适用于同一入参的缓存:
<!--web-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-plus-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.22</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.20</version>
</dependency>
<!--swagger2文档-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.yzgu.</groupId>
<artifactId>common</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
<version>2.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--springboot单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
编写 缓存测试类
/**
* springboot-cache yzgu
*/
@RequestMapping("/cache")
@Controller
public class HomeCacheController {
@Autowired
private TransportRecordService transportRecordService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
@ResponseBody
@Cacheable(value = "helloCache")
public String home(){
System.out.println("测试是否走缓存");
return "hello world!";
}
/**
* 这里根据入参可以缓存数据,只要是name 多次访问,就直接从缓存中获取,不会一直查询数据库
* @param name
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/list")
@ResponseBody
public Object test(String name){
List<TransportRecord> list = transportRecordService.getList(name);
System.out.println("测试list是否走缓存");
return list;
}
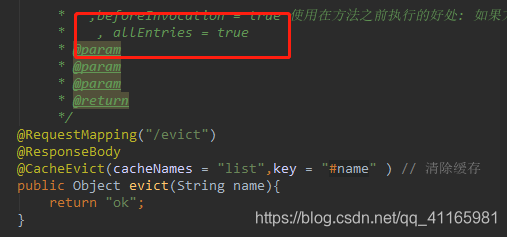
/**
* 这里 指定的list 是 上面方法 设置的缓存
* cacheNames list 上面缓存的大key
* key:指定要清除缓存中的某条数据 key ="123" name 参数 为123的缓存
* allEntries=true:删除缓存中的所有数据
*
* ,beforeInvocation = true 使用在方法之前执行的好处: 如果方法出现异常,缓存依旧会被删除
* , allEntries = true
* @param
* @param
* @param
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/evict")
@ResponseBody
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "list",key = "#name" ) // 清除缓存
public Object evict(String name){
return "ok";
}
/**
* 当 name 的长度小于4 才缓存
* @param name
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/condition")
@ResponseBody
@org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable(value = "conditionCache", condition = "#name.length() <= 4")
public Object test2(String name){
System.out.println("测试condition是否走缓存");
return "abc" + name;
}
上面的方法
1: 调用 http://localhost:9002/yzgu/cache/list?name=123
后端会缓存 name =123的那条记录
2: 再次查询,不会走service 层
调用结果如下
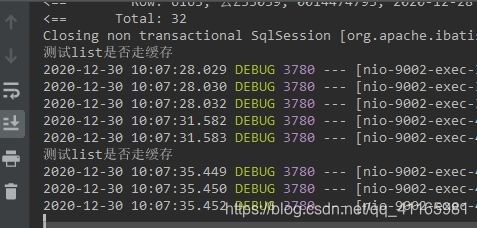
3、调用 name = 456 也会缓存
http://localhost:9002/yzgu/cache/list?name=456
4、 然后清除单条缓存 123的缓存
http://localhost:9002/yzgu/cache/evict?name=123
再次调用 http://localhost:9002/yzgu/cache/list?name=123
还是会走数据库查询
![]()
如果 想清楚所有缓存 可以指定





 本文档展示了如何在Spring Boot应用中使用缓存,通过`@Cacheable`和`@CacheEvict`注解实现数据缓存,并进行缓存测试。例子包括根据入参缓存、清除指定缓存以及条件性缓存。通过测试用例,演示了缓存的存取和清除流程。
本文档展示了如何在Spring Boot应用中使用缓存,通过`@Cacheable`和`@CacheEvict`注解实现数据缓存,并进行缓存测试。例子包括根据入参缓存、清除指定缓存以及条件性缓存。通过测试用例,演示了缓存的存取和清除流程。

















 548
548












