一、列表( List )
列表是 Python 中最基本的数据结构。列表中的每个元素都分配一个数字(即它的位置)称为索引,第一个索引是 0,第二个索引是 1,依此类推。
1、列表的增
- append( )
append( ) 方法用于在列表末尾添加新的对象。
list.append(self, x)
- insert( )
insert( ) 函数用于将指定对象插入列表的指定位置。
list.insert(self, i, x)
- extend( )
extend( ) 函数用于在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表)。
list.extend(self, t)
- 实例(Python 3.0+)
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
list1 = []
print(list1) # 打印 list1
list1.append('Springer') # 在末尾添加元素
list1.append('Karen')
print(list1)
list1.insert(1,'Simple') # 在指定位置添加元素或者列表
print(list1)
list1.extend('abcd') # 可迭代,分解成元素添加在末尾。
print(list1)

2、列表的删
- pop( )
pop( ) 函数用于移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值。
list.pop(self, i)
- remove( )
remove( ) 函数用于移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项。
list.remove(self, x)
- clear( )
clear( ) 函数用于清空列表,类似于 del a[:]。
list.clear(self)
- del
del 语句可以用来删除列表或其中的元素。
del list
- 实例(Python 3.0+)
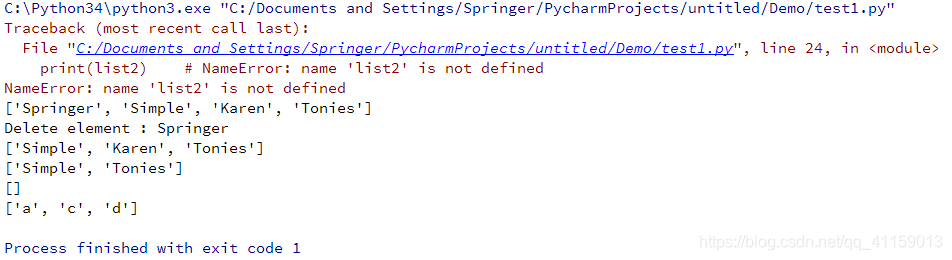
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
list1 = ['Springer', 'Simple', 'Karen', 'Tonies']
list2 = list(('a', 'b', 'c', 'd'))
print(list1)
del_ele = list1.pop(0) # 直接输入下标即可,删除后可返回删除元素
print('Delete element :', del_ele)
print(list1)
list1.remove('Karen') # 只能输入要删除的元素,无返回值
print(list1)
list1.clear() # 清空列表内数据
print(list1)
del list2[1:2] # 切片删除
print(list2)
del list2 # 删除列表
print(list2) # 因为 list2 已经不存在,所以报错 : NameError: name 'list2' is not defined
3、列表的改
- 重新赋值
- 分片赋值
- 实例(Python 3.0+)
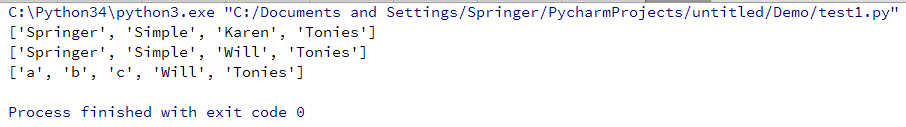
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
list1 = ['Springer', 'Simple', 'Karen', 'Tonies']
print(list1)
list1[2] = 'Will'
print(list1)
list1[0:2] = ['a', 'b', 'c']
print(list1)
3、列表的查
查询列表可通过下标和切片的方式。
- 实例(Python 3.0+)
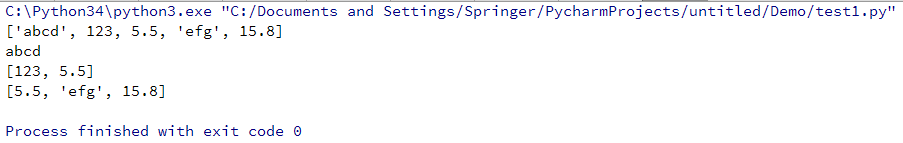
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
