目录
实验原理
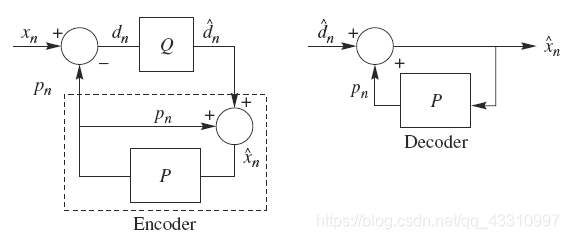
DPCM
是差分预测编码调制的缩写,是比较典型的预测编码系统。在
DPCM
系统中,
需要注意的是预测器的输入是已经解码以后的样本。之所以不用原始样本来做预测,是
因为在解码端无法得到原始样本,只能得到存在误差的样本。因此,在
DPCM
编码器中实
际内嵌了一个解码器,如编码器中虚线框中所示。在
DPCM
编码器实现的过程中可同时输出预测误差图像和重建图像。
在一个
DPCM
系统中,有两个因素需要设计:预测器和量化器。理想情况下,预测器
和量化器应进行联合优化。实际中,采用一种次优的设计方法:分别进行线性预测器和
量化器的优化设计。
说明:
在本次实验中,采用固定预测器和均匀量化器。预测器采用左侧预测。
实验目标
1. 使用DPCM编码器输出预测误差图像和重建图像,量化器分别采用8bit,6bit,4bit,2bit,1bit均匀量化。
2. 将该文件输入Huffman编码器,得到输出码流、给出概率分布图并计算压缩比。
3. 将原始图像文件输入输入Huffman编码器,得到输出码流、给出概率分布图并计算压缩比。
4. 比较两种系统(DPCM+熵编码和仅进行熵编码)之间的编码效率(压缩比和图像质量)
实验内容
主要代码
DPCM
/* w图像宽度,h图像高度,yBuff原始图像,errBuff预测误差图像,reBuff重建图像,Qbit量化级数 */
void DPCM(int w, int h, unsigned char* yBuff, unsigned char* errBuff, unsigned char* reBuff, int Qbit)
{
int m = 512 / pow(2, Qbit);
int* a;
a = (int*)malloc((sizeof(int)) * w * h);
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
a[j * w + i] = (yBuff[j * w + i] - 128) / m + 128;
reBuff[j * w + i] = (a[j * w + i] - 128) * m + 128;
}
else
{
a[j * w + i] = (yBuff[j * w + i] - reBuff[(j - 1) * w + i]) / m + 128;
reBuff[j * w + i] = (a[j * w + i] - 128) * m + reBuff[(j - 1) * w + i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < w*h; i++)
errBuff[i] = (unsigned char)a[i];
}
PSNR
“Peak Signal to Noise Ratio”的缩写,即峰值信噪比,是一种评价图像的客观标准,它具有局限性,一般是用于最大值信号和背景噪音之间的一个工程项目。
均方误差MSE
