1, -1, -1;查询的时候,再通过计算还原出来原始序列
编码属于用计算时间换存储空间

create timeseries root.yaozaifactory.chejian1.oven.temp3
with datatype = double, encoding = RLE
4:数据的压缩
数据压缩,主要是减少冗余信息,只传输必要的数据。有损压缩通过牺牲一些数据质量来实现更高的压缩率,而无损压缩则保持原始数据的完整性和质量。
我的理解:通过简化记录少量的信息去描述更多的信息。
用户可以制定数据存储时采用的压缩方法。
IoTDB 允许在创建一个时间序列的时候指定该列的压缩方式。现阶段 IoTDB 支持以下几种压缩方式:
- UNCOMPRESSED(不压缩)
- SNAPPY 压缩
- LZ4 压缩,系统默认为我们选择这个
- GZIP 压缩
- ZSTD 压缩
- LZMA2 压缩
create timeseries root.yaozaifactory.chejian1.oven.temp4
with datatype = double, encoding = RLE, compressor = snappy
四:IotDB语句大全
1:DDL-数据定义语言
存储组
-- 创建存储组
SET STORAGE GROUP TO root.ln;
SET STORAGE GROUP TO root.sg.cc;
-- 查看存储组
SHOW STORAGE GROUP;
-- 查看指定存储组
SHOW STORAGE GROUP ON root.ln.*;
-- 删除存储组
DELETE STORAGE GROUP root.ln;
DELETE STORAGE GROUP root.sg, root.ln;
时间序列
-- 创建时间序列
CREATE TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.wt01.status
WITH DATATYPE=BOOLEAN, ENCODING=PLAIN;
CREATE TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.wt01.temperature
WITH DATATYPE=FLOAT, ENCODING=RLE, COMPRESSOR=SNAPPY;
-- 创建对齐时间序列(属于同一设备的一组传感器,时间戳对齐存储)
CREATE ALIGNED TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.GPS(
longitude FLOAT ENCODING=GORILLA,
latitude FLOAT ENCODING=GORILLA
);
-- 查看时间序列
SHOW TIMESERIES; -- 查看所有
SHOW TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.**; -- 查看特定路径下所有
SHOW TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.wt01.status; -- 查看特定序列
SHOW TIMESERIES WHERE DATATYPE=INT32; -- 带条件查询
设备模板
-- 创建模板
CREATE SCHEMA TEMPLATE sensor_template(
temperature FLOAT ENCODING=GORILLA,
status BOOLEAN ENCODING=PLAIN,
velocity INT32 ENCODING=RLE
)
-- 挂载和卸载模板
SET SCHEMA TEMPLATE sensor_template TO root.ln.wf01;
UNSET SCHEMA TEMPLATE sensor_template FROM root.ln.wf01;
-- 激活和查看模板
ACTIVATE SCHEMA TEMPLATE sensor_template ON root.ln.wf01.wt01; -- 为具体设备激活
SHOW SCHEMA TEMPLATES; -- 查看所有模板
SHOW NODES IN SCHEMA TEMPLATE sensor_template; -- 查看模板内容
SHOW PATHS SET SCHEMA TEMPLATE sensor_template; -- 查看模板挂载路径
触发器
-- 创建触发器
CREATE STATELESS TRIGGER `alert_trigger`
BEFORE INSERT
ON root.ln.wf01.wt01.temperature
AS 'org.apache.iotdb.trigger.AlertingService'
WITH (
'error' = '5',
'severity' = 'critical'
)
-- 查看/删除触发器
SHOW TRIGGERS;
DROP TRIGGER `alert_trigger`;
连续查询
-- 创建连续查询
CREATE CONTINUOUS QUERY cq1
RESAMPLE EVERY 10s
BEGIN
SELECT max_value(temperature) INTO temperature_max FROM root.ln.*.* GROUP BY time(10s)
END
-- 查看和删除连续查询
SHOW CONTINUOUS QUERIES;
DROP CONTINUOUS QUERY cq1;
2:DML-数据操作语言
插入
-- 插入多条非对齐数据
INSERT INTO root.ln.wf01.wt01 (timestamp, temperature, status)
VALUES
(1637841234500, 25.1, true),
(1637841234600, 26.2, false);
-- 插入对齐数据(针对对齐时间序列设备)
INSERT INTO root.ln.wf01.GPS (timestamp, longitude, latitude)
VALUES (1637841234500, 116.410, 39.910);
-- 插入空值
INSERT INTO root.ln.wf01.wt01 (timestamp, temperature)
VALUES (1637841234700, NULL);
删除
DELETE FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01.temperature
WHERE time <= 1637841234600;
DELETE FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01.*
WHERE time >= 1637841234500 AND time < 1637841234700;
更新数据
UPDATE root.ln.wf01.wt01
SET temperature = 27.5
WHERE time = 1637841234500;
3:DQL-数据查询语言
基础查询
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01;
SELECT temperature,status FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01;
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
WHERE time > 1637841234500;
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
WHERE time >= 2023-11-25T00:00:00+08:00 AND time <= 2023-11-26T00:00:00+08:00;
降采样查询(group by)
-- 按照时间窗口聚合
SELECT
max_value(temperature),
avg(temperature)
FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
GROUP BY ([1637841230000, 1637841300000), 1m); -- 按1分钟间隔分组
-- 按路径层级分组
SELECT count(status) FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01 GROUP BY LEVEL=3; -- 按第3层(如wt01)分组
-- 按标签分组(需先为时间序列设置标签)
-- 假设为序列设置了`unit`标签
SELECT avg(temperature) FROM root.ln.** GROUP BY TAGS(unit);
条件过滤
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
