基于尚学堂视频课程的学习
目录
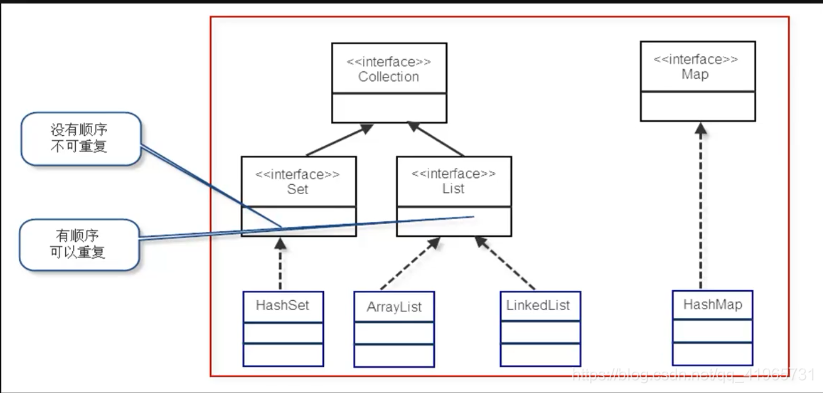
Irerator迭代器遍历容器元素(LIst,map,set)
数组也是一种容器,可以用来放对象或是基本数据类型
- 优点:
- 快速访问数组,效率高
- 简单的线性序列
- 缺点:
- 不灵活,数组需要实现定义好容量
泛型:
泛型是JDK1.5后加入的,它是帮助我们建立类型安全的集合;
泛型的本质是“ 数据类型的参数化 ”,可以把泛型理解为数据类型的一个占位符(形式参数),告诉编译器,在传入的时候一定要传入实际类型。
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CollectionTest<String> ct = new CollectionTest<String>();
ct.setData("1111",0);
//如果我们没有用泛型,因为在CollectionTest定义的结合为Object,我们需要
//String i =(String)ct.getData(0);
String i = ct.getData(0);
}
}
//类似于是一个集合类(满足存取的功能)
class CollectionTest<E>{ //字符可以是任何标识符,一般采用<T,V,E>
Object[] obj = new Object[5];
public void setData(E o,int index){
obj[index] = o;
}
public E getData(int index){
return (E)obj[index];
}
}
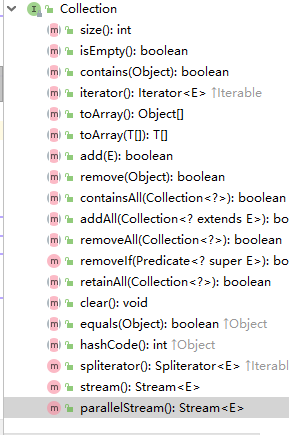
Collection接口中的方法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionTest0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> ct = new ArrayList<String>();
System.out.println(ct.size());
System.out.println(ct.isEmpty());
ct.add("田坤");
ct.add("田大坤");
ct.add("田小坤");
System.out.println(ct.size());
System.out.println(ct);
Object[] a= ct.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
ct.remove("田大坤");
System.out.println(ct);
System.out.println(ct.contains("田坤"));
ct.clear();
System.out.println(ct.isEmpty());
//这里面有的方法没有写到,后面再说。
//因为后面的讲的LIST SET 都是Collection的子类,所以,这些以上方法都是类似的,后不在重复
}
}
0
true
3
[田坤, 田大坤, 田小坤]
[田坤, 田大坤, 田小坤]
[田坤, 田小坤]
true
true
多个容器的操作
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionTest0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<Integer> ct1 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ct1.add(1);
ct1.add(2);
ct1.add(3);
Collection<Integer> ct2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
ct2.add(1);
ct2.add(2);
ct2.add(6);
// ct1.addAll(ct2);
System.out.println(ct1);
//在ct1中移除所以含有ct2中的数据
// ct1.removeAll(ct2);
System.out.println(ct1);
ct1.retainAll(ct2);
System.out.println(ct1);
}
}List
有序,可重复的容器
有序:LIst中每个元素都有索引标记,可以根据元素的索引标记(List中的位置)访问元素,从而精确的控制这些元素
可重复:List加入重复的元素, 满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素重复加入容器
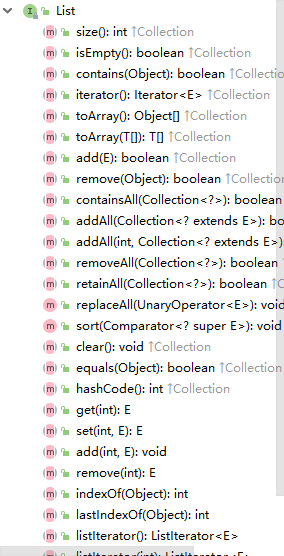
List接口的三个实现类:
- ArrayList(数组)
- LinkedList(链表)
- Vector
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.List;
public class CollectionTest0 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
}
public static void test1(){
List<String> list1 = new ArrayList<String>();
list1.add("A");
list1.add("B");
list1.add("C");
list1.add(2,"田坤");
System.out.println(list1);
list1.remove(3);
System.out.println(list1);
list1.set(1,"E");
System.out.println(list1);
list1.add("C");
list1.add("E");
System.out.println(list1);
System.out.println(list1.indexOf("E"));
System.out.println(list1.lastIndexOf("E"));
}
}
[A, B, 田坤, C]
[A, B, 田坤]
