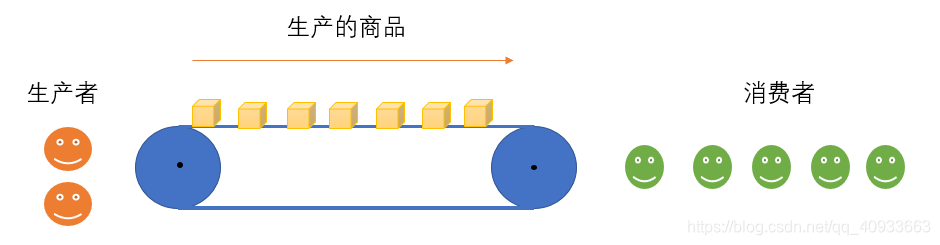
生产者消费者模型:
- 生产和消费的速度不匹配的问题;
- 软件开发的组件解耦。
开发领域:
- 内存数据库 Redis 多个应用程序之间共享数据(A程序写,B程序读)
- 消息服务器 ActiveMQ
理解三种方法:wait()方法,notify()方法,notifyAll()方法。
wait()方法
—— 使得线程停止运行
- 作用:使得当前执行代码的线程进行等待,wait()方法是Object类的方法。用来将当前线程植入“预执行队列”中,并且在wait()所在的代码出停止执行,知道街道通知或被中断为止;
- 只能在同步方法中或者同步块中调用。如果调用wait()时,没有持有适当的锁,会抛出异常;
- wait()方法执行后,当前线程释放,线程与其他线程竞争重新获取锁。
notify()方法
—— 使停止的线程继续运行
- 在同步方法中或者同步块中调用,该方法时用来通知那些可能等待该对象的对象锁的其他线程,对其发出通知notify,并使得它们重新获取对象锁。如果有多个线程等待,则线程规划器随机挑选出一个呈wait()状态的线程。
- 在nitofy()之后,当签线程不会立即释放该对象锁,要等到执行notify()放啊发的现车给将程序执行完,也就是退出同步代码块之后才会释放对象锁。
notifyAll()方法
—— 一次唤醒所有的等待线程
实例
ConfigPC存放值:
package pc;
public class ConfigPC {
public static final int MAX_CAPACITY = 10;
public static final int MAX_PRODUCER = 5;
public static final int MAX_CUSTOMER = 4;
}
生产者:设置一个商品的队列,如果队列还有商品没被消费,等待消费者消费,否则继续生产商品,生产完商品后通知消费者线程可以消费了。
package pc;
import java.util.Queue;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_CAPACITY;
/**
* 生产者
*/
public class Producter implements Runnable {
private final Queue<Goods> queue;
public Producter(Queue<Goods> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (queue) {
if (queue.size() < MAX_CAPACITY) {
Goods goods = new Goods(String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()), "商品");
queue.add(goods);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":生产商品" + goods);
} else {
try {
queue.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
消费者:同样设置一个商品队列,如果队列上的商品为空,则等待生产者生产商品;否则,每次从队列消耗一个商品,消费完告知生产者线程可以继续生产了。
package pc;
import java.util.Queue;
/**
* 消费者
*/
public class Customer implements Runnable {
private final Queue<Goods> queue;
public Customer(Queue<Goods> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (queue) {
if(queue.isEmpty()) {
queue.notifyAll();
} else {
Goods goods = queue.poll();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":消费商品" + goods);
}
}
}
}
}
测试:(多线程)
package pc;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_CAPACITY;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_CUSTOMER;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_PRODUCER;
public class TestPC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 缓冲池
final Queue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(MAX_CAPACITY);
// 生产者线程
final Runnable producter = new Producter(queue);
for(int i=0; i<MAX_PRODUCER; i++) {
Thread pThread = new Thread(producter, "Thread-Producter-" + i);
pThread.start();
}
final Runnable customer = new Customer(queue);
for (int i=0; i<MAX_CUSTOMER; i++) {
Thread cThread = new Thread(customer,"Thread-Customer -" + i);
cThread.start();
}
}
}
测试结果:

测试2:使用线程池
package pc;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_CAPACITY;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_CUSTOMER;
import static pc.ConfigPC.MAX_PRODUCER;
public class TestPC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 缓冲池
final Queue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue(MAX_CAPACITY);
// 生产者任务
final Runnable producter = new Producter(queue);
// 消费者任务
final Runnable customer = new Customer(queue);
// 任务的队列
final ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable> blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(9,
10,1,TimeUnit.MINUTES,blockingQueue);
for(int i=0; i<MAX_PRODUCER; i++) {
executor.execute(producter);
}
for(int i=0; i<MAX_CUSTOMER; i++) {
executor.execute(customer);
}
}
}
测试结果:





 本文深入探讨了生产者消费者模型的实现方式,包括如何通过线程间的wait()、notify()和notifyAll()方法来解决生产与消费速度不匹配的问题。通过具体代码示例,展示了在多线程环境下如何有效管理商品队列,确保生产者和消费者之间的协调工作。
本文深入探讨了生产者消费者模型的实现方式,包括如何通过线程间的wait()、notify()和notifyAll()方法来解决生产与消费速度不匹配的问题。通过具体代码示例,展示了在多线程环境下如何有效管理商品队列,确保生产者和消费者之间的协调工作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