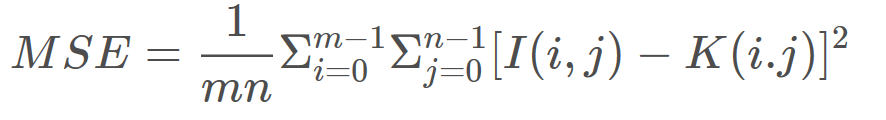
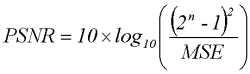
double MSE(unsigned char* infile, unsigned char* outfile, int height, int width, int imgSize)
{
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < imgSize; i++)
{
double temp = pow((double)(infile[i] - outfile[i]),2);
sum += temp;
}
double mse = sum / imgSize;
return mse;
}
double PSNR(unsigned char* infile, unsigned char* outfile, int height, int width, int imgSize)
{
double mse = MSE(infile, outfile, height, width,imgSize);
double psnr = 10 * log10(255.0 * 255.0 / mse);
return psnr;
}改变量化比特数
原图 768*512

| 量化 比特数 | 预测误差图像+重建图像 | PSNR |
|---|---|---|
| 8bit | 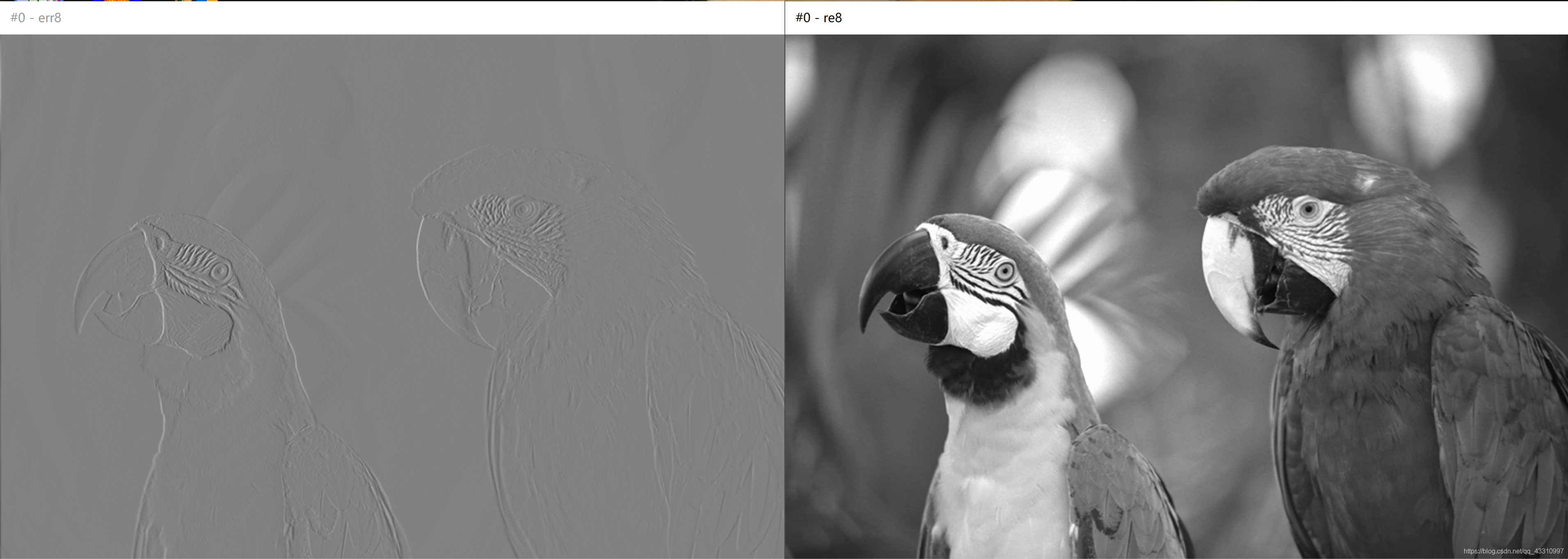 | 51.0519dB |
| 6bit | 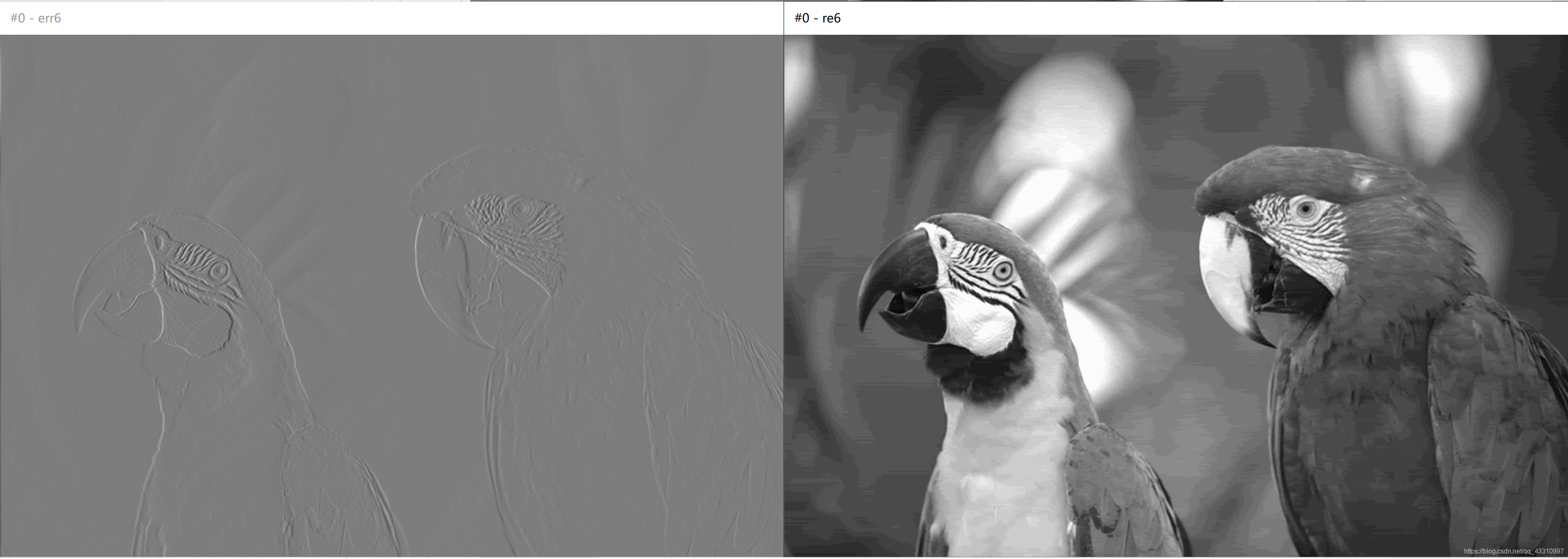 | 36.9645dB |
| 4bit |  | 25.172dB |
| 3bit |  | 19.1597dB |
结论:量化比特数越大,预测误差越小,重建的图像质量越好。
两种编码方案比较
DPCM编码(8bit)结果
测试图片 1—6(256*256)
| 原图 | 预测误差图像 | 重建图像 | PSNR(dB) |
 |  |  | 51.1124 |
 | 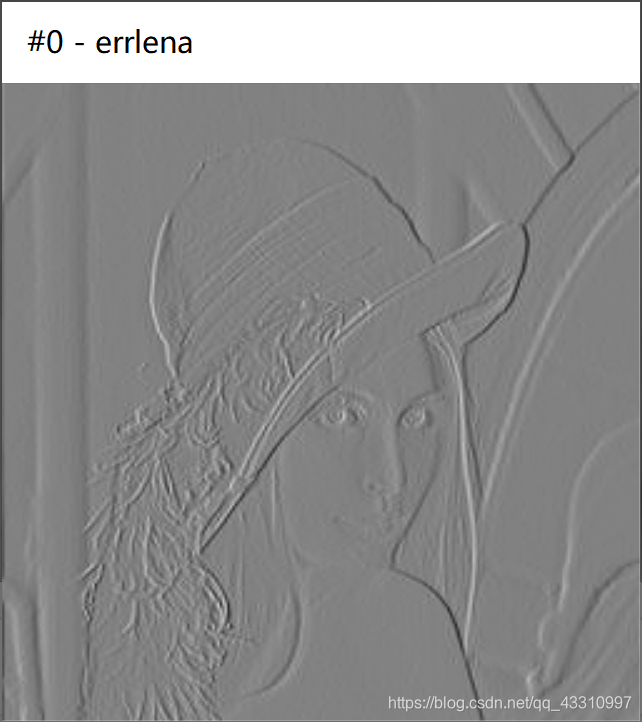 |  | 51.1391 |
 |  |  | 48.9599 |
 | 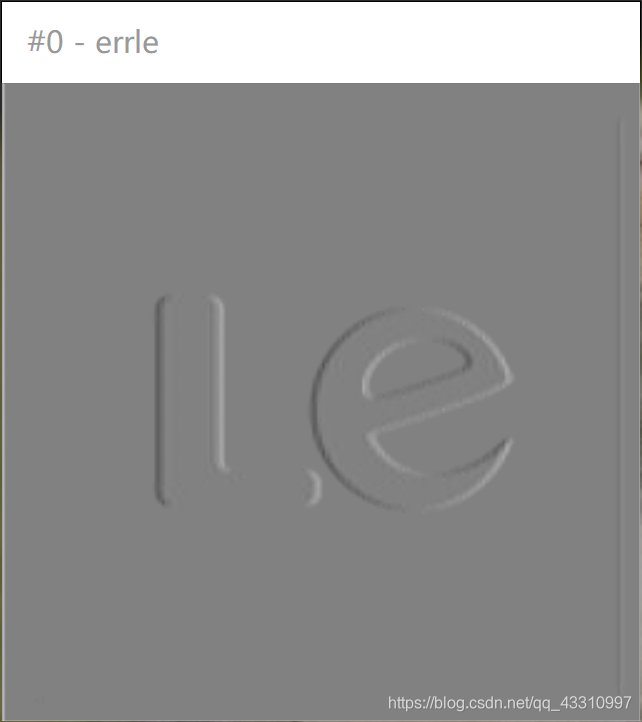 |  | 48.4233 |
 |  |  | 51.174 |
 | 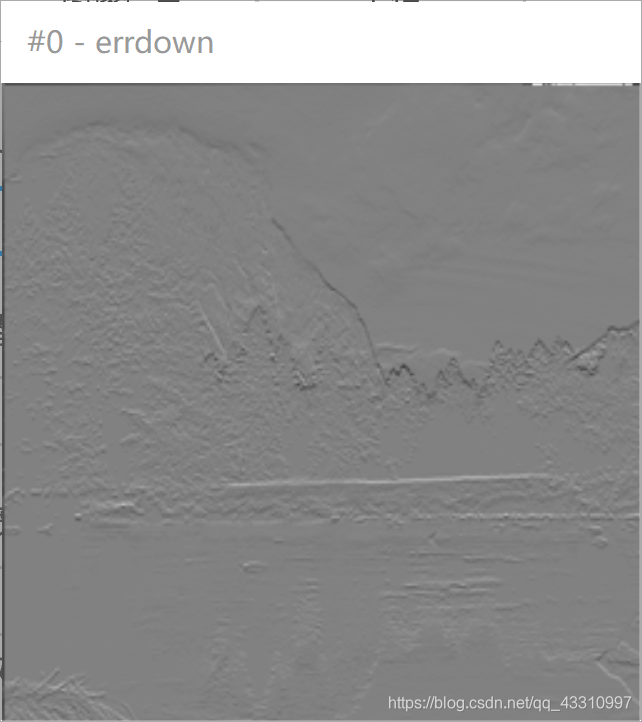 |  | 51.4117 |
DPCM+熵编码和仅进行熵编码的概率分布图和压缩比
1.生成.huff和.txt
2.计算信源符号概率分布
void Count(unsigned char* Buff, double* freq, FILE* outfile)
{
int num[256] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width * height; j++)