[A, E, 田坤]
[A, E, 田坤, C, E]
1
4
手工方法实现ArrayList
package com.tk.collection;
/**
* 手工实现Arraylist的简单原理 get add set toString remove size
* @data :2019-5-11上午10:14:42
* @author :田坤
*/
public class List02<E> {
//定义一个数组
Object[] arr = null;
//数据的默认大小
private static final int ARRAY_OPACITY = 10;
//容器的大小
private int size = 0;
public List02() {
arr = new Object[ARRAY_OPACITY];
}
public List02(int count){
if(count <0)
throw new RuntimeException("数组个数不能小于0");
else if(count == 0)
arr = new Object[ARRAY_OPACITY];
else arr = new Object[count];
}
//取
public E get(int index){
return (E)arr[index];
}
//放
public void add(E obj){
//扩容
if(size == arr.length){
Object[] newarr = new Object[size+(size>>1)]; //size + size/2
System.arraycopy(arr, 0, newarr, 0, size);
arr = newarr;
}
arr[size] = (E)obj;
size++;
}
//移除某个元素
public void remove(int index){
if(index <0 || index >=size)
throw new RuntimeException("索引越界");
System.arraycopy(arr, index+1, arr, index,size-index-1);
arr[size] = null;
size --;
}
//修改某个索引的数据
public void set(int index,E obj){
if(index<0 || index >=size)
throw new RuntimeException("索引越界");
arr[index] = obj;
}
//数组的大小
public int size(){
return size;
}
//
public String toString(){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if(arr[i]!= null)
sb.append(""+arr[i]+",");
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length()-1, ']');
return sb.toString();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
List02<String> list = new List02<>(0);
for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
list.add("田坤"+i);
}
System.out.println(list.get(2));
list.set(2, "宋旭东");
list.remove(-1);
System.out.println(list.toString());
}
}
LinkedList
linkedList底层使用双向链表实现的存储。
特点:查询效率低,增删效率高,线程不安全
双向链表:每个数据节点都有俩个指针,分别指向前一个和后一个节点
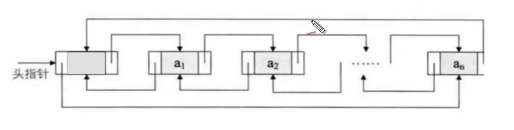
每个节点中的内容
public class Node {
public Node previous; //前指针
public Object value; //节点数据
public Node next; //后指针
package com.tk.collection;
/**
* 自定义一个链表
* @data :2019-5-11上午11:28:30
* @author :田坤
*/
public class LinkedList01<E>{
private Node first;
private Node last;
private int size = 0;
public E get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new RuntimeException("索引越界");
Node node = new Node();
node = first;
for(int i = 0; i < index;i++ ){
node = node.next;
}
return (E) node.value;
}
public Node getNode(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new RuntimeException("索引越界");
Node node = new Node();
node = first;
for(int i = 0; i < index;i++ ){
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
//添加数据
public void add(E obj){
Node node = new Node(obj);
if(first == null){
first = node;
last = node;
size ++;
}else{
node.previous = last;
node.next = null;
last.next = node;
last = node;
size ++;
}
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
