1.上篇博客程序优化:主要是将学习率设置为逐渐减小
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data",one_hot=True)
#每个批次的大小
batch_size = 100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
keep_prob=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
lr = tf.Variable(0.001, dtype=tf.float32)
#创建一个简单的神经网络
W1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([784,500],stddev=0.1))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([500])+0.1)
L1 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(x,W1)+b1)
L1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(L1,keep_prob)
W2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([500,300],stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([300])+0.1)
L2 = tf.nn.tanh(tf.matmul(L1_drop,W2)+b2)
L2_drop = tf.nn.dropout(L2,keep_prob)
W3 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([300,10],stddev=0.1))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])+0.1)
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(L2_drop,W3)+b3)
#交叉熵代价函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
#训练
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(51):
sess.run(tf.assign(lr, 0.001 * (0.95 ** epoch)))
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys,keep_prob:1.0})
learning_rate = sess.run(lr)
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels,keep_prob:1.0})
print ("Iter " + str(epoch) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(acc) + ", Learning Rate= " + str(learning_rate))2.tensorboard绘制网络结构
程序:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# In[3]:
#载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data",one_hot=True)
#每个批次的大小
batch_size = 100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
#命名空间
with tf.name_scope("input"):
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope("layer"):
with tf.name_scope("weights"):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='W')
with tf.name_scope("biases"):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='b')
with tf.name_scope("Wx_plus_b"):
Wx_plus_b=tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope("softmax"):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W)+b)
#二次代价函数
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
#使用梯度下降法
with tf.name_scope("train"):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
with tf.name_scope("correct_prediction"):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
#求准确率
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)
for epoch in range(1):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter " + str(epoch) + ",Testing Accuracy " + str(acc))
在当前目录下创建了一个logs文件,里面生成了:
打开:
复制上面的网址:
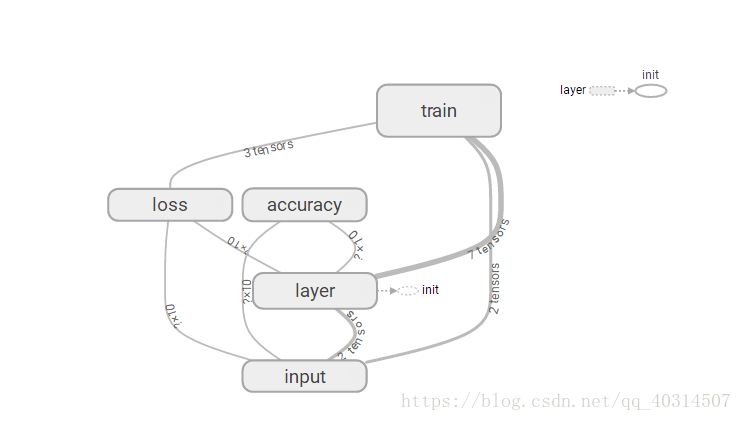
点开graphs能看到图:
3.查看网络运行时的数据
程序:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
# In[3]:
#载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data",one_hot=True)
#每个批次的大小
batch_size = 100
#计算一共有多少个批次
