目录
单链表的定义:
LinkedList.h文件
#ifndef LINKEDLIST_H_
#define LINKEDLIST_H_
#include <iostream>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
typedef int ElemType;
typedef int status;
typedef struct LNode
{
ElemType data;//数据域
LNode *next;//指针域
} LNode, *LinkList;//定义结点和链表
status CreatLkList(LinkList &L, int n); //前插法创建n个元素的链表
status InsertLkList(LinkList &L, int i, ElemType e);//在第i个位置插入元素e
status DeleteLkList(LinkList &L, int i); //删除第i个元素
status DeleteLkList(LinkList &L, ElemType mmin, ElemType mmax);//删除区间(mmin,mmax)的元素
status DestoryLkList(LinkList &L); //销毁链表
int FindOrInsert(LinkList &L, ElemType x); //查找元素返回位序没有将其插入合适位置
LNode* reverseList(LinkList &L, int flag); //递归反转链表
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, LinkList L); //重载<<打印链表
#endif // !LINKEDLIST单链表的实现:
LinkedList.cpp文件
#include "LinkedList.h"
using namespace std;
status CreatLkList(LinkList & L, int n)//前插法创建,顺序与输入顺序相反
{
L = new LNode;//创建头结点
L->next = NULL;
cout << "Input the element value reversing:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
LNode* p = new LNode;
cin >> p->data;
p->next = L->next;
L->next = p;
}
cout << "The Linklist as follow:\n";
cout << "L->";
LNode * t = L->next;
while (t)
{
cout << t->data << "->";
t = t->next;
}
cout << "NULL";
return OK;
}
status InsertLkList(LinkList & L, int i, ElemType e)
{
LNode *p = L;
int j = 0;
//i的合法范围为1~L.length+1
while (p&&j < i - 1)//定位到第i-1个结点
{
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if (!p || j > i - 1)//i>L.length或i<1
return ERROR;
LNode* t = new LNode;//创建新结点
t->data = e;
t->next = p->next;
p->next = t;//插入到第i-1个后面
return OK;
}
status DeleteLkList(LinkList & L, int i)
{
LNode* p = L;
int j = 0;
//i的合法范围为1~L.length
while (p->next&&j < i - 1)
{
p = p->next;
j++;
}
if (!p->next || j > i - 1)//i>L.length+1或i<1
{
cout << "\nThe value of i is out of bounds!\n";
return ERROR;
}
LNode* t = p->next;//临时保存被删结点
p->next = t->next;
delete t;
return OK;
}
status DeleteLkList(LinkList & L, ElemType mmin, ElemType mmax)
{
LNode *pre = L;//初始头节点,修改前驱
LNode *now = pre->next;//当前工作指针
LNode *t;//临时缓存
while (now && now->data < mmax)//因升序,大于mmax提前跳出
{
if (now->data > mmin&&now->data < mmax)
{
t = now;
now = now->next;
pre->next = now;
delete t;
}
else {
pre = pre->next;
now = now->next;
}
}
return OK;
}
status DestoryLkList(LinkList & L)
{
LNode* t;
while (L)
{
t = L;//保存头节点
L = L->next;
delete t;
}
cout << "\nThe LinkList is Destoryed!\n";
return OK;
}
int FindOrInsert(LinkList & L, ElemType x)
{
int i = 0;
LNode *pre = L;
LNode *now = pre->next;
while (now && now->data <= x)
{
if (now->data == x)//找到返回位序
return i;
now = now->next;
pre = pre->next;
i++;
}
LNode *t = new LNode;
t->data = x;
t->next = now;
pre->next = t;
cout << "未找到 " << x << " 将其插入成功!\n";
return 0;//失败返回位序0
}
LNode * reverseList(LinkList & L, int flag)//flag当前是否指向头结点标签
{
if (!L->next || (!L->next->next && flag==1))//空表或一个元素
return NULL;
if (!L->next->next)//递归出口,L指向倒数第2个结点
{
LNode *tair = L->next;//保存尾结点
tair->next = L;
L->next = NULL;
return tair;//返回尾节点
}
else
{
LNode* tair=reverseList(L->next, 0);
if (flag)//L指向头结点
{
L->next->next = NULL;//原首元结点指向空
L->next = tair;//头结点指向原尾结点
}
else//指向L指向首元结点到倒数第3个结点
{
L->next->next = L;
L->next = NULL;
}
return tair;
}
}
ostream & operator<<(ostream & os, LinkList L)
{
LNode * p = L->next;
if (!p) {
os << "The empty LinkedList" << endl;
return os;
}
cout << "L->";
while (p)
{
os << p->data << "->";
p = p->next;
}
os << "NULL";
return os;
}
链表使用:
useList.cpp使用
#include "LinkedList.h"
using namespace std;
void Init(LinkList &L);
int main()
{
LinkList L;
Init(L);//创建链表
reverseList(L,1);//反转链表,传入标签1
cout << "反转后:" << L << endl;
}
void Init(LinkList &L)
{
int n;
cout << "输入元素个数:";
cin >> n;
CreatLkList(L, n);
cout << endl;
}
测试结果:
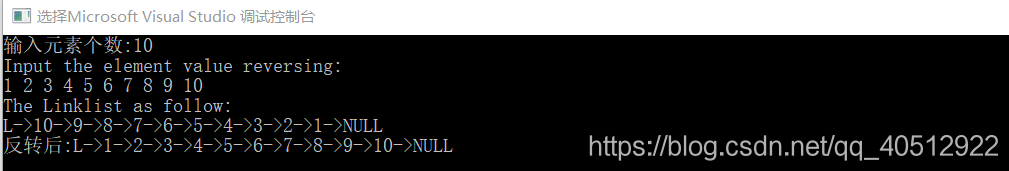




 本文详细介绍了单链表的C++实现方法,包括链表的创建、插入、删除、反转等操作,并提供了完整的代码示例。通过递归方式实现了链表的反转,展示了链表作为一种基本数据结构的灵活应用。
本文详细介绍了单链表的C++实现方法,包括链表的创建、插入、删除、反转等操作,并提供了完整的代码示例。通过递归方式实现了链表的反转,展示了链表作为一种基本数据结构的灵活应用。
















 943
943

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