public void ToString() {
Node node = new Node();
node = first;
while(node!=null){
System.out.println(node.value);
node = node.next;
}
}
public void remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new RuntimeException("索引越界");
Node node = getNode(index);
node.next.previous = node.previous;
node.previous.next = node.next;
size --;
}
public void insert(int index,E value){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new RuntimeException("索引越界");
Node node = new Node(value);
Node temp = getNode(index);
node.previous = temp.previous;
node.next = temp;
temp.previous.next = node;
temp.previous = node;
size ++;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
LinkedList01<String> ll = new LinkedList01();
ll.add("11");
ll.add("22");
ll.add("33");
ll.ToString();
System.out.println(ll.get(2));
System.out.println(ll.size());
ll.remove(1);
ll.insert(1, "4444");
ll.ToString();
}
}
Vector
底层启用数组实现了List接口,相关方法加入了同步检测,所以“效率低,安全性高”
Vector中的 get方法
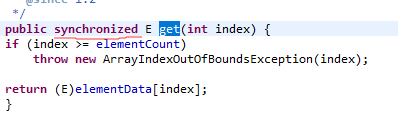
如何选择AarryLis、LiinkedLst、Vector
- 需要线程安全时,使用vector
- 不存在多线程安全问题,并且查找比较多用ArrayList
- 不存在多线程安全问题,并且增加和删除元素多用LinkedList
Map接口
package com.tk.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class Map01 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Map<Integer, String> m1 = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
m1.put(1, "111");
m1.put(2, "222");
m1.put(3, "333");
System.out.println(m1.toString());
System.out.println(m1.get(1));
System.out.println(m1.size());
System.out.println(m1.isEmpty());
System.out.println(m1.containsKey(1));
System.out.println(m1.containsValue(222));
Map<Integer, String> m2 = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
m2.put(4, "444");
m2.put(5, "555");
m1.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m1);
//map键不能重复,如果有重复的(根据equals来判断),则新的覆盖旧的
m1.put(2, "666");
System.out.println(m1);
}
}
HashMap
HashMap底层实现使用了Hash表,这是一种非常重要的数据结构,对于我们很多的技术都有帮助(如:redis的核心技术和HashMap一样)。
数据结构中由数组和链表来实现对数据的存储:
数组:占用中间连续,寻址容易,查询速度快,但是增加和删除效率低
链表:占用空间不连续,寻址困难,查询速度慢,但是,增加和删除效率非常高
哈希表的本质就是= 数组 + 链表
HashMap源码中数据的初始化
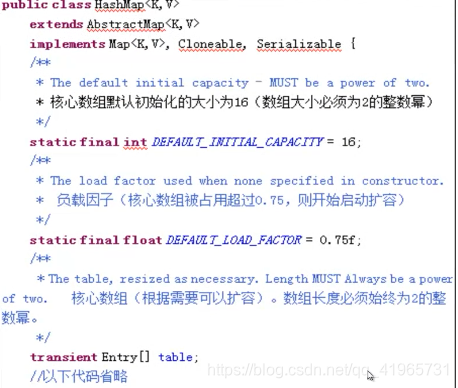
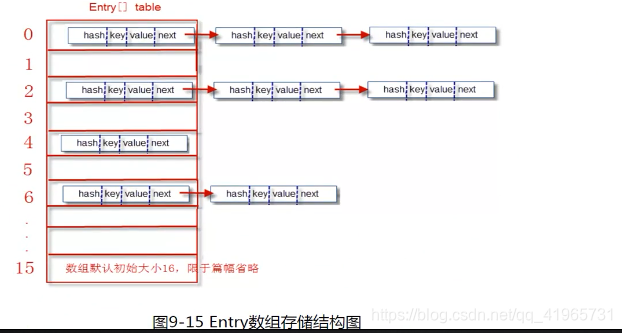
Entry[ ] table是HashMap的核心数组结构,我们称之为“位桶结构”,Entry是HashMap中的静态内部类。数据的初始化
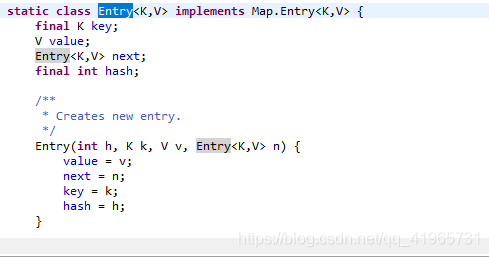
Entry中的对象:
- key :键对象
- value : 值对象
- next :下一个节点
- hash :键对象的Hash值
每一个Entry都是一个单向链表结构,
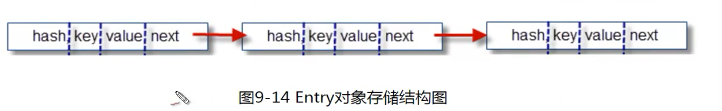
Entry [] 的数组结构为:(HashMap的结构)
1、存储数据的过程:put(key , value)
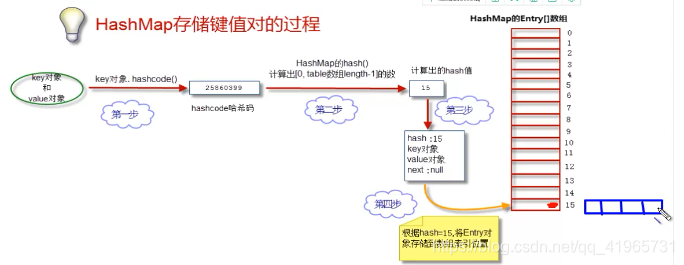
我们的目的是将"ket value"俩个对象存储到Entry数组中去
1、获取key对象的hashcode()
hashcode()方法
2、根据hashcode方法计算出hash值(要求在【0-数组长度-1】区间中)
(1)、计算算法
hash = hashcode / hashcode
键值对对象都会存储到索引值为1的位置,每存储一个对象,就会发生 hash冲突 hashMap会 退化成一个链表
(2)、简单和常用的算法(相除取余算法)
hash = hashcode / 数组长度
