RecyclerView有4级缓存如下:
| 层级 | 缓存变量 | 缓存名 | 容量 | 数据结构 | 缓存用途 |
| 1 | mChangeScrap | 可见缓存 | x(无限制) | ArrayList | 用于屏幕中可见View的回收和复用 |
| 2 | mCachedViews | 缓存列表 | 2 | ArrayList | 用于移除屏幕的View的回收和复用,不会清空数据 |
| 3 | mViewCacheExtension | 自定义缓存 | x | 一般不使用这个 | |
| 4 | RecyclerViewPool | 缓存池 | 5 | SparseArray | 用于移除屏幕的View的回收和复用,会将ViewHolder的数据重置 |
一级缓存mChangeScrap,是来缓存当前屏幕中可见的View,当列表数据发生变化时,屏幕内的数据可以直接拿来复用。
这里二级缓存mCachedViews和四级缓存RecyclerViewPool,都是用来缓存移除屏幕的View。它们的区别在于,二级缓存mCachedViews只缓存移除屏幕的前2个View,当超过第3个View时,会把mCachedViews中的最先缓存的那个View移除掉(根据FIFO原则),并把它缓存到四级缓存RecyclerViewPool中去。保存在二级缓存mCachedViews的是携带了原来的ViewHolder的所有数据信息,数据可以直接来拿来复用。
从二级缓存mCachedViews里面移出的ViewHolder再存入四级缓存RecyclerViewPool之前ViewHolder的数据会被全部重置,相当于一个新的ViewHolder,而且二级缓存mCachedViews是根据position来获取ViewHolder,而RecycledViewPool是根据itemType获取的。
因为RecycledViewPool缓存的ViewHolder是全新的,所以取出来的时候需要走onBindViewHolder()方法。
第四级缓存RecyclerViewPool中,SparseArray是一个2维数组,不同类型的ViewHolder会存储在它们各自的ArrayList当中:
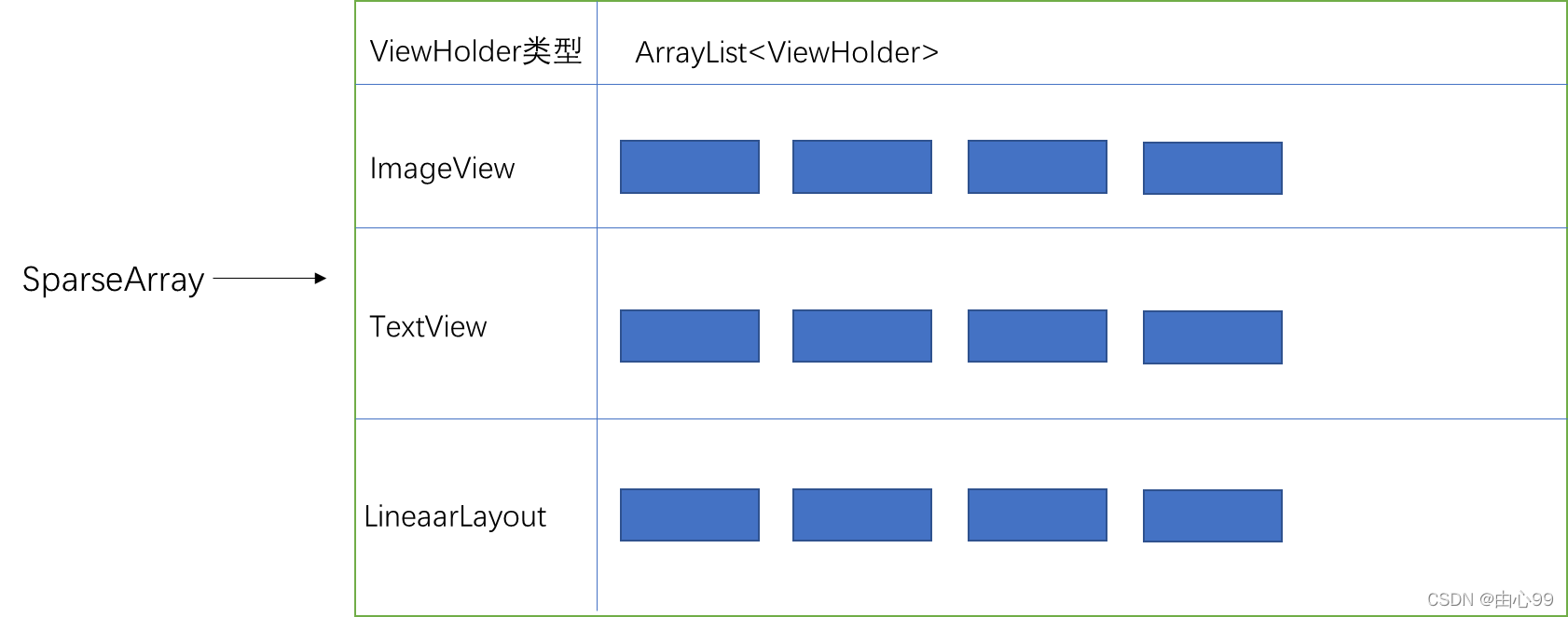
回收View:
在RecyclerView的源码当中,有个回收View的关键方法void recycleViewHolderInternal(ViewHolder holder):
这里删掉了部分源码,只看关键的地方,免得看的太杂。
在回收View时,会先去存在二级缓存mCachedViews里,要是二级缓存满了,就去缓存到四级缓存RecyclerViewPool
void recycleViewHolderInternal(ViewHolder holder) {
......
if (forceRecycle || holder.isRecyclable()) {
if (mViewCacheMax > 0
&& !holder.hasAnyOfTheFlags(ViewHolder.FLAG_INVALID
| ViewHolder.FLAG_REMOVED
| ViewHolder.FLAG_UPDATE
| ViewHolder.FLAG_ADAPTER_POSITION_UNKNOWN)) {
// Retire oldest cached view
//先尝试放到cacheView中
int cachedViewSize = mCachedViews.size();
