You are given a set of n axis-aligned rectangles in a 2D plane. For this problem, two rectangles are considered to intersect if their boundaries contain any common points (in particular, two nesting rectangles don’t count as intersecting). Determine if some pair of rectangles intersect.
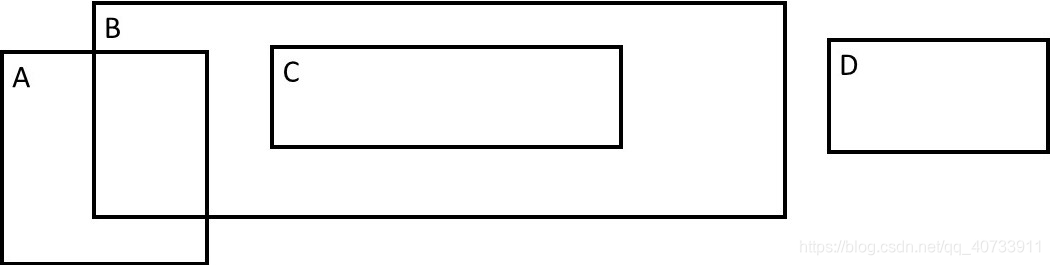
In this example, only rectangles A and B intersect.
Input
Each test case will begin with a line with a single integer n (1≤n≤105), which is the number of rectangles.
Each of the next n lines will contain four space-separated integers:
x1 y1 x2 y2
(−109≤x1,y1,x2,y2≤109,x1<x2,y1<y2), which describe a rectangle, where (x1,y1) is the lower left corner and (x2,y2) is the upper right corner. All x values will be distinct. All y values will be distinct.
Output
Output a single integer, which is 1 if some pair of rectangles intersect, 0 if no pair of rectangles intersect.
Sample Input
3 0 0 2 2 1 1 3 4 5 7 6 8
Sample Output
1
Sample Input
4 0 0 20 20 1 1 3 4 2 10 9 12 11 3 19 18
Sample Output
0
题目大意:给n个矩形,问是否有相交的矩形,不存在重复的边,每个矩形用左下角和右上角两个点表示
思路:扫描线+树状数组或者线段树
之前做过一个求矩形面积的,用的是线段树维护,发现很麻烦,那个题用树状数组维护应该也是可以的
树状数组的话直接用一维的单点更新和区间查询就行。
每个矩形看作两条线,按y排好序,从下往上扫描
遇见下边(flag==1的线)就判断一下这个区间是否有数字,也就是区间被加过,没有就更改两个端点,当作区间更新,否则break。
遇见上边(flag=0的线) 就两个端点都减1,减完后判断区间里面是否还有数字,有就break,说明中间夹杂着其他的线。
最后代码处理的话还要离散化一下数据即可,还有就是数组要开大,因为存的是线,是n的2倍
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=1e5+100;
typedef long long ll;
int c[maxn<<2]; //树状数组
int len ;
struct line
{
int l,r,h,flag;
}a[maxn<<2];
int lowbit(int x){
return x&(-x);
}
void update(int i,int k){ //在i位置加上k
while(i <= maxn*2){
c[i] += k;
i += lowbit(i);
}
}
int getsum(int i){ //求A[1 - i]的和
int res = 0;
while(i > 0){
res += c[i];
i -= lowbit(i);
}
return res;
}
bool cmp(line l1,line l2)
{
return l1.h<l2.h;
}
vector<int> v;
int getid(int x)
{
return lower_bound(v.begin(),v.end(),x)-v.begin()+1;
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
int cnt=0;
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
v.push_back(x1);
v.push_back(x2);
a[cnt++]={x1,x2,y1,1};
a[cnt++]={x1,x2,y2,-1};
}
sort(a,a+cnt,cmp);
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
v.erase( unique(v.begin(),v.end()) , v.end());//去重
int l,r;
int ff=0;
for(int i=0;i<cnt;i++)
{
l=getid(a[i].l);
r=getid(a[i].r);
int sum;
if(a[i].flag==1)
{
sum=getsum(r)-getsum(l-1);
if(sum!=0)
{
ff=1;break;
}
update(l,1);
update(r,1);
}
else
{
update(l,-1);
update(r,-1);
sum=getsum(r)-getsum(l-1);
if(sum!=0)
{
ff=1;break;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ff);
return 0;
}
/*
2
0 0 2 2
1 1 3 4
3
0 0 9 9
1 1 8 8
2 2 7 7
2
0 0 5 5
2 2 9 9
2
0 0 9 9
5 1 20 2
2
3 2 8 3
4 1 5 4
2
1 1 4 3
2 2 3 4
2
1 2 4 4
*/





 本文介绍了一种使用扫描线和树状数组检测二维平面上多个轴对齐矩形是否相交的算法。通过将每个矩形转换为两条线,并按Y坐标排序,算法能够高效地确定是否存在至少一对相交的矩形。
本文介绍了一种使用扫描线和树状数组检测二维平面上多个轴对齐矩形是否相交的算法。通过将每个矩形转换为两条线,并按Y坐标排序,算法能够高效地确定是否存在至少一对相交的矩形。
















 305
305

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