list1 = [ 'abcd', 123 , 5.5, 'efg', 15.8 ]
print (list1) # 输出完整列表
print (list1[0]) # 输出列表第一个元素
print (list1[1:3]) # 从第二个开始输出到第三个元素
print (list1[2:]) # 输出从第三个元素开始的所有元素
4、列表的其它方法
- index( )
index( ) 方法用于获取指定元素的下标。
list.index(self, x, i, j)
- count( )
count( ) 方法用于统计字符串里某个字符出现的次数。可选参数为在字符串搜索的开始与结束位置。
list.count(self,x)
- sort( )
sort( ) 函数用于对原列表进行排序,如果指定参数,则使用比较函数指定的比较函数。
list.sort(self, cmp, key, reverse)
- reverse( )
reverse( ) 函数用于反向列表中元素。该方法没有返回值,但是会对列表的元素进行反向排序。
list.reverse(self)
- copy( )
copy( ) 函数用于复制列表,类似于 a[:]。
list.copy(self)
- 实例(Python 3.0+)
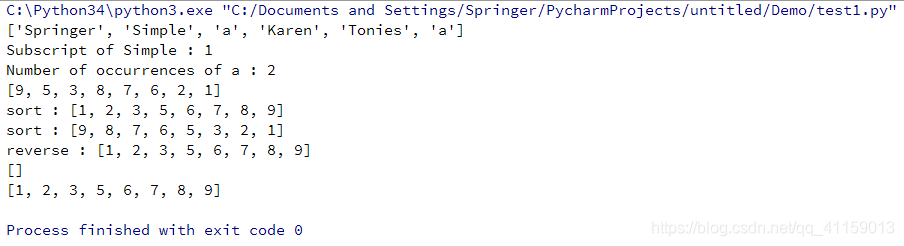
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
list1 = ['Springer', 'Simple', 'a', 'Karen', 'Tonies', 'a']
list2 = [9, 5, 3, 8, 7, 6, 2, 1]
list3 = []
print (list1) # 输出完整列表
a = list1.index('Simple')
print('Subscript of Simple :', a)
a = list1.count('a')
print('Number of occurrences of a :', a)
print(list2)
list2.sort() # 默认 reverse = False
print('sort :', list2)
list2.sort(reverse = True)
print('sort :', list2)
list2.reverse()
print('reverse :', list2)
print(list3)
list3 = list2.copy()
print(list3)
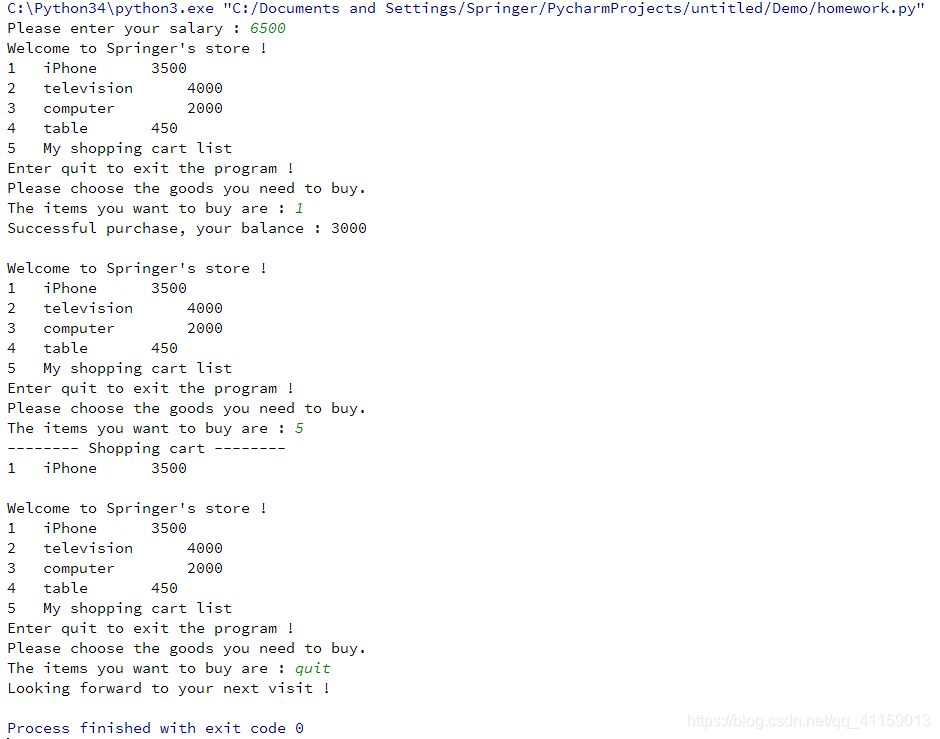
二、购物车样例(Python 3.0+)
#!-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# author : Springer
# 创建一个菜单列表
list_commodity = (['iPhone', 3500], ['television', 4000], ['computer', 2000], ['table', 450])
list_userbuy = []
# 开始函数
def judje_input():
_salary = input("Please enter your salary : ") # 初始化工资
if _salary.isdigit(): # 判断输入是否符合条件
_salary = int(_salary)
show_welcome(_salary) # 调用函数
else: # 输入不符合条件
print("Please input as required.")
judje_input() # 重新输入
# 消费过程
def show_welcome(_salary):
print("Welcome to Springer's store !")
for i in range(len(list_commodity)): # 输出消费列表
print(i + 1, end='\t')
print(list_commodity[i][0], end='\t\t') # 输出商品名称