if (cachedViewSize >= mViewCacheMax && cachedViewSize > 0) {
// 如果 mCachedViews 已经满了,把第0个位置的移除并放到 缓存池中
recycleCachedViewAt(0);
cachedViewSize--;
}
}
......
if (!cached) {
// 如果CacheView中没放进去,就放到 缓存池中
addViewHolderToRecycledViewPool(holder, true);
recycled = true;
}
......
}
}复用View:
在RecyclerView的源码当中,有个复用View的关键方法ViewHolder tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline(int position, boolean dryRun, long deadlineNs):
@Nullable
ViewHolder tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline(int position,
boolean dryRun, long deadlineNs) {
......
ViewHolder holder = null;
if (mState.isPreLayout()) {
//从一级缓存changed scrap取
holder = getChangedScrapViewForPosition(position);
fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache = holder != null;
}
......
final int type = mAdapter.getItemViewType(offsetPosition);
if (mAdapter.hasStableIds()) {
//如果holder=null,就从二级缓存取
holder = getScrapOrCachedViewForId(mAdapter.getItemId(offsetPosition),
type, dryRun);
}
if (holder == null && mViewCacheExtension != null) {
//如果holder=null, 从三级缓存 CacheExtension 中取(一般不用)
final View view = mViewCacheExtension
.getViewForPositionAndType(this, position, type)
if (holder == null) { // fallback to pool
// 如果holder=null, 从四级缓存缓存池中取
holder = getRecycledViewPool().getRecycledView(type);
}
if (holder == null) {
//)缓存中都没有拿到值,就直接创建
holder = mAdapter.createViewHolder(RecyclerView.this, type);
}
}
boolean bound = false;
//已经 bind过了,不会再去绑定,未绑定过时,进行绑定
if (mState.isPreLayout() && holder.isBound()) {
// do not update unless we absolutely have to.
