动态代理含义:在程序运行期间JVM根据需要通过反射等机制动态地创建代理类及其代理对象。
例:在CalculatorService中有add,sub,div,mul四种方法,由于每个方法中重复的地方有很多,我们想实现代码的复用,于是采用了动态代理。
CalculatorService实现ICalculatorService接口。
package com.jd.test;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import com.jd.calculator.CalculatorService;
import com.jd.calculator.ICalculatorService;
public class Test {
//动态(程序运行时实现和目标类相同接口的java类)代理()
CalculatorService calculatorService;
public Test(CalculatorService calculatorService) {
this.calculatorService = calculatorService;
}
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String name = method.getName();
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":The "+name+" method begins.");
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":Parameters of the "+name+" method: ["+args[0]+","+args[1]+"]");
Object result = method.invoke(calculatorService, args);//目标方法
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":Result of the "+name+" method:"+result);
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":The "+name+" method ends.");
return result;
}
};
public Object get() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Test.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {ICalculatorService.class}, h);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");
Test test = new Test(new CalculatorService()); //赋值
ICalculatorService calculatorService = (ICalculatorService) test.get();
int result = calculatorService.add(1, 1);
System.out.println("-->"+result);
}
}
整个过程十分复杂。我们一点一点看。
public Object get() {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Test.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] {ICalculatorService.class}, h);
}
作用是产生一个动态class类的对象。Proxy是动态代理类 ,proxy是代理对象。Test.class.getClassLoader()是类加载器;
new Class[] {ICalculatorService.class}是要实现的接口;h是一个增强对象,这里是一个匿名内部类。
1. 摁住Ctrl进入newProxyInstance,我们可以找到这样一行代码, 这就是产生的动态class类。
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
2. cos是这个动态类里的构造函数的对象
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
3 .返回的则是通过构造构造函数对象实例化一个动态类的对象。h是传的参数
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
然后解释main方法:
1. 这一行生成一个编译对象($Proxy.class)。
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");
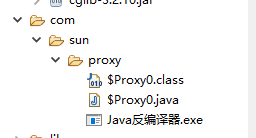
我们可以在项目管理栏,右键选中Properties找到生成的class文件。再通过Java反编译器生成$Proxy.java,然后刷新工程
2. 这一行是为上面声明的calculatorService赋值。
Test test = new Test(new CalculatorService());
3. 调用上面的get方法,生成一个动态类的对象就是$Proxy.java。赋值给calculatorService
ICalculatorService calculatorService = (ICalculatorService) test.get();
4.这一行是动态类对象调用add方法
int result = calculatorService.add(1, 1);
在 $Proxy.java中我们可以找到如下代码。 代理类的构造函数,其参数正是是InvocationHandler实例,Proxy.newInstance方法就是通过这个构造函数来创建代理实例的
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationhandler)
{
super(invocationhandler);
}
uper.h.invoke是调用Test.java匿名内部类中的invoke()方法。其中传入的值,this就是调用invoke方法的对象,calculatorService的值,也就是代理对象; 这里的method就是m4,也就是代理类静态代码块中加载的ICalculatorService接口中的add方法; 向add中传入的常量值i,j 。intValue()是先将二者转换成了Integer类型
try
{
return ((Integer)er)super.h.invoke(thi(this, m4, new Object[] {
Integer.valueOf(i),(i), ), Integer.valueOf(j)
(j)
})).intValue();
下面是被调用的那个invoke方法。
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
String name = method.getName();
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":The "+name+" method begins.");
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":Parameters of the "+name+" method: ["+args[0]+","+args[1]+"]");
Object result = method.invoke(calculatorService, args);//目标方法
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":Result of the "+name+" method:"+result);
System.out.println(calculatorService.getClass().getName()+":The "+name+" method ends.");
return result;
}
};
5.输出result
附加部分:
CGLib动态代理
程序执行时通过ASM(开源的Java字节码编辑库,操作字节码)jar包动态地为被代理类生成一个代理子类,通过该代理子类创建代理对象,由于存在继承关系,所以父类不能使用final修饰。
JDK动态代理与CGLib动态代理区别:
1、JDK动态代理基于接口实现,所以实现JDK动态代理,必须先定义接口;CGLib动态代理基于类实现;
2、JDK动态代理机制是委托机制,委托hanlder调用原始实现类方法;CGLib则使用继承机制,被代理类和代理类是继承关系,所以代理类是可以赋值给被代理类的,如果被代理类有接口,那么代理类也可以赋值给接口。
动态代理优点:
1、静态代理在程序执行前需手动创建代理类,如果需要很多代理类,每一个都手动创建不仅浪费时间,而且可能产生大量重复性代码,此时我们就可以采用动态代理。
2、动态代理通过InvocationHandler接口invoke方法或MethodInterceptor接口intercept方法为被代理对象中的方法增加额外功能,这种方式比静态代理中通过代理类逐一为被代理对象中的方法增加额外功能,更加的灵活。




 本文介绍了Java动态代理,包括其含义,即在程序运行期间JVM动态创建代理类及对象。以CalculatorService为例说明实现过程,还介绍了CGLib动态代理,它通过ASM操作字节码为被代理类生成子类。对比了JDK和CGLib动态代理的区别,并阐述了动态代理可节省时间、更灵活的优点。
本文介绍了Java动态代理,包括其含义,即在程序运行期间JVM动态创建代理类及对象。以CalculatorService为例说明实现过程,还介绍了CGLib动态代理,它通过ASM操作字节码为被代理类生成子类。对比了JDK和CGLib动态代理的区别,并阐述了动态代理可节省时间、更灵活的优点。
















 23万+
23万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








