| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 14544 | Accepted: 7125 |
Description
Each minute, one of the two apple trees drops an apple. Bessie, having much practice, can catch an apple if she is standing under a tree from which one falls. While Bessie can walk between the two trees quickly (in much less than a minute), she can stand under only one tree at any time. Moreover, cows do not get a lot of exercise, so she is not willing to walk back and forth between the trees endlessly (and thus misses some apples).
Apples fall (one each minute) for T (1 <= T <= 1,000) minutes. Bessie is willing to walk back and forth at most W (1 <= W <= 30) times. Given which tree will drop an apple each minute, determine the maximum number of apples which Bessie can catch. Bessie starts at tree 1.
Input
* Lines 2..T+1: 1 or 2: the tree that will drop an apple each minute.
Output
Sample Input
7 2 2 1 1 2 2 1 1
Sample Output
6
Hint
Seven apples fall - one from tree 2, then two in a row from tree 1, then two in a row from tree 2, then two in a row from tree 1. Bessie is willing to walk from one tree to the other twice.
OUTPUT DETAILS:
Bessie can catch six apples by staying under tree 1 until the first two have dropped, then moving to tree 2 for the next two, then returning back to tree 1 for the final two.
Source
很好的一道DP题。感谢大佬提供的思路 大佬思路
思路:
在这道题中奶牛是可以移动w步的,而且它面前只有两棵树,我刚开始是用递归做的。(一直超时,从不停歇)。
其实,在递归超时之后。大家就应该想到用递推来做。(DP不容易想,需要多加思考)
那么,在这道题中,我们可以这样想一下。奶牛移动之后面对的只有两棵树。那么,我们的移动步数和这两棵树之间是否有一些关系呢。说到这,我们就很容易想到(令j为步数) 则j%2+1 就可以很好的理解为奶牛现在所面对的树。
那么我们就可以判断奶牛此时面对的树与题目给定的掉落苹果的树之间的关系--->flag = (j%2+1 == a[i]).
dp[i][j]数组为奶牛移动步数之后能得到的苹果树 其中i为秒数 j为步数
所以,由上边我们就可以得知:
当flag为true时我们的dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j-1],dp[i-1][j])+1;
反之 dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j-1],dp[i-1][j]);
代码如下
附一张样例dp数组截图 可以好好参照理解一下
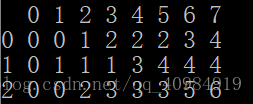
#include<map>
#include<stack>
#include<math.h>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#define pi acos(-1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAX_N=100000+50;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int dp[1010][1010];
int a[MAX_N];
int main()
{
int t,w;
while(cin>>t>>w)
{
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++)
{
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0];
if(a[i] == 1)
dp[i][0]++;
for(int j = 1;j <= w; j++)
{
if(j % 2 + 1 == a[i])
{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1]) + 1;
}
else
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j], dp[i-1][j-1]);
}
}
int maxv=0;
for(int i = 0; i <= w ; i++)
{
maxv = max(maxv,dp[t][i]);
}
cout<<maxv<<endl;
}
return 0;
}







 本文介绍了一道经典的动态规划问题——Apple Catching,通过分析奶牛Bessie如何在两棵树之间移动以捕获最多数量的苹果。文章详细解释了使用DP方法解决问题的过程,并附带了解决该问题的C++代码。
本文介绍了一道经典的动态规划问题——Apple Catching,通过分析奶牛Bessie如何在两棵树之间移动以捕获最多数量的苹果。文章详细解释了使用DP方法解决问题的过程,并附带了解决该问题的C++代码。

















 694
694

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