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
#参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean=tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean',mean)
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev=tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var-mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev',stddev)
tf.summary.scalar('max',tf.reduce_max(var))
tf.summary.scalar('min',tf.reduce_min(var))
tf.summary.histogram('histogram',var)
#命名空间
with tf.name_scope("input"):
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
with tf.name_scope("layer"):
with tf.name_scope("weights"):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope("biases"):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='b')
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope("Wx_plus_b"):
Wx_plus_b=tf.matmul(x,W)+b
with tf.name_scope("softmax"):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(Wx_plus_b)
#二次代价函数
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
#使用梯度下降法
with tf.name_scope("train"):
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.2).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
with tf.name_scope("correct_prediction"):
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
#求准确率
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy)
#合并所有的summary
merge=tf.summary.merge_all()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
writer=tf.summary.FileWriter('logs/',sess.graph)
for epoch in range(51):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
summary,_=sess.run([merge,train_step],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
writer.add_summary(summary,epoch)
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print("Iter " + str(epoch) + ",Testing Accuracy " + str(acc))
打开生成的log文件:
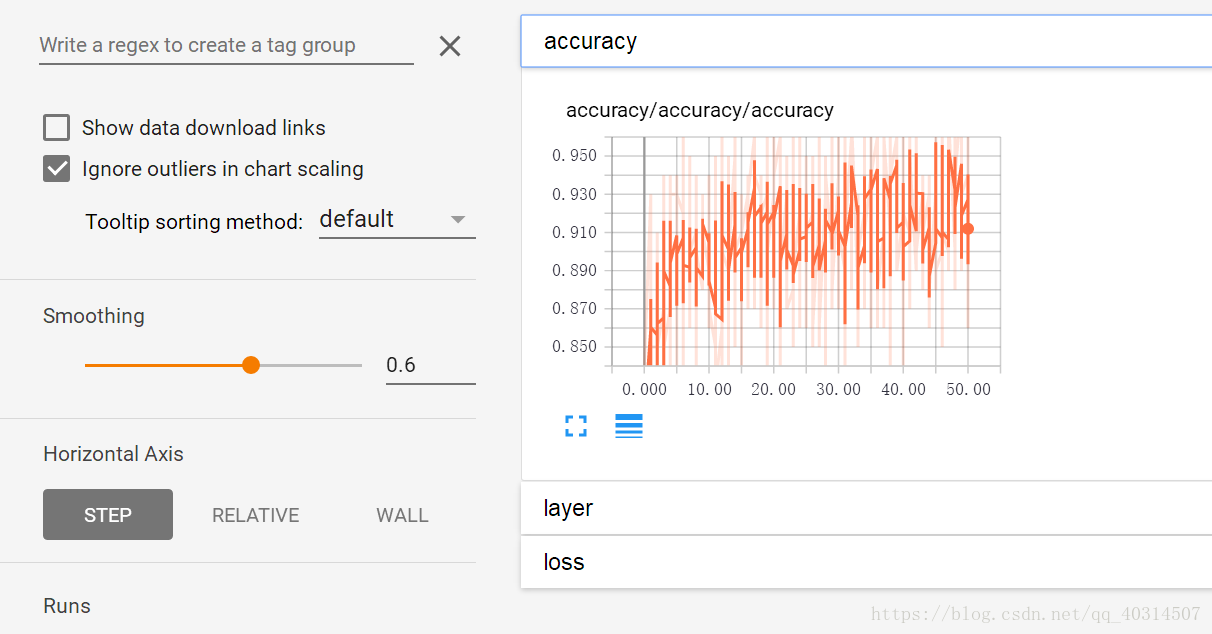
4.tensorflow可视化
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
from tensorflow.contrib.tensorboard.plugins import projector
# In[2]:
#载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot=True)
#运行次数
max_steps = 1001
#图片数量
image_num = 3000
#文件路径
DIR = "D:/software/mycodes/python35/py3/"
#定义会话
sess = tf.Session()
#载入图片
embedding = tf.Variable(tf.stack(mnist.test.images[:image_num]), trainable=False, name='embedding')
#参数概要
def variable_summaries(var):
with tf.name_scope('summaries'):
mean = tf.reduce_mean(var)
tf.summary.scalar('mean', mean)#平均值
with tf.name_scope('stddev'):
stddev = tf.sqrt(tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(var - mean)))
tf.summary.scalar('stddev', stddev)#标准差
tf.summary.scalar('max', tf.reduce_max(var))#最大值
tf.summary.scalar('min', tf.reduce_min(var))#最小值
tf.summary.histogram('histogram', var)#直方图
#命名空间
with tf.name_scope('input'):
#这里的none表示第一个维度可以是任意的长度
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input')
#正确的标签
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input')
#显示图片
with tf.name_scope('input_reshape'):