WHERE temperature > 25 AND status = true;
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
WHERE temperature BETWEEN 20 AND 30;
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
WHERE status IS NULL;
分页和排序
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
LIMIT 10; -- 返回前10条
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
LIMIT 10 OFFSET 5; -- 跳过前5条,返回接下来的10条
SELECT * FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01
ORDER BY TIME DESC; -- 按时间降序
表达式和函数
-- 使用表达式
SELECT temperature + 10 AS temp_plus_10 FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01;
-- 使用内置函数
SELECT
SIN(temperature),
DIFF(temperature), -- 计算差分
TOP_K(temperature, 5) -- 计算前5大的值
FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01;
-- 空值填充
SELECT temperature FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01 FILL(LINEAR); -- 线性填充
SELECT temperature FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01 FILL(PREVIOUS); -- 用前一个值填充
SELECT temperature FROM root.ln.wf01.wt01 FILL(100); -- 用固定值填充
4:DCL-数据控制语言
用户管理
-- 创建和删除用户
CREATE USER thulab 'passw0rd'; -- 创建用户`thulab`,密码`passw0rd`
DROP USER thulab;
-- 修改密码
ALTER USER thulab SET PASSWORD 'newpassw0rd';
权限管理
GRANT ALL ON root.ln.** TO USER thulab; -- 授予所有权限
GRANT READ ON root.ln.wf01.* TO USER thulab; -- 只授予读权限
-- 撤销权限
REVOKE ALL ON root.ln.wf01.* FROM USER thulab;
REVOKE WRITE ON root.ln.** FROM USER thulab;
-- 查看权限
LIST PRIVILEGES OF USER thulab;
角色权限
-- 创建和删除角色
CREATE ROLE admin;
DROP ROLE admin;
-- 角色授权
GRANT ALL ON root.** TO ROLE admin;
-- 角色赋予用户
GRANT ROLE admin TO thulab;
REVOKE ROLE admin FROM thulab;
5:其他实用语句
-- 触发 Level-Compaction 和 Cross-Compaction
MERGE;
-- 或
COMPACT;
-- 将内存中的数据刷写到磁盘
FLUSH;
FLUSH ON root.ln; -- 刷写特定存储组
-- 终止正在执行的查询会话
KILL QUERY <queryId>; -- 需要先从`SHOW QUERY PROCESSLIST`中获取queryId
-- 查看版本/时间戳格式
SHOW VERSION;
SHOW TIMESTAMP_PRECISION; -- 显示时间戳精度(ms/μs/ns)
-- 查看查询进程列表
SHOW QUERY PROCESSLIST;
-- 检查时间序列是否存在
SHOW TIMESERIES root.ln.wf01.wt01.status; -- 存在则显示信息,不存在则返回空
-- 计数
COUNT TIMESERIES root.ln.**; -- 统计时间序列数量
COUNT NODES root.ln.** LEVEL=3; -- 统计指定层级的节点数
COUNT DEVICES; -- 统计设备数量
五:最佳Java实践
IoTDB 提供两种主要的 Java 连接方式:
- 原生 JDBC: 最常用,兼容性好,支持标准 SQL。
- Session Pool: IoTDB 自定义的高效会话池,性能更高,但 API 非标准。
最佳实践:推荐使用 JDBC,因为它更通用,与生态工具(如 Spring JPA, MyBatis)集成更方便,代码可移植性更强。
<!-- IoTDB JDBC 驱动 (核心依赖) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.iotdb</groupId>
<artifactId>iotdb-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.2.2</version> <!-- 请使用最新版本 -->
</dependency>
<!-- 可选:如果需要连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.11.1</version>
</dependency>
1:最佳实践清单
- 连接池是必须的:使用 HikariCP 管理 IoTDB 连接。
- 批处理写入:使用
PreparedStatement.addBatch()进行批量插入,并定期executeBatch()。 - 使用 Try-With-Resources:确保所有 JDBC 资源(Connection, Statement, ResultSet)都被正确关闭。
- 服务器端聚合:使用
GROUP BY和聚合函数在数据库端完成计算,减少数据传输量。 - 参数化查询:始终使用
PreparedStatement防止 SQL 注入并提升性能。 - 明智的重试机制:对网络异常实现带退避策略的重试逻辑。
- 监控与日志:记录关键的操作日志,并监控连接池状态和 SQL 执行性能。
- 模式设计先行:在编码前,根据业务查询模式设计好存储组、设备模板和序列,这对性能至关重要。
2:spring boot最佳实战
package com.example.config;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* IoTDB数据库连接配置类
*
* # application-iotdb.yml
* iotdb:
* enabled: true
* driver: org.apache.iotdb.jdbc.IoTDBDriver
* url: jdbc:iotdb://127.0.0.1:6667/
* username: root
* password: root
* pool:
* max-total: 20
* max-idle: 10
* min-idle: 2
* max-wait-millis: 10000
* test-on-borrow: true
* test-on-return: false
* test-while-idle: true
* time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 30000
* connection:
* timeout-ms: 5000
* fetch-size: 10000
* auto-commit: true
*
*
* @author cui haida
*/
@Configuration("myIoTConfig")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "iotdb")
@Data
public class MyIoTDBConfig {
private Boolean enabled; // 是否启用
private String driver; // 驱动名称
private String url; // 数据库连接地址
private String username; // 用户名
private String password; // 密码
// 连接池配置类 & 连接配置类
private PoolConfig pool = new PoolConfig();
private ConnectionConfig connection = new ConnectionConfig();