print(list_commodity[i][1], end='\n') # 输出商品金额
print(len(list_commodity) + 1, "\tMy shopping cart list")
print("Enter quit to exit the program !")
print("Please choose the goods you need to buy.")
_user_input = input("The items you want to buy are : ") # 输入需要购买的商品
if _user_input.isdigit(): # 判断输入是否符合条件
if 0 < int(_user_input) < (len(list_commodity) + 1):
start_shopping(_user_input, _salary) # 调用函数
elif int(_user_input) == len(list_commodity) + 1: # 显示已购买的货物
show_shoppinglist()
show_welcome(_salary)
else: # 输入不符合条件
print("Input contains illegal characters, please re-enter ! ", end="\n\n")
show_welcome(_salary)
elif _user_input == 'quit': # 退出购买
print("Looking forward to your next visit !")
else: # 输入不符合条件
print("Input contains illegal characters, please re-enter ! ", end = "\n\n")
show_welcome(_salary)
# 显示购物车中商品
def show_shoppinglist():
print("-------- Shopping cart --------")
for i in range(len(list_userbuy)):
print(i + 1, end='\t')
print(list_userbuy[i][0], end='\t\t')
print(list_userbuy[i][1], end='\n')
print()
# 减少总金额并将商品加入购物车
def start_shopping(_user_input, _salary):
_salary_temp = _salary - list_commodity[int(_user_input) - 1][1]
if _salary_temp >= 0:
print("Successful purchase, your balance :", _salary_temp, end = "\n\n")
list_userbuy.append(list_commodity[int(_user_input) - 1])
_salary = _salary_temp
show_welcome(_salary)
else:
print("Your balance is insufficient !It's %s less."%(0 - _salary_temp), end = "\n\n")
show_welcome(_salary)
# 调用开始函数
judje_input()
本文内容部分取自百度内容,如有雷同部分请见谅。




 这篇博客介绍了Python中的列表数据结构,包括增、删、改、查等基本操作,如append、insert、extend、pop、remove、clear等,并通过购物车样例展示了如何在Python 3.0+中应用这些概念。
这篇博客介绍了Python中的列表数据结构,包括增、删、改、查等基本操作,如append、insert、extend、pop、remove、clear等,并通过购物车样例展示了如何在Python 3.0+中应用这些概念。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








