目录
2.Merge Two Sorted Lists (easy)
2.Kth Largest Element in an Array(mid)
Maximum Gap(hard)(找到相邻两数之间的最大间距)
排序算法总结
(1)排序算法总结
1.(带动图,必看!):https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/yushiyi6453/article/details/76407640
2.面试角度的分析,排序算法必须好好掌握:https://www.cnblogs.com/yuzhangcmu/p/4198942.html
(2)c++ sort函数使用:
1.形式:
sort(begin,end,compare)compare为比较函数,注意要定义成static,否则会报错
2.参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/hfultrastrong/p/6428109.html
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/zhangpiu/article/details/50564064
3.sort的时间复杂度是O(nlogn)
插入排序
Insertion Sort List (easy)
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.

A graphical example of insertion sort. The partial sorted list (black) initially contains only the first element in the list.
With each iteration one element (red) is removed from the input data and inserted in-place into the sorted list
思路:下面就是我写的基础的插入排序在链表的实践,使用了一个辅助节点,方便后续操作,注意最后返回的是dummy_head->next,而不是head
时间复杂度是排序算法的O(n^2),空间复杂度是O(1)
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* insertionSortList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode *dummy_head = new ListNode(-1);
dummy_head->next = head;
ListNode *cur = head;
ListNode *sort_h,*temp;
while(cur->next){
sort_h = dummy_head;
while(sort_h != cur){
if(sort_h->next->val >= cur->next->val){
temp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
temp->next = sort_h->next;
sort_h->next = temp;
break;
}
sort_h = sort_h->next;
}
if(sort_h == cur) cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy_head->next;
}
};
归并排序
总结
参考博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3602369.html
关于链表的排序题使用归并排序较多!
(1)将两个的有序数列合并成一个有序数列,我们称之为"归并"。