/**
* 连接池配置类
*/
@Data
public static class PoolConfig {
private int maxTotal = 20;
private int maxIdle = 10;
private int minIdle = 2;
private long maxWaitMillis = 10000;
private boolean testOnBorrow = true;
private boolean testOnReturn = false;
private boolean testWhileIdle = true;
private long timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis = 30000;
}
/**
* 连接配置类
*/
@Data
public static class ConnectionConfig {
private int timeoutMs = 5000;
private int fetchSize = 10000;
private boolean autoCommit = true;
}
}
package com.example.config;
import com.example.manager.IoTDBConnectionPool;
import com.example.manager.IoTDBMonitor;
import com.example.utils.IoTDBMetadataUtil;
import com.example.utils.IoTDBTemplate;
import com.example.utils.SqlBuildUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureAfter;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* 自动配置
*
* @author cui haida
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(IoTDBTemplate.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MyIoTDBConfig.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
public class IoTDBAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "iotdb", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
public IoTDBConnectionPool iotdbConnectionPool(MyIoTDBConfig config) {
return new IoTDBConnectionPool(config);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnBean(IoTDBConnectionPool.class)
public IoTDBTemplate iotdbTemplate(IoTDBConnectionPool connectionPool, @Qualifier("myIoTConfig") MyIoTDBConfig config) {
return new IoTDBTemplate(connectionPool, config);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlBuildUtils iotdbSqlBuilder() {
return new SqlBuildUtils();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IoTDBMetadataUtil iotdbMetadataUtil() {
return new IoTDBMetadataUtil();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IoTDBMonitor iotdbMonitor() {
return new IoTDBMonitor();
}
}
package com.example.manager;
import com.example.config.MyIoTDBConfig;
import com.example.exception.IoTDBConnectionException;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.pool2.BasePooledObjectFactory;
import org.apache.commons.pool2.PooledObject;
import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.DefaultPooledObject;
import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPool;
import org.apache.commons.pool2.impl.GenericObjectPoolConfig;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* 连接池配置
*
* @author cui haida
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class IoTDBConnectionPool implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
private final MyIoTDBConfig config;
private GenericObjectPool<Connection> connectionPool;
public IoTDBConnectionPool(@Qualifier("myIoTConfig") MyIoTDBConfig config) {
this.config = config;
}
/**
* 初始化IoTDB连接池
*
* @throws Exception 当初始化过程中发生错误时抛出异常
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// 检查IoTDB是否启用
if (!Boolean.TRUE.equals(config.getEnabled())) {
log.warn("iot db 禁用中");
return;
}
try {
// 加载数据库驱动
Class.forName(config.getDriver());
// 创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory(
config.getUrl(), config.getUsername(), config.getPassword());
// 配置连接池参数
GenericObjectPoolConfig<Connection> poolConfig = getPoolConfig();
// 初始化连接池
this.connectionPool = new GenericObjectPool<>(connectionFactory, poolConfig);
log.info("IoTDB connection pool initialized successfully");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Failed to initialize IoTDB connection pool", e);
throw new IoTDBConnectionException("IoTDB connection pool initialization failed", e);
}
}
/**
* 获取连接池配置
*
* @return 连接池配置
*/
private GenericObjectPoolConfig<Connection> getPoolConfig() {
GenericObjectPoolConfig<Connection> poolConfig = new GenericObjectPoolConfig<>();
poolConfig.setMaxTotal(config.getPool().getMaxTotal());
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(config.getPool().getMaxIdle());