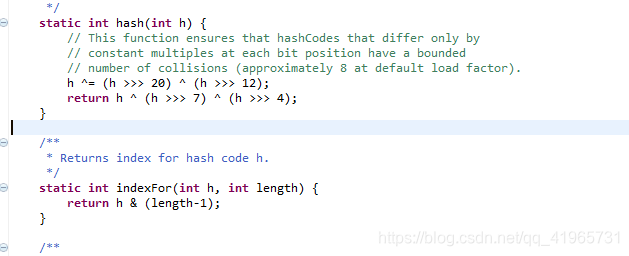
但是除法效率低下,JDK在后来改进了算法,首先约定数组的长度必须是2的整数幂,然后采用位运算进行取余
hash值 = hashcode & (数组长度-1)
为了更好的散列效果,JDK对hashcode进行了俩次散列处理(核心目的是为了分布的更加均匀)
(3)、生成Entry对象
(4)、将Entry对象放到table数组中
如果数组中没有值,直接将entry对象放到数组中去,并且entry对象的next值为 null ,如果数组对应位置有数据,将其放在next后
JDK8时,如果链表长度大于8时,链表就换成了红黑树,大大提高了查询的效率
2、获取数据的过程:get(key )
先需要获取键值对对象,进而在返回value值
(1)、获取键对象的hashcode,获取到hash值。定位到数组的位置
(2)、在链表上个挨个比较key对象(equals比较)
(3)、返回equals为true的节点对象
JAVA规定俩个内容相同(equals为true)的对象必须有相同的hashcode.
手动实现一个HashMap
1、HashMap的节点类
/**
* HashCode的节点类
* @data :2019-5-11下午4:44:16
* @author :田坤
*/
public class Node0 {
public int hash;
public Object key;
public Object value;
public Node0 next;2、HashMap的实现
package com.tk.collection;
/**
* 自定义实现HashMap
* @data :2019-5-11下午4:43:42
* @author :田坤
*/
public class MyMap<K,V> {
Node0[] table; //位桶数组
int size = 0; //节点的个数
private static final int HASHMAP_OPACITY = 16; //HashMap数组的默认大小 2的整数幂
public MyMap(){
table = new Node0[HASHMAP_OPACITY];
}
public void put(K key,V value){
Node0 node = new Node0();
node.hash = myHash(key.hashCode(), HASHMAP_OPACITY);
node.value = value;
node.key = key;
node.next = null;
Node0 lastNode = null; //在遍历的最后一个节点
//根据此节点的hash值获取到hash值相对应的链表中
Node0 temp = new Node0();
temp = table[node.hash];
//如果索引为hash索引的下标没有数据
if(temp == null){
//节点为空直接将节点放进去
table[node.hash] = node;
}else{
//数组元素不为空,遍历
while(temp != null){
if(temp.key.equals(key)){
temp.value = value;
}
else{
lastNode = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
}
lastNode.next = node;
}
}
private int myHash(int hashCode,int length){
System.out.println("hash in myHash"+(hashCode%(length-1))); //取模运算效率低
System.out.println("hash in myHash"+(hashCode&(length-1))); //直接位运算,效率高
return hashCode&(length-1);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
sb.append("{");
for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) {
Node0 temp = table[i];
while(temp != null){
sb.append(""+temp.key+":"+temp.value+",");
temp = temp.next;
}
}
sb.setCharAt(sb.length()-1, '}');
return sb.toString();
}
public K get(K key){
int hash = myHash(key.hashCode(), HASHMAP_OPACITY);
Node0 temp = table[hash];
while(temp != null){
if(temp.key.equals(key))
break;
temp = temp.next;
}
return (K)temp.value;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
MyMap<Integer,String> mm = new MyMap<>();
mm.put(1, "111");
mm.put(2, "222");
mm.put(3, "333");
mm.put(16, "333");
mm.put(17, "333");
System.out.println(mm.toString());
System.out.println(mm.get(3));
}
}
HashMap和HashTable的区别
HashMap:线程不安全,效率高 。允许key和value为null
HashTable:线程安全,效率低。 允许key和value为null
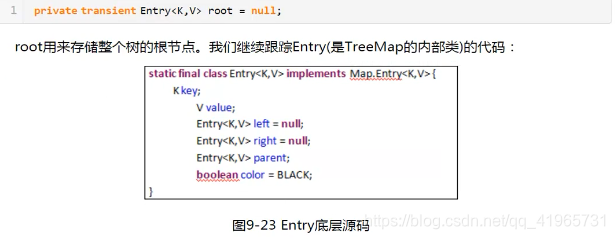
TreeMap
TreeMap是红黑二叉树的经典实现
package com.tk.collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Map<Integer,String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, "11");