(2)归并排序的最主要想法和实现,归并排序的做法是:
将一个数组一直对半分,问题的规模就减小了,再重复进行这个过程,直到元素的个数为一个时,一个元素就相当于是排好顺序的。归并排序是“分治”算法的一个经典运用。
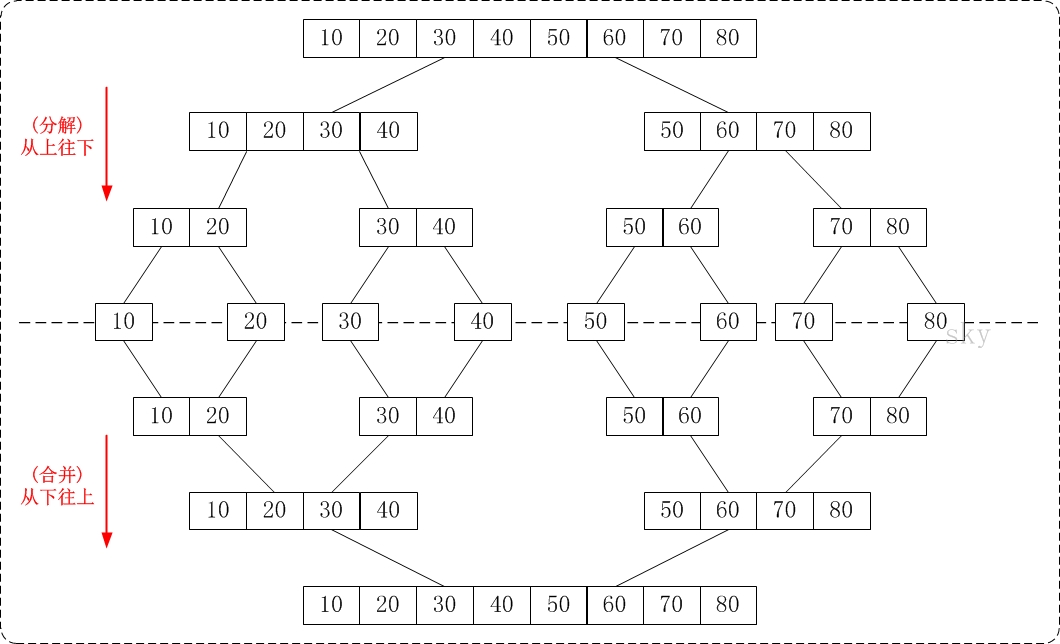
(3)归并排序(Merge Sort)就是利用归并思想对数列进行排序。根据具体的实现,归并排序包括"从上往下"和"从下往上"2种方式。
1. 从下往上的归并排序:将待排序的数列分成若干个长度为1的子数列,然后将这些数列两两合并;得到若干个长度为2的有序数列,再将这些数列两两合并;得到若干个长度为4的有序数列,再将它们两两合并;直接合并成一个数列为止。这样就得到了我们想要的排序结果。(参考下面的图片)
2. 从上往下的归并排序:它与"从下往上"在排序上是反方向的。它基本包括3步:
① 分解 -- 将当前区间一分为二,即求分裂点 mid = (low + high)/2;
② 求解 -- 递归地对两个子区间a[low...mid] 和 a[mid+1...high]进行归并排序。递归的终结条件是子区间长度为1。
③ 合并 -- 将已排序的两个子区间a[low...mid]和 a[mid+1...high]归并为一个有序的区间a[low...high]。
下面的图片很清晰的反映了"从下往上"和"从上往下"的归并排序的区别。
(4)提高排序速度的两个重要的途径:一个是减少比较次数,一个是减少交换次数。
对于归并排序而言,我们来从之前的例子应该可以看到,两个数组的合并过程是线性时间的,也就是说我们每一次比较都可以确定出一个元素的位置。这是一个重要的性质。
我们来看一个可以用一个例子来体会一下假如有这样一个数组{ 3,7,2,5,1,0,4,6 },
冒泡和选择排序的比较次数是25次。
直接插入排序用了15次。
而归并排序的次数是相对稳定的,由我们上面提到的比较次数的计算方法,我们的例子要合并4对长度为1的,2对长度为2的,和1对长度为4的。
归并排序的最多的比较次数为4 * 1 + 2 * 3 + 7 = 17次。
再次说明一下,这个例子依然只是为了好理解,不能作为典型例子来看。
因为元素的随机性,直接插入排序也可能是相当悲剧的。但我们应该从中看到的是归并排序在比较次数上的优势。
至于在种优势是怎么来的,我个人不成熟的总结一下,就是尽量的让上一次操作的结果为下一次操作服务。
我们每一次合并出来的数组,是不是就是为下一次合并做准备的。因为两个要合并的数组是有序的,我们才可能高效地进行合并。
归并排序的时间复杂度和稳定性
归并排序时间复杂度
更加详细的证明:https://www.cnblogs.com/sheeva/p/6600666.html
归并排序的时间复杂度是O(N*lgN)。
假设被排序的数列中有N个数。遍历一趟的时间复杂度是O(N),需要遍历多少次呢?
归并排序的形式就是一棵二叉树,它需要遍历的次数就是二叉树的深度,而根据完全二叉树的可以得出它的时间复杂度是O(N*lgN)。
归并排序稳定性
归并排序是稳定的算法,它满足稳定算法的定义。
算法稳定性 -- 假设在数列中存在a[i]=a[j],若在排序之前,a[i]在a[j]前面;并且排序之后,a[i]仍然在a[j]前面。则这个排序算法是稳定的!
1.Merge Sorted Array
Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
Note:
- The number of elements initialized in nums1 and nums2 are m and n respectively.
- You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is greater or equal to m + n) to hold additional elements from nums2.