poolConfig.setMinIdle(config.getPool().getMinIdle());
poolConfig.setMaxWait(Duration.ofMillis(config.getPool().getMaxWaitMillis()));
poolConfig.setTestOnBorrow(config.getPool().isTestOnBorrow());
poolConfig.setTestOnReturn(config.getPool().isTestOnReturn());
poolConfig.setTestWhileIdle(config.getPool().isTestWhileIdle());
poolConfig.setTimeBetweenEvictionRuns(
Duration.ofMillis(config.getPool().getTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis()));
return poolConfig;
}
/**
* 获取IoTDB连接
*
* @return 连接对象
* @throws IoTDBConnectionException 当获取连接时发生错误时抛出异常
*/
public Connection getConnection() throws IoTDBConnectionException {
try {
Connection connection = connectionPool.borrowObject();
connection.setAutoCommit(config.getConnection().isAutoCommit());
return connection;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IoTDBConnectionException("Failed to get IoTDB connection", e);
}
}
/**
* 归还IoTDB连接
*
* @param connection 连接对象
*/
public void returnConnection(Connection connection) {
if (connection != null) {
connectionPool.returnObject(connection);
}
}
/**
* 废弃IoTDB连接
*
* @param connection 废弃的连接对象
*/
public void invalidateConnection(Connection connection) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connectionPool.invalidateObject(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Failed to invalidate connection", e);
}
}
}
/**
* 获取连接池统计信息
*
* @return 连接池统计信息
*/
public PoolStats getPoolStats() {
return new PoolStats(
connectionPool.getNumActive(),
connectionPool.getNumIdle(),
connectionPool.getBorrowedCount(),
connectionPool.getReturnedCount(),
connectionPool.getCreatedCount(),
connectionPool.getDestroyedCount()
);
}
/**
* 销毁IoTDB连接池
*
* @throws Exception 当销毁连接池时发生错误时抛出异常
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
if (connectionPool != null) {
connectionPool.close();
log.info("IoTDB connection pool closed");
}
}
/**
* 连接池统计信息
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public static class PoolStats {
private int numActive;
private int numIdle;
private long borrowedCount;
private long returnedCount;
private long createdCount;
private long destroyedCount;
}
private static class ConnectionFactory extends BasePooledObjectFactory<Connection> {
private final String url;
private final String username;
private final String password;
public ConnectionFactory(String url, String username, String password) {
this.url = url;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public Connection create() throws Exception {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
@Override
public PooledObject<Connection> wrap(Connection connection) {
return new DefaultPooledObject<>(connection);
}
@Override
public boolean validateObject(PooledObject<Connection> p) {
try {
Connection conn = p.getObject();
return conn != null && !conn.isClosed() && conn.isValid(5);
} catch (SQLException e) {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void destroyObject(PooledObject<Connection> p) throws Exception {
Connection conn = p.getObject();
if (conn != null && !conn.isClosed()) {
conn.close();
}
}
}
}
package com.example.utils;
import com.example.config.MyIoTDBConfig;
import com.example.exception.IoTDBException;
import com.example.exception.IoTDBInsertException;
import com.example.exception.IoTDBQueryException;
import com.example.manager.IoTDBConnectionPool;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* iot db 模板类
*
* @author cui haida
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class IoTDBTemplate {
/**
* 连接池
*/
private final IoTDBConnectionPool connectionPool;
/**
* 配置
*/
private final MyIoTDBConfig config;
public IoTDBTemplate(IoTDBConnectionPool connectionPool, @Qualifier("myIoTConfig") MyIoTDBConfig config) {
this.connectionPool = connectionPool;
this.config = config;
}
/**
* 执行查询并处理结果
* @param sql 查询语句
* @param handler 处理结果集的接口
*/