map.put(3, "33");
map.put(6, "66");
map.put(4, "44");
System.out.println(map.toString());
Map<Student, String> stumap = new HashMap<Student, String>();
stumap.put(new Student(1, 88), "张三");
stumap.put(new Student(3, 99), "李四");
stumap.put(new Student(5, 88), "王五");
stumap.put(new Student(15, 55), "赵六");
for (Student stu : stumap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(stu);
}
}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
int id;
int grade;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public int getGrade() {
return grade;
}
public void setGrade(int grade) {
this.grade = grade;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [id=" + id + ", grade=" + grade + "]";
}
public Student(int id, int grade) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.grade = grade;
}
public Student() {
super();
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) { //负数: 小于 0 :等于 正数:大于
if(this.grade>o.grade)
return 1;
else if(this.grade<o.grade)
return -1;
else if(this.id > o.id)
return 1;
else if(this.id < o.id)
return -1;
return 0;
}
}
Tree
Set

HashSet源码
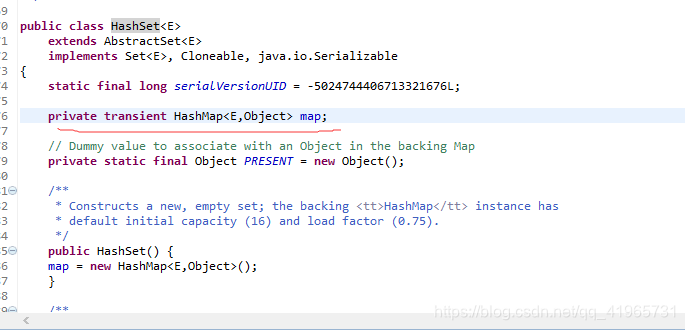
hashset是基于hashmap实现的
Irerator迭代器遍历容器元素(LIst,map,set)
package com.tk.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
public class iteratorTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
map1();
list1();
set();
}
public static void map1(){
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put(1, "111");
map.put(2, "222");
map.put(3, "333");
Set<Entry<Integer, String>> entrySet = map.entrySet();
Iterator<Entry<Integer, String>> iterator = entrySet.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Entry<Integer, String> next = iterator.next();
System.out.println(next.getKey()+"-------"+next.getValue());
}
Set<Integer> keySet = map.keySet();
Iterator<Integer> iterator2 = keySet.iterator();
while(iterator2.hasNext()){
int key = iterator2.next();
System.out.println(key+"-------"+map.get(key));
}
}
public static void list1(){
List<String> ls = new ArrayList<String>();
ls.add("11");
ls.add("22");
ls.add("33");
ls.add("44");
Iterator<String> iterator = ls.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
public static void set(){
Set<String> set= new HashSet<>();
set.add("11");
set.add("22");
set.add("33");
Iterator<String> iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
Connections工具类的使用






 本文深入讲解Java集合框架,包括泛型、List、Set、Map等核心接口与其实现类,如ArrayList、LinkedList、HashMap、TreeMap的特性及使用场景,同时探讨了容器操作、迭代器遍历以及自定义容器实现。
本文深入讲解Java集合框架,包括泛型、List、Set、Map等核心接口与其实现类,如ArrayList、LinkedList、HashMap、TreeMap的特性及使用场景,同时探讨了容器操作、迭代器遍历以及自定义容器实现。
















 352
352

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








