1.问题如下,why?
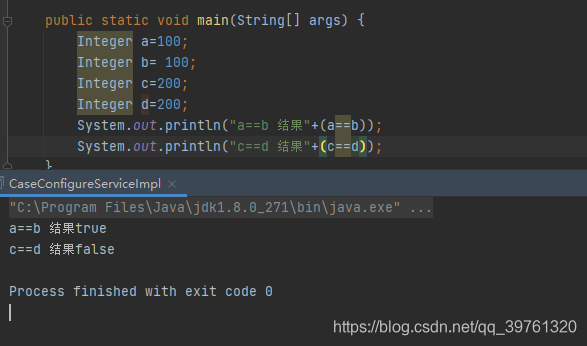
首先,java的==比较的确实是对象的地址。但是我们指导Integer是int的装箱,但是Integer为了有些数字会被频繁被使用,所以使用了缓存(私有静态内部类IntegerCache),这样便不会一直创建对象了。如下图:
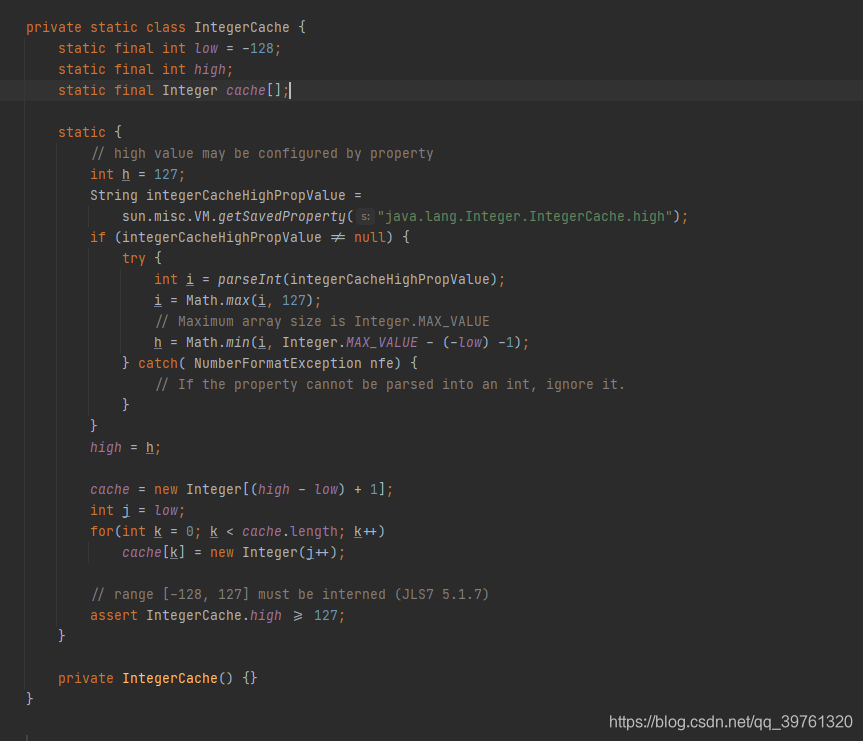
其中Integer cache[]即为缓存的数组,

但是如果
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer testa = new Integer(100);
Integer testb = new Integer(100);
Integer testc = new Integer(200);
Integer testd = new Integer(200);
System.out.println(testa.hashCode());
System.out.println(testb.hashCode());
System.out.println(testa==testb);
System.out.println("========");
System.out.println(testc.hashCode());
System.out.println(testd.hashCode());
System.out.println(testc==testd);
}
输出:
100
100
false
========
200
200
false
这样相当于调用了Integer的构造方法,便没有调用IntegerCache的static块来缓存。
同理,通过方法也是一样的
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(aIn().hashCode());
System.out.println(bIn().hashCode());
System.out.println(aIn()==bIn());
System.out.println(aIn().hashCode()==bIn().hashCode());
}
public static Integer aIn(){
return 100;
}
public static Integer bIn(){
return 100;
}
输出:
100
100
true
true
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(aIn().hashCode());
System.out.println(bIn().hashCode());
System.out.println(aIn()==bIn());
System.out.println(aIn().hashCode()==bIn().hashCode());
}
public static Integer aIn(){
return 200;
}
public static Integer bIn(){
return 200;
}
输出:
100
100
false
true
那为什么上面的Integer的hashcode总是相同?
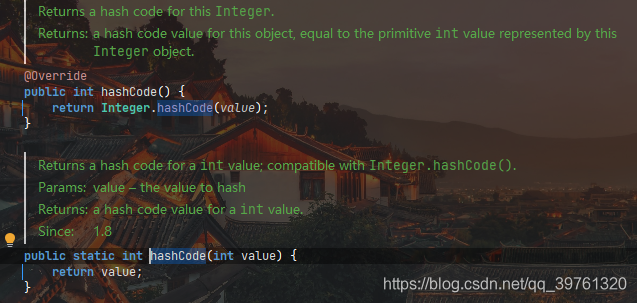
因为Integer的hashCode是直接返回传入的int值。
那对于其他对象的hashCode呢?
两个对象 == 不相等,hashCode有可能相等
因为当输入数据量太大,哈希值却是固定32长度的,这意味着哈希值是一个有限集合,无法建立一对一关系,所以hashcode相等是有可能会发生的。
所以hashCode()是不可靠的!
那它不可靠为什么还要用它?因为它计算起来快啊!
这涉及到两个对象之间的比较
1.equals()相等的两个对象他们的hashCode()肯定相等,也就是用equals()对比是绝对可靠的。
2.hashCode()相等的两个对象他们的equal()不一定相等,也就是hashCode()不是绝对可靠的。
再来看为什么用hashCode()
如果现在有大量的对象需要比较,每个都用equals() 效率是很低的,但hashCode()效率很高
所以有这种设计:先用hashCode()判断,如果hashCode()不同,则对象不等,如果hashCode()相同,再比较equals() ,大大提高了效率
那么接着说下为什么重写euqal()时要重写hashCode()?
1.Object的equal()方法是通过比较hashCode()后再通过==来比较是否相等。
2.当两个对象 equals 比较为 true,那么 hashcode 值应当相等,反之亦然,因为当两个对象hashcode 值相等,但是 equals 比较为 false,那么在 HashMap 中会产生链表,影响查询性能。





 本文探讨了Java中Integer缓存机制及其对HashCode的影响,解释了为何通过new关键字创建的Integer对象即使值相同,其地址也不相同。此外,还讨论了HashCode与对象相等性的关系,以及如何在实现equals方法时正确地处理HashCode。
本文探讨了Java中Integer缓存机制及其对HashCode的影响,解释了为何通过new关键字创建的Integer对象即使值相同,其地址也不相同。此外,还讨论了HashCode与对象相等性的关系,以及如何在实现equals方法时正确地处理HashCode。
















 611
611

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