Example:
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]思路:谁能想到我竟然被卡住了,这个主要nums1后面是有0,已经将长度固定了,所以不能用insert去做,而应该从nums1和nums2数组的末尾开始一个一个比较,把较大的数,按顺序从后往前加入混合之后的数组末尾。
class Solution {
public:
void merge(vector<int>& nums1, int m, vector<int>& nums2, int n) {
int i = m-1,j = n-1,k = m+n-1;
while(i >= 0 && j >= 0){
if(nums1[i] > nums2[j]) nums1[k--] = nums1[i--];
else nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}
while(j >= 0) nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}
};
2.Merge Two Sorted Lists (easy)
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Example:
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4思路:常规链表归并题
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *h1 = l1,*h2 = l2;
ListNode* dummy_head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* temp,*cur = dummy_head;
while(h1 && h2){
if(h1->val < h2->val){
cur->next = h1;
h1 = h1->next;
cur = cur->next;
}else{
cur->next = h2;
h2 = h2->next;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
if(h2) h1 = h2;
cur->next = h1;
return dummy_head->next;
}
};
3.Merge k Sorted Lists(hard)
Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
Example:
Input:
[
1->4->5,
1->3->4,
2->6
]
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6思路:
分治与堆排序,考察的其实是N个目标怎样最快速的两两合并
解法一:直接不断两两合并
不管合并几个,基本还是要两两合并,两个先合并,合并好了再跟第三个,然后第四个直到第k个。这样的思路是对的,但是效率不高(时间复杂度为O(nk*nk))。我们只能换一种思路,这里就需要用到分治法 Divide and Conquer Approach。简单来说就是不停的对半划分。
简单来说就是不停的对半划分,比如k个链表先划分为合并两个k/2个链表的任务,再不停的往下划分,直到划分成只有一个或两个链表的任务,开始合并。
举个例子来说比如合并6个链表:
(1)那么按照分治法,0,1,2,3,4,5,找到中点3(6/2),然后在3前面的去加上3((6+1)/2),我们首先分别合并0和3,1和4,2和5。
(2)这样下一次只需合并3个链表,0,1,2,找到中点2(3/2),1前面的加上2((3+1)/2),我们再合并1和3,最后和2合并就可以了。
代码中的new_end是通过 (n+1)/2 计算的,这里为啥要加1呢,这是为了当n为奇数的时候,k能始终从后半段开始,比如当n=5时,那么此时k=3,则0和3合并,1和4合并,最中间的2空出来。当n是偶数的时候,加1也不会有影响,比如当n=4时,此时k=2,那么0和2合并,1和3合并,完美解决问题
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
// 边界判断
if (lists.empty()) return NULL;
int end = lists.size();
while(end > 1){
// 这里为(end+1)/2
int new_end = (end+1)/2;
// 这里为end
for(int i = 0;i < end/2;i++){
lists[i] = mergeTwoLists(lists[i],lists[i+new_end]);
}
end = new_end;
}
return lists[0];
}
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode *l1,ListNode *l2){
if(!l1) return l2;
if(!l2) return l1;
if(l1->val < l2->val){
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};复杂度分析:
但是这道题由于存的都是指针,就具有了更大的操作灵活性,可以不用递归来实现分治。就是先两两合并后在两两合并。。。一直下去直到最后成了一个。(相当于分治算法的那棵二叉树从底向上走了)。
第一次两两合并是进行了k/2次,每次处理2n个值。
第二次两两合并是进行了k/4次,每次处理4n个值。
。。。
最后一次两两合并是进行了k/(2^logk)次,每次处理2^logK*N个值。
所以时间复杂度:
O((2N) * (K / 2) + (4N) * (K / 4) + (8N) * (K / 8) + .............. + (2^logK*N) * (K / (2 ^logK)) )=O( logK*KN)
(每一项都是NK,然后一共有logK项)
空间复杂度是O(1)。
解法2:递归
做法是将原链表分成两段,然后对每段调用递归函数,suppose返回的left和right已经合并好了,然后再对left和right进行合并
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
return mergeNLists(lists,0,lists.size()-1);
}
ListNode* mergeNLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists,int start,int end) {
if(start > end) return NULL;
if(start == end) return lists[start];
int mid = start + (end-start)/2;
ListNode *left = mergeNLists(lists,start,mid);
ListNode *right = mergeNLists(lists,mid+1,end);
return mergeTwoLists(left,right);
}
// 递归写法
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode *l1,ListNode *l2){
if(!l1) return l2;
if(!l2) return l1;
if(l1->val < l2->val){
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next,l2);
return l1;
}else{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};复杂度分析:
时间复杂度为O(nklogk),空间复杂度为O(logk),为栈的大小
解法3:堆排序(与上面两个不同)
基本思路:
把k个链表开头的值排个序,每次取最小的一个值放到答案链表中,这次取完之后更新这个值为它后面的一个值。接着这么取一直到全部取完。
那么每次更新之后怎么对当前这k个值重新排序以便知道当前最小的是谁呢?用优先队列(或者堆)来维护这k个值就好啦!