public <T> T executeQuery(String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> handler) throws IoTDBQueryException {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = connectionPool.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.setQueryTimeout(config.getConnection().getTimeoutMs() / 1000);
statement.setFetchSize(config.getConnection().getFetchSize());
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
return handler.handle(resultSet);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IoTDBQueryException("Failed to execute query: " + sql, e);
} finally {
closeResources(resultSet, statement, connection);
}
}
/**
* 执行更新操作
*/
public int executeUpdate(String sql) throws IoTDBException {
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = connectionPool.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.setQueryTimeout(config.getConnection().getTimeoutMs() / 1000);
return statement.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IoTDBException("Failed to execute update: " + sql, e);
} finally {
closeResources(null, statement, connection);
}
}
/**
* 批量执行SQL
*/
public int[] executeBatch(List<String> sqlList) throws IoTDBException {
if (sqlList == null || sqlList.isEmpty()) {
return new int[0];
}
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
try {
connection = connectionPool.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement();
statement.setQueryTimeout(config.getConnection().getTimeoutMs() / 1000);
for (String sql : sqlList) {
statement.addBatch(sql);
}
return statement.executeBatch();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IoTDBException("Failed to execute batch", e);
} finally {
closeResources(null, statement, connection);
}
}
/**
* 使用预编译语句执行批量插入
*/
public int[] executePreparedBatch(String sql, List<Object[]> paramsList) throws IoTDBInsertException {
if (paramsList == null || paramsList.isEmpty()) {
return new int[0];
}
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = connectionPool.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setQueryTimeout(config.getConnection().getTimeoutMs() / 1000);
for (Object[] params : paramsList) {
for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, params[i]);
}
preparedStatement.addBatch();
}
return preparedStatement.executeBatch();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IoTDBInsertException("Failed to execute prepared batch", e);
} finally {
closeResources(null, preparedStatement, connection);
}
}
/**
* 执行事务操作
*/
public <T> T executeInTransaction(TransactionCallback<T> callback) throws IoTDBException {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = connectionPool.getConnection();
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
T result = callback.doInTransaction(connection);
connection.commit();
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
log.warn("Failed to rollback transaction", ex);
}
}
throw new IoTDBException("Transaction execution failed", e);
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.warn("Failed to reset auto-commit", e);
}
connectionPool.returnConnection(connection);
}
}
}
/**
* 关闭资源
*/
private void closeResources(ResultSet resultSet, Statement statement, Connection connection) {
try {
if (resultSet != null) {
resultSet.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.warn("Failed to close result set", e);
}
try {
if (statement != null) {
statement.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.warn("Failed to close statement", e);
}
try {
if (connection != null) {
connectionPool.returnConnection(connection);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("Failed to return connection to pool", e);
}
}
/**
* 结果集处理器接口
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ResultSetHandler<T> {
T handle(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException;
}
/**
* 事务回调接口
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TransactionCallback<T> {
T doInTransaction(Connection connection) throws SQLException;
}
}
package com.example.utils;
import com.example.exception.IoTDBException;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 元数据操作工具
