1、IO流的分类
- 操作数据单位:字节流、字符流
- 数据的流向:输入流、输出流
- 流的角色:节点流、处理流
2、流的体系结构
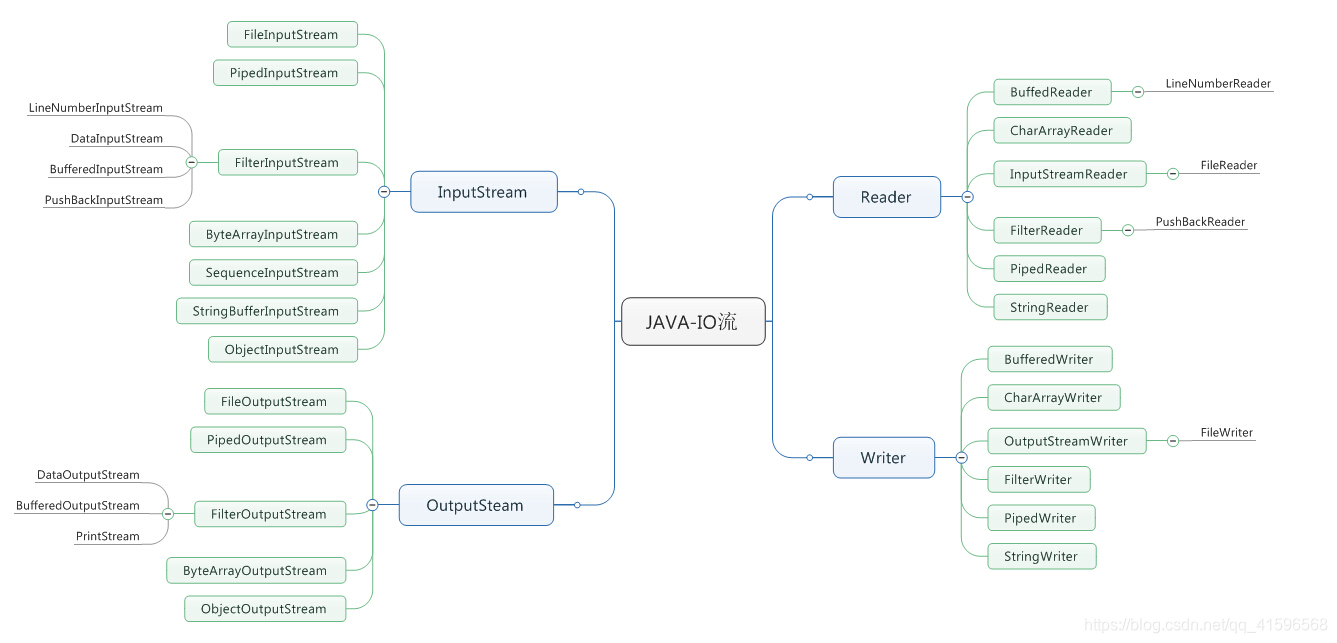
3、常用的流

4、输入/输出的流程
① 创建File类的对象,指明读取/写入的数据的来源。(读取时要求此文件存在)
② 创建相应的输入/输出流,将File类的对象作为参数,传入流的构造器中
③ 具体的读入/写入过程:创建相应的byte[] 或 char[]。
④ 关闭流资源
注:程序中出现的异常需要使用try-catch-finally处理。
5、使用节点流(文件流)实现文件复制
流: FileInputStream/ FileOutputStream
package JavaSE.IO;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author LFuser
* @create 2019-06-19-21:33
*/
public class FileInputStreamTest {
public static void copyFile(String str,String dest){
//提供读入,复制的文件
File file1 = new File(str);
File file2 = new File(dest);
//提供相应的流
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
//实现文件的复制
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = fis.read(b))!=-1){
fos.write(b,0,len); //重点:是len,不是b.length
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fis != null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fos !=null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
6、使用缓冲流实现文件复制
流:BufferedInputStream/BufferedOutputStream
package JavaSE.IO;
import java.io.*;
/**
* @author LFuser
* @create 2019-06-19-22:05
*/
public class BufferedSteramTest {
public static void copyFile(String str , String dest){
//准备相应文件
File file1 = new File(str);
File file2 = new File(dest);
BufferedInputStream bis = null;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null;
try {
//准备相应流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//复制
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len ;
while((len = bis.read(b))!=-1){
bos.write(b,0,len);
bos.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(bis != null){
try {
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(bos != null){
try {
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
7、转换流
- InputStreamReader:将一个字节的输入流转换为字符的输入流
- OutputStreamWriter:将一个字符的输出流转换为字节的输出流
/*使用InputStreamReader和OutputStreamWriter*/
public void test() throws Exception {
//1.创建文件、流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("dbcp.txt"));
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("dbcp_gbk.txt"));
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8");
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"gbk");
//2.读写过程
char[] c = new char[20];
int len;
while((len = isr.read(c)) != -1){
osw.write(c,0,len);
}
//3.关闭资源
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
8、对象流(了解)
(1)对象流: ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
(2)作用:
ObjectOutputStream:内存中的对象—>存储中的文件、通过网络传输出去:序列化过程
ObjectInputStream:存储中的文件、通过网络接收过来 —>内存中的对象:反序列化过程
(3)对象的序列化机制:
对象序列化机制允许把内存中的Java对象转换成平台无关的二进制流,从而允许把这种二进制流持久地保存在磁盘上,或通过网络将这种二进制流传输到另一个网络节点。当其它程序获取了这种二进制流,就可以恢复成原来的Java对象
(4)实现序列化的对象所属的类需要满足:
- 需要实现接口:Serializable
- 当前类提供一个全局常量:serialVersionUID
- 除了当前Person类需要实现Serializable接口之外,还必须保证其内部所属性也必须是可序列化的。(默认情况下,基本数据类型可序列化)
- 不能序列化static和transient修饰的成员变量
9、其他流(了解)
- 标准的输入输出流:
System.in:标准的输入流,默认从键盘输入
System.out:标准的输出流,默认从控制台输出 - 打印流:PrintStream 和PrintWriter
- 数据流:DataInputStream 和 DataOutputStream





 本文围绕Java的IO流展开,介绍了其分类、体系结构、常用流等知识。详细说明了输入/输出流程,还给出使用节点流和缓冲流实现文件复制的方法。此外,讲解了转换流、对象流和其他流的相关内容,如对象序列化机制等。
本文围绕Java的IO流展开,介绍了其分类、体系结构、常用流等知识。详细说明了输入/输出流程,还给出使用节点流和缓冲流实现文件复制的方法。此外,讲解了转换流、对象流和其他流的相关内容,如对象序列化机制等。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