优先队列使用:https://www.cnblogs.com/icode-girl/p/4978837.html
class Solution {
public:
struct cmp{
bool operator() (const ListNode *h1,const ListNode *h2){
return h1->val > h2->val;
}
};
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,cmp> q;
ListNode *dummy_head = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode *cur = dummy_head,*tmp;
for(auto &h : lists){
// 这句判断很有必要,不能把空的加入队列。比如这组数据:[[],[]]
if(h) q.push(h);
}
while(!q.empty()){
tmp = q.top();q.pop();
if(tmp->next) q.push(tmp->next);
cur->next = tmp;
cur = cur->next;
}
return dummy_head->next;
}
};复杂度分析:
由于每个值都要取一次,一共取nk次。每次更新优先队列要logk的复杂度。所以总时间复杂度为O(nklogk);
空间复杂度为优先队列所占空间,为O(k)。
关于堆:
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenweichu/articles/5710567.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenweichu/articles/5710635.html
使用堆实现本题:https://www.cnblogs.com/skysand/p/4300711.html(这个详细看一下)
堆的实现待二刷的时候动手实现一下!!!
4.Sort List
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5思路:常见排序方法有很多,插入排序,选择排序,堆排序,快速排序,冒泡排序,归并排序,桶排序等等。它们的时间复杂度不尽相同,而这里题目限定了时间必须为O(nlgn),符合要求只有快速排序,归并排序,堆排序,而根据单链表的特点,最适于用归并排序。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode *slow = head,*fast = head,*pre;
while(fast && fast->next){
pre = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
pre->next = NULL;
// O(logN)
return merge(sortList(head),sortList(slow));
}
// O(N)
ListNode* merge(ListNode* h1,ListNode* h2){
if(!h1) return h2;
if(!h2) return h1;
if(h1->val < h2->val){
h1->next = merge(h1->next,h2);
return h1;
}else{
h2->next = merge(h1,h2->next);
return h2;
}
}
};
快速排序
1.Sort Colors(mid)
Given an array with n objects colored red, white or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white and blue.
Here, we will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue respectively.
Note: You are not suppose to use the library's sort function for this problem.