image_shaped_input = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
tf.summary.image('input', image_shaped_input, 10)
with tf.name_scope('layer'):
#创建一个简单神经网络
with tf.name_scope('weights'):
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]),name='W')
variable_summaries(W)
with tf.name_scope('biases'):
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]),name='b')
variable_summaries(b)
with tf.name_scope('wx_plus_b'):
wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(x,W) + b
with tf.name_scope('softmax'):
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(wx_plus_b)
with tf.name_scope('loss'):
#交叉熵代价函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
tf.summary.scalar('loss',loss)
with tf.name_scope('train'):
#使用梯度下降法
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'):
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1))#argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))#把correct_prediction变为float32类型
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy)
#产生metadata文件
if tf.gfile.Exists(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv'):
tf.gfile.DeleteRecursively(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv')
with open(DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv', 'w') as f:
labels = sess.run(tf.argmax(mnist.test.labels[:],1))
for i in range(image_num):
f.write(str(labels[i]) + '\n')
#合并所有的summary
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
projector_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(DIR + 'projector/projector',sess.graph)
saver = tf.train.Saver()
config = projector.ProjectorConfig()
embed = config.embeddings.add()
embed.tensor_name = embedding.name
embed.metadata_path = DIR + 'projector/projector/metadata.tsv'
embed.sprite.image_path = DIR + 'projector/data/mnist_10k_sprite.png'
embed.sprite.single_image_dim.extend([28,28])
projector.visualize_embeddings(projector_writer,config)
for i in range(max_steps):
#每个批次100个样本
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
run_options = tf.RunOptions(trace_level=tf.RunOptions.FULL_TRACE)
run_metadata = tf.RunMetadata()
summary,_ = sess.run([merged,train_step],feed_dict={x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys},options=run_options,run_metadata=run_metadata)
projector_writer.add_run_metadata(run_metadata, 'step%03d' % i)
projector_writer.add_summary(summary, i)
if i%100 == 0:
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print ("Iter " + str(i) + ", Testing Accuracy= " + str(acc))
saver.save(sess, DIR + 'projector/projector/a_model.ckpt', global_step=max_steps)
projector_writer.close()
sess.close()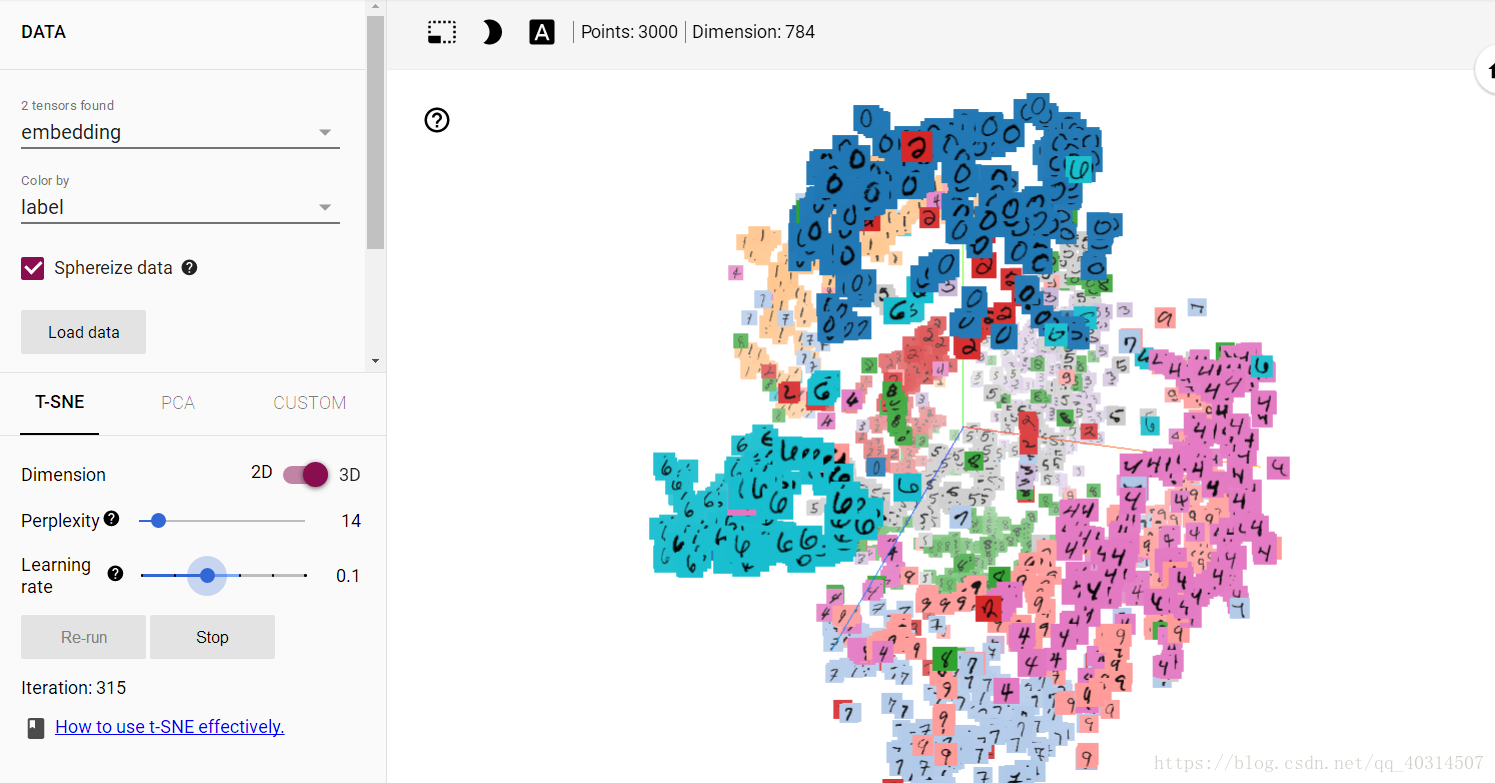







 本文通过三个实战案例介绍如何利用TensorFlow进行神经网络优化、绘制网络结构并监控运行数据,还展示了如何实现TensorFlow可视化。
本文通过三个实战案例介绍如何利用TensorFlow进行神经网络优化、绘制网络结构并监控运行数据,还展示了如何实现TensorFlow可视化。
















 9427
9427

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