*
* @author cui haida
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class IoTDBMetadataUtil {
@Resource
private IoTDBTemplate ioTDBTemplate;
/**
* 检查存储组是否存在
*/
public boolean storageGroupExists(String storageGroup) throws IoTDBException {
String sql = "SHOW STORAGE GROUP";
return ioTDBTemplate.executeQuery(sql, resultSet -> {
while (resultSet.next()) {
if (storageGroup.equals(resultSet.getString(1))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
});
}
/**
* 创建存储组
*/
public void createStorageGroup(String storageGroup) throws IoTDBException {
String sql = "CREATE STORAGE GROUP " + storageGroup;
ioTDBTemplate.executeUpdate(sql);
}
/**
* 删除存储组
*/
public void deleteStorageGroup(String storageGroup) throws IoTDBException {
String sql = "DELETE STORAGE GROUP " + storageGroup;
ioTDBTemplate.executeUpdate(sql);
}
/**
* 获取所有时间序列
*/
public List<String> getAllTimeSeries() throws IoTDBException {
String sql = "SHOW TIMESERIES";
return ioTDBTemplate.executeQuery(sql, resultSet -> {
List<String> timeseries = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
timeseries.add(resultSet.getString("timeseries"));
}
return timeseries;
});
}
/**
* 获取设备列表
*/
public List<String> getDevices() throws IoTDBException {
String sql = "SHOW DEVICES";
return ioTDBTemplate.executeQuery(sql, resultSet -> {
List<String> devices = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
devices.add(resultSet.getString(1));
}
return devices;
});
}
/**
* 创建时间序列
*/
public void createTimeSeries(String timeSeries, String dataType, String encoding, String compression)
throws IoTDBException {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("CREATE TIMESERIES ");
sql.append(timeSeries).append(" WITH DATATYPE=").append(dataType);
if (encoding != null) {
sql.append(", ENCODING=").append(encoding);
}
if (compression != null) {
sql.append(", COMPRESSOR=").append(compression);
}
ioTDBTemplate.executeUpdate(sql.toString());
}
}
package com.example.utils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.Validate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* packageName com.example.utils
*
* @author cui haida
* @version JDK 8
* 2025/9/9
*/
@Component
public class SqlBuildUtils {
/**
* 构建查询SQL
* @param tableName 表名
* @param fields 想要返回的字段
* @param conditions 查询条件
* @param startTime 查询时间范围
* @param endTime 查询时间范围
* @param limit 查询数量
* @param offset 查询偏移量
* @param orderBy 排序字段
* @param orderAsc 是否升序(true -> 升序,false -> 降序)
* @return 构建的查询SQL
*/
public String buildQuerySql(String tableName, List<String> fields, Map<String, Object> conditions,
Long startTime, Long endTime, Integer limit, Integer offset, String orderBy, Boolean orderAsc) {
// 构建SQL
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("SELECT ");
// 选择字段
if (fields == null || fields.isEmpty()) {
sql.append("*");
} else {
sql.append(String.join(", ", fields));
}
sql.append(" FROM ").append(tableName);
// 构建where条件
List<String> whereClauses = buildWhereClauses(conditions, startTime, endTime);
if (!whereClauses.isEmpty()) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(String.join(" AND ", whereClauses));
}
// 排序条件
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(orderBy)) {
sql.append(" ORDER BY ").append(orderBy);
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(orderAsc)) {
sql.append(" DESC");
}
}
// 分页
if (limit != null) {
sql.append(" LIMIT ").append(limit);
if (offset != null && offset > 0) {
sql.append(" OFFSET ").append(offset);
}
}
return sql.toString();
}
/**
* 构建插入SQL
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param data 插入的数据,键为字段名,值为字段值
* @return 构建的插入SQL
*/
public String buildInsertSql(String tableName, Map<String, Object> data) {
Validate.notEmpty(data, "Insert data cannot be empty");
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("INSERT INTO ");
sql.append(tableName).append("(");
List<String> columns = new ArrayList<>(data.keySet());
sql.append(String.join(", ", columns));