{
if (i == Buff[j])
{
num[i]++;
}
}
}
fprintf(outfile, "symbol\tfreq\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
freq[i] = double(num[i]) / (width * height);
fprintf(outfile, "%d\t%f\n", i, freq[i]);
}
}3.结果汇总(图1-4)
概率分布图做法:在excel中导入自文本(freq.txt文件)再进行绘图
| 图像 | 原始图像概率分布图 | 预测误差图像概率分布图 | 熵编码压缩比 | DPCM+熵编码压缩比 |
| 1 | 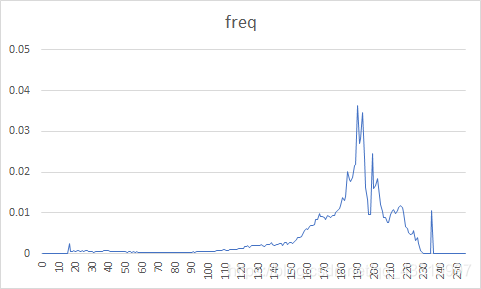 | 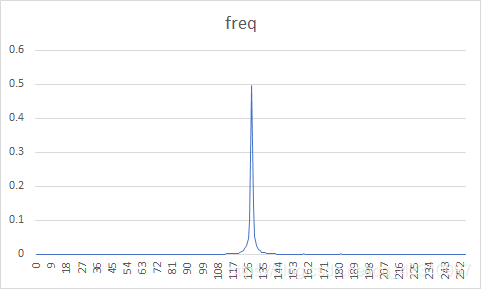 | 89.58% | 36.46% |
| 2 | 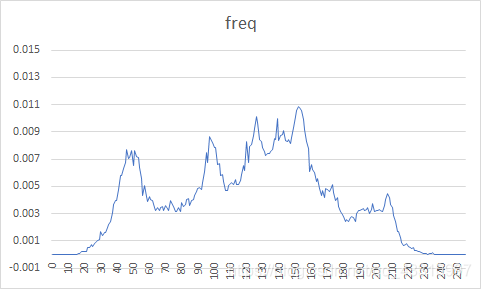 | 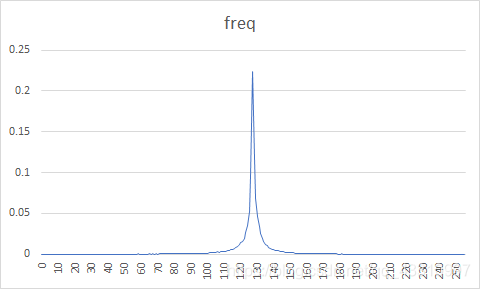 | 93.75% | 51.04% |
| 3 | 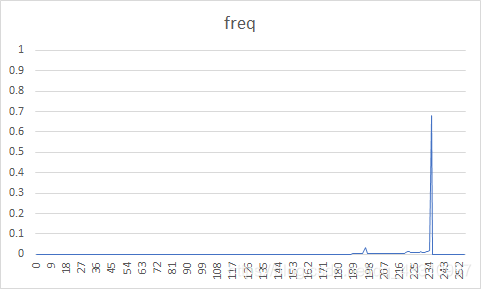 | 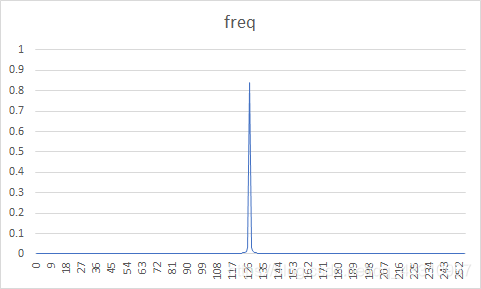 | 51.04% | 30.21% |
| 4 | 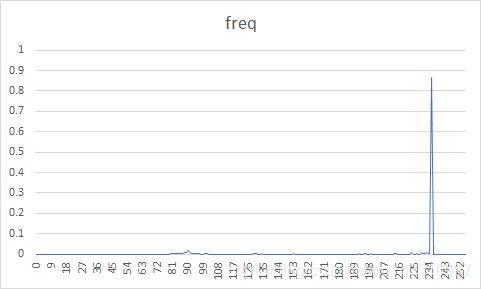 | 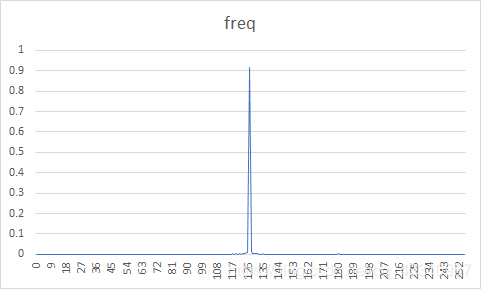 | 30.21% | 29.17% |
实验结论
原图概率分布图较为随机,而经过DPCM编码后的误差图像信源符号集中在128电平。
对预测误差进行量化编码得到的压缩比明显小于直接编码原文件,说明DPCM+熵编码比仅熵编码压缩效率更高。
完整代码
DPCM的main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "PSNR.h"
using namespace std;
constexpr auto width = 256;
constexpr auto height = 256;
constexpr auto imgSize = width * height;
void DPCM(int w, int h, unsigned char* yBuff, unsigned char* errBuff, unsigned char* reBuff, int Qbit)
{
int m = 512 / pow(2, Qbit);
int* a;
a = (int*)malloc((sizeof(int)) * w * h);
for (int j = 0; j < h; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; i++)