Example:
Input: [2,0,2,1,1,0]
Output: [0,0,1,1,2,2]解法1:使用计数排序
时间复杂度O(2N),两次遍历
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> color(3,0);
int idx = 0;
// 这里使用vector进行计数,写法更加简明
for(int i = 0;i < nums.size();i++) color[nums[i]]++;
for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < color[i];j++){
// idx和j分开,直接用j第一个颜色结束后,后面两个不会再循环
nums[idx++] = i;
}
}
}
};解法2:
时间复杂度O(N),一次遍历
用双指针来做,分别从原数组的首尾往中心移动。
- 定义red指针指向开头位置,blue指针指向末尾位置
- 从头开始遍历原数组,如果遇到0,则交换该值和red指针指向的值,并将red指针后移一位。若遇到2,则交换该值和blue指针指向的值,并将blue指针前移一位。若遇到1,则继续遍历。
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(vector<int>& nums) {
int red = 0,blue = nums.size()-1;
for(int i = 0;i <= blue;i++){
if(nums[i] == 0) swap(nums[i],nums[red++]);
// 注意这里的i--,与后面的blue交换后,不能保证从后面换上来的数的情况,所以要重新判断
else if(nums[i] == 2) swap(nums[i--],nums[blue--]);
}
}
};
2.Kth Largest Element in an Array(mid)
Find the kth largest element in an unsorted array. Note that it is the kth largest element in the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Example 1:
Input: [3,2,1,5,6,4] and k = 2
Output: 5
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] and k = 4
Output: 4
解法1:冒泡排序(时间复杂度为O(K*n))
我的想法是使用冒泡排序找到第k个大的返回即可
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int end = nums.size()-1;
while(k){
for(int i = 0;i < end;i++){
if(nums[i] > nums[i+1]) swap(nums[i],nums[i+1]);
}
k--;
end--;
}
return nums[end+1];
}
};
解法2:快速排序(这种解法更快)
因为事实上,第k点前面的数不需要有序,第k后面的数也不需要有序,所以冒泡排序其实多排了
快速排序:
每次都要先找一个中枢点Pivot,然后遍历其他所有的数字,像这道题从大往小排的话,就把大于中枢点的数字放到左半边,把小于中枢点的放在右半边,这样中枢点是整个数组中第几大的数字就确定了,虽然左右两部分各自不一定是完全有序的,但是并不影响本题要求的结果,因为左半部分的所有值都大于右半部分的任意值,所以我们求出中枢点的位置,
(1)如果正好是k-1,那么直接返回该位置上的数字;
(2)如果大于k-1,说明要求的数字在左半部分,更新右边界,再求新的中枢点位置;
(3)反之则更新右半部分,求中枢点的位置;
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int start = 0,end = nums.size()-1;
while(true){
int idx = fastSort(nums,start,end);
if(idx == k-1) return nums[idx];
if(idx < k-1) start = idx+1;
else end = idx-1;
}
}
// 从大到小排序
int fastSort(vector<int>& nums,int start,int end){
int pivot = start,l = start+1,r = end;
while(l <= r){
// 这里注意为if,不能用while一直做循环,否则可能产生l和r超出边界的情况
if(nums[l] < nums[pivot] && nums[r] > nums[pivot]) swap(nums[l++],nums[r--]);
if(nums[l] >= nums[pivot]) l++;
if(nums[r] <= nums[pivot]) r--;
}
swap(nums[pivot],nums[r]);
return r;
}
};
桶排序
First Missing Positive(hard)
Given an unsorted integer array, find the smallest missing positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,0]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: [3,4,-1,1]
Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: [7,8,9,11,12]
Output: 1Note:
Your algorithm should run in O(n) time and uses constant extra space.
思路:必须在O(N)时间内完成,所以不能使用普通排序。这里因为是顺序正数,需要利用到数组的下标信息,我们的思路是把1放在数组第一个位置nums[0],2放在第二个位置nums[1],即需要把nums[i]放在nums[nums[i] - 1]上,那么我们遍历整个数组,如果nums[i] != i + 1, 而nums[i]为整数且不大于n,另外nums[i]不等于nums[nums[i] - 1]的话,我们将两者位置调换,如果不满足上述条件直接跳过,最后我们再遍历一遍数组,如果对应位置上的数不正确则返回正确的数
这里有个注意点,已经出现两次这个问题了,快速排序里也是,当交换位置以后,必须 i--,重新判断位置 i 的情况
class Solution {
public:
int firstMissingPositive(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
// 这里要判断nums[i] != nums[nums[i]-1],否则两数相同时,或者该数字本来就在原位时,会陷入死循环!!!