sql.append(") VALUES(");
List<String> values = columns.stream()
.map(col -> formatValue(data.get(col)))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
sql.append(String.join(", ", values));
sql.append(")");
return sql.toString();
}
/**
* 构建批量INSERT语句
*/
public List<String> buildBatchInsertsSql(String measurement, List<Map<String, Object>> dataList) {
Validate.notEmpty(dataList, "Data list cannot be empty");
return dataList.stream()
.map(data -> buildInsertSql(measurement, data))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 构建更新SQL
*
* @param tableName 表名
* @param data 更新的数据,键为字段名,值为字段值
* @param conditions 更新条件
* @param startTime 更新时间范围
* @param endTime 更新时间范围
* @return 构建的更新SQL
*/
/**
* 构建DELETE语句
*/
public String buildDelete(String measurement, Map<String, Object> conditions,
Long startTime, Long endTime) {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder("DELETE FROM ").append(measurement);
List<String> whereClauses = buildWhereClauses(conditions, startTime, endTime);
if (!whereClauses.isEmpty()) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(String.join(" AND ", whereClauses));
}
return sql.toString();
}
/**
* 构建WHERE子句列表
*
* @param conditions 条件映射,键为字段名,值为条件值
* @param startTime 开始时间戳,如果非空则添加时间范围条件
* @param endTime 结束时间戳,如果非空则添加时间范围条件
* @return 包含WHERE子句的字符串列表
*/
private List<String> buildWhereClauses(Map<String, Object> conditions, Long startTime, Long endTime) {
List<String> clauses = new ArrayList<>();
// 时间范围条件
if (startTime != null) {
clauses.add("time >= " + startTime);
}
if (endTime != null) {
clauses.add("time <= " + endTime);
}
// 其他条件
if (conditions != null) {
conditions.forEach((key, value) -> {
if (value != null) {
clauses.add(key + " = " + formatValue(value));
}
});
}
return clauses;
}
/**
* 格式化对象值为字符串表示形式
*
* @param value 需要格式化的对象值
* @return 格式化后的字符串表示
*/
private String formatValue(Object value) {
if (value == null) {
return "null";
}
// 根据对象类型进行相应的格式化处理
if (value instanceof String) {
return "'" + escapeString((String) value) + "'";
} else if (value instanceof Date) {
return "'" + new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS").format((Date) value) + "'";
} else if (value instanceof Boolean) {
return (Boolean) value ? "true" : "false";
} else if (value instanceof Number) {
return value.toString();
} else {
return "'" + value + "'";
}
}
/**
* 对字符串进行转义处理,将单引号替换为两个单引号
*
* @param str 需要转义的字符串
* @return 转义后的字符串
*/
private String escapeString(String str) {
return str.replace("'", "''");
}
}
package com.example.manager;
import com.example.exception.IoTDBException;
import com.example.utils.IoTDBTemplate;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* packageName com.example.manager
*
* @author cui haida
* @version JDK 8
* 2025/9/9
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class IoTDBMonitor {
@Autowired
private IoTDBConnectionPool connectionPool;
@Autowired
private IoTDBTemplate ioTDBTemplate;
/**
* 获取连接池状态
*/
public IoTDBConnectionPool.PoolStats getConnectionPoolStats() {
return connectionPool.getPoolStats();
}
/**
* 检查数据库连接状态
*/
public boolean checkConnection() {
try {
String sql = "SHOW VERSION";
ioTDBTemplate.executeQuery(sql, resultSet -> {
if (resultSet.next()) {
return resultSet.getString(1);
}
return null;
});
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn("IoTDB connection check failed", e);
return false;
}
}
/**
* 获取数据库版本
*/
public String getVersion() throws IoTDBException {
String sql = "SHOW VERSION";
return ioTDBTemplate.executeQuery(sql, resultSet -> {
if (resultSet.next()) {
return resultSet.getString(1);
}
return null;
});
}
/**
* 获取数据库状态信息
*/
public Map<String, Object> getDatabaseStatus() throws IoTDBException {
Map<String, Object> status = new HashMap<>();
status.put("version", getVersion());
status.put("connectionPool", getConnectionPoolStats());
status.put("isConnected", checkConnection());
return status;
}
}





















 4597
4597

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