{
if (i == 0)
{
a[j * w + i] = (yBuff[j * w + i] - 128) / m + 128;
reBuff[j * w + i] = (a[j * w + i] - 128) * m + 128;
}
else
{
a[j * w + i] = (yBuff[j * w + i] - reBuff[j * w + i - 1]) / m + 128;
reBuff[j * w + i] = (a[j * w + i] - 128) * m + reBuff[j * w + i - 1];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < w * h; i++)
errBuff[i] = (unsigned char)a[i] ;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
FILE* yuvFile = NULL;
FILE* errFile = NULL;
FILE* reFile = NULL;
errno_t err;
err = fopen_s(&yuvFile, argv[1], "rb");
if (err == 0)
{
printf("打开yuv文件成功!\n");
}
else printf("打开yuv文件失败!\n");
err = fopen_s(&errFile, argv[2], "wb");
if (err == 0)
{
printf("打开err文件成功!\n");
}
else printf("打开err文件失败!\n");
err = fopen_s(&reFile, argv[3], "wb");
if (err == 0)
{
printf("打开re文件成功!\n");
}
else printf("打开re文件失败!\n");
unsigned char* yBuff, * uBuff, * vBuff = NULL, * errBuff, * reBuff = NULL;
yBuff = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * imgSize);
errBuff = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * imgSize);
reBuff = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * imgSize);
uBuff = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * imgSize / 2);
vBuff = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * imgSize / 2);
fread(yBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize, yuvFile);