holder.mPreLayoutPosition = position;
} else if (!holder.isBound() || holder.needsUpdate() || holder.isInvalid()) {
if (DEBUG && holder.isRemoved()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Removed holder should be bound and it should"
+ " come here only in pre-layout. Holder: " + holder
+ exceptionLabel());
}
final int offsetPosition = mAdapterHelper.findPositionOffset(position);
// 尝试 bindView
bound = tryBindViewHolderByDeadline(holder, offsetPosition, position, deadlineNs);
}
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = holder.itemView.getLayoutParams();
final LayoutParams rvLayoutParams;
if (lp == null) {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) generateDefaultLayoutParams();
holder.itemView.setLayoutParams(rvLayoutParams);
} else if (!checkLayoutParams(lp)) {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) generateLayoutParams(lp);
holder.itemView.setLayoutParams(rvLayoutParams);
} else {
rvLayoutParams = (LayoutParams) lp;
}
rvLayoutParams.mViewHolder = holder;
rvLayoutParams.mPendingInvalidate = fromScrapOrHiddenOrCache && bound;
return holder;
}源码看着有点长,总结下就是:
- tryGetViewHolderForPositionByDeadline;
- 从一级缓存 mChangeScrap 中取,方法 getChangedScrapViewForPosition(int position);
- 如果holder为空,从二级缓存 mCachedViews中取,方法 getScrapOrCachedViewForId(long id, int type, boolean dryRun);
- 如果holder为空,从三级缓存 mViewCacheExtension 中取;
- 如果holder为空,从四级缓存缓存池中取,方法 getRecycledView(int viewType);
- 缓存中都没有拿到值,就直接创建;
- 未绑定过时,进行绑定;
从复用View的过程中,可以知道,recyclerView会先去缓存中先看看有没有可复用的View,缓存没有的话,才会去找Adapter,使用onCreaterViewHolder()创建,再绑定。
着重看下四级缓存缓存池getRecycledView(int viewType):
public ViewHolder getRecycledView(int viewType) {
//从mScrap中根据view的类型来取出一个
final ScrapData scrapData = mScrap.get(viewType);
if (scrapData != null && !scrapData.mScrapHeap.isEmpty()) {
final ArrayList<ViewHolder> scrapHeap = scrapData.mScrapHeap;
//从 scrapData 中拿最后一个数据,先进后出
return scrapHeap.remove(scrapHeap.size() - 1);
}
return null;
}
static class ScrapData {
//ViewHolder是作为一个List被存进来的
ArrayList<ViewHolder> mScrapHeap = new ArrayList<>();
// 缓存池中 list的大小是5,也就是每个类型的view缓存池中存储5个
int mMaxScrap = 5;
long mCreateRunningAverageNs = 0;
}
getRecycledView(int viewType)方法中,有个内部类ScrapData,这个ScrapData里面有个列表ArrayList<ViewHolder> mScrapHeap,用来存不同类型的ViewHolder,当外部调用getRecycledView(int viewType)时,会先判断viewType,根据这个viewType来获取特定的ViewHolder,并返回。





 本文介绍了RecyclerView的四级缓存机制,包括一级缓存mChangeScrap、二级缓存mCachedViews、四级缓存RecyclerViewPool的工作原理。在回收View时,满员的二级缓存会将View移至四级缓存。复用View时,首先尝试从一级缓存获取,否则依次检查二级、三级和四级缓存。四级缓存通过ScrapData存储不同类型的ViewHolder。了解这些有助于优化RecyclerView的性能。
本文介绍了RecyclerView的四级缓存机制,包括一级缓存mChangeScrap、二级缓存mCachedViews、四级缓存RecyclerViewPool的工作原理。在回收View时,满员的二级缓存会将View移至四级缓存。复用View时,首先尝试从一级缓存获取,否则依次检查二级、三级和四级缓存。四级缓存通过ScrapData存储不同类型的ViewHolder。了解这些有助于优化RecyclerView的性能。
















 2667
2667

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