if(nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= n && nums[i] != nums[nums[i]-1]){
swap(nums[i],nums[nums[i]-1]);
// 这里要i--,交换以后需要重新判断i的位置
i--;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(nums[i] != i+1) return i+1;
}
// 这里返回的是n+1注意,使用i去返回会有问题,主要针对[]和里面本来就是123这种顺序数组的情况
return n+1;
}
};
计数排序
1.计数排序是一种非常快捷的稳定性强的排序方法,时间复杂度O(n+k),其中n为要排序的数的个数,k为要排序的数的组大值。计数排序对一定量的整数排序时候的速度非常快,一般快于其他排序算法。但计数排序局限性比较大,只限于对整数进行排序。计数排序是消耗空间发杂度来获取快捷的排序方法,其空间发展度为O(K)同理K为要排序的最大值。
2.基本思想:
一组数在排序之前先统计这组数中其他数小于这个数的个数,则可以确定这个数的位置。例如要排序的数为 7 4 2 1 5 3 1 5;则比7小的有7个数,所有7应该在排序好的数列的第八位,同理3在第四位,对于重复的数字,1在1位和2位(暂且认为第一个1比第二个1小),5和1一样位于6位和7位。
3.实现:
首先需要三个数组,第一个数组记录A要排序的数列大小为n,第二个数组B要记录比某个数小的其他数字的个数所以第二个数组的大小应当为K(数列中最大数的大小),第三个数组C为记录排序好了的数列的数组,大小应当为n。
接着需要确定数组最大值并确定B数组的大小。并对每个数由小到大的记录数列中每个数的出现次数。因为是有小到大通过出现次数可以通过前面的所有数的出现次数来确定比这个数小的数的个数,从而确定其位置。
对于重复的数,每排好一个数则对其位置数进行减减操作,以此对完成其余相同的数字进行排位。
H-Index(mid)
Given an array of citations (each citation is a non-negative integer) of a researcher, write a function to compute the researcher's h-index.
According to the definition of h-index on Wikipedia: "A scientist has index h if h of his/her N papers have at least h citations each, and the other N − h papers have no more than h citations each."
Example:
Input:citations = [3,0,6,1,5]Output: 3 Explanation:[3,0,6,1,5] means the researcher has 5 papers in total and each of them had received 3, 0, 6, 1, 5 citations respectively. Since the researcher has 3 papers with at least 3 citations each and the remaining two with no more than 3 citations each, her h-index is 3.Note: If there are several possible values for h, the maximum one is taken as the h-index.
题意:h-index计算是有h篇文章其引用指数等于或者超过h
思路一:全排序
从大到小排序,然后从左往右,找到第一个nums[i] 小于 i 的点,就是所求结果。
比如:6,5,2,1,0到2的时候就返回,6,5,3,1,0到3的时候返回,[100] 返回 1
class Solution {
public:
int hIndex(vector<int>& citations) {
// 降序排序
sort(citations.begin(),citations.end(),my_cmp);
// 从大到小,这样有重复时取大
int i = 0;
for(;i < citations.size();i++){
// 此时的i就是h-index,表示前面有i个超过i的数字
if(citations[i] <= i) break;
}
return i;
}
static bool my_cmp(int a,int b){
return a>b;
}
};
思路二:用空间换时间
一个hint:实际上h-index值最大就是paper数目,不可能大于paper数目
使用一个与paper数目 N 大小相同的数组record,用于记录 0-N 次引用次数的各有几篇文章(引用次数大于N的按照N次计算)遍历数组,统计过后,遍历一次统计数组record,即可算出h值的最大值。时间复杂度为O(n)。
举例:100,3,5,7
record[0,0,0,1,3](对应下标:0,1,2,3,4),实际比 i 大的引用数目为[0,0,0,4,3],故h-index为数组下标3
class Solution {
public:
int hIndex(vector<int>& citations) {
int n = citations.size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
vector<int> record(n+1);
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
if(citations[i] > n) record[n]++;
else record[citations[i]]++;
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = n;i >=0;i--){
sum += record[i];
if(sum >= i) return i;
}
return 0;
}
};
桶排序
Maximum Gap(hard)(找到相邻两数之间的最大间距)
Given an unsorted array, find the maximum difference between the successive elements in its sorted form.
Return 0 if the array contains less than 2 elements.