for (int i = 0; i < imgSize / 2; i++)
{
uBuff[i] = 128;
vBuff[i] = 128;
}
int Qbit;
cout << "请输入量化比特数: ";
cin >> Qbit;
cout << "Qbit="<<Qbit<<endl;
int m = 512 / pow(2, Qbit);
DPCM(width, height, yBuff, errBuff, reBuff,Qbit);
double psnr = PSNR(yBuff, reBuff, height, width, imgSize);
cout << "PSNR=" << psnr<<endl;
fwrite(errBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize, errFile);
fwrite(uBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize / 2, errFile);
fwrite(vBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize / 2, errFile);
fwrite(reBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize, reFile);
fwrite(uBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize / 2, reFile);
fwrite(vBuff, sizeof(unsigned char), imgSize / 2, reFile);
}PSNR.h
double MSE(unsigned char* infile, unsigned char* outfile, int height, int width, int imgSize);
double PSNR(unsigned char* infile, unsigned char* outfile, int height, int width, int imgSize);
#pragma oncePSNR.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "math.h"
double MSE(unsigned char* infile, unsigned char* outfile, int height, int width, int imgSize)
{
double sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < imgSize; i++)
{
double temp = pow((double)(infile[i] - outfile[i]),2);
sum += temp;
}
double mse = sum / imgSize;
return mse;
}
double PSNR(unsigned char* infile, unsigned char* outfile, int height, int width, int imgSize)
{
double mse = MSE(infile, outfile, height, width,imgSize);
double psnr = 10 * log10(255.0 * 255.0 / mse);
return psnr;
}freq的main.cpp
#include <iostream>
constexpr auto width = 256;
constexpr auto height = 256;
void Count(unsigned char* Buff, double* freq, FILE* outfile)
{
int num[256] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width * height; j++)
{
if (i == Buff[j])
{
num[i]++;
}
}
}
fprintf(outfile, "symbol\tfreq\n");
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
{
freq[i] = double(num[i]) / (width * height);
fprintf(outfile, "%d\t%f\n", i, freq[i]);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
FILE* infile;
FILE* outfile;
errno_t err;
err = fopen_s(&infile, argv[1], "rb");
if (err == 0)
{
printf("打开文件成功!\n");
}
else printf("打开文件失败!\n");
err = fopen_s(&outfile, argv[2], "wb");
if (err == 0)
{
printf("打开文件成功!\n");
}
else printf("打开文件失败!\n");
unsigned char* buffer;
buffer = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * width * height);
fread(buffer, sizeof(unsigned char), width * height, infile);
double freq[256];
Count(buffer, freq, outfile);
}




















 582
582

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