Example 1:
Input: [3,6,9,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: The sorted form of the array is [1,3,6,9], either
(3,6) or (6,9) has the maximum difference 3.Example 2:
Input: [10]
Output: 0
Explanation: The array contains less than 2 elements, therefore return 0.Note:
- You may assume all elements in the array are non-negative integers and fit in the 32-bit signed integer range.
- Try to solve it in linear time/space.
思路:
遇到这类问题肯定先想到的是要给数组排序,但是题目要求是要线性的时间和空间,那么只能用桶排序或者基排序。
这里参考网上思路用桶排序Bucket Sort来做
(1)首先找出数组的最大值和最小值,然后要确定每个桶的容量,即为(最大值 - 最小值) / 个数 + 1
(2)再确定桶的个数,即为(最大值 - 最小值) / 桶的容量 + 1
(3)然后需要在每个桶中找出局部最大值和最小值,而最大间距的两个数不会在同一个桶中,而是一个桶的最小值和另一个桶的最大值之间的间距。
(4)这里注意有些桶会为空,要注意在最后遍历最大最小值时判断
举例:

class Solution {
public:
int maximumGap(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size() < 2) return 0;
int max_num = nums[0],min_num = nums[0];
for(int i = 0;i < nums.size();i++){
max_num = max(max_num,nums[i]);
min_num = min(min_num,nums[i]);
}
// 桶的容量
int contain = (max_num-min_num)/nums.size()+1;
// 桶的个数
int container_num = (max_num-min_num)/contain+1;
// 保存最大最小值
vector<int> min_container(container_num,INT_MAX);
vector<int> max_container(container_num,INT_MIN);
for(int i = 0;i < nums.size();i++){
int container_idx = (nums[i]-min_num)/contain;
if(min_container[container_idx] > nums[i]) min_container[container_idx] = nums[i];
if(max_container[container_idx] < nums[i]) max_container[container_idx] = nums[i];
}
// 计算gap
int max_gap = 0;
int pre = 0;
for(int i = 1;i < container_num;i++){
// 有些桶为空,得注意跳过!!!!
if(min_container[i] == INT_MAX || max_container[i] == INT_MIN) continue;
if(min_container[i]-max_container[pre] > max_gap) max_gap = min_container[i]-max_container[pre];
pre = i;
}
return max_gap;
}
};
其他排序
Largest Number(mid)
Given a list of non negative integers, arrange them such that they form the largest number.
Example 1:
Input: [10,2]
Output: "210"Example 2:
Input: [3,30,34,5,9]
Output: "9534330"
Note: The result may be very large, so you need to return a string instead of an integer.思路:这题我没什么想法,看了网上的思路,对于两个数字a和b来说,如果将其都转为字符串,如果ab > ba,则a排在前面,比如9和34,由于934>349,所以9排在前面,再比如说30和3,由于303<330,所以3排在30的前面。按照这种规则对原数组进行排序后,将每个数字转化为字符串再连接起来就是最终结果。
一种比较独特的排序方式,值得一记
class Solution {
public:
string largestNumber(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<string> str_nums;
for(int i = 0;i < nums.size();i++) str_nums.push_back(to_string(nums[i]));
sort(str_nums.begin(),str_nums.end(),my_cmp);
string res;
for(int i = 0;i < str_nums.size();i++){
res += str_nums[i];
}
// [0,0]这种情况返回0
return res[0] == '0'? "0":res;
}
static bool my_cmp(const string &a,const string &b){
return a+b > b+a;
}
};





 本文深入讲解各种排序算法,包括插入排序、归并排序、快速排序、桶排序等,提供算法总结、时间复杂度分析及代码实现,适用于算法学习与面试准备。
本文深入讲解各种排序算法,包括插入排序、归并排序、快速排序、桶排序等,提供算法总结、时间复杂度分析及代码实现,适用于算法学习与面试准备。
















 1442
1442

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








