文章目录
参考:设计模式之禅,https://www.runoob.com/
1.最简单的 例子
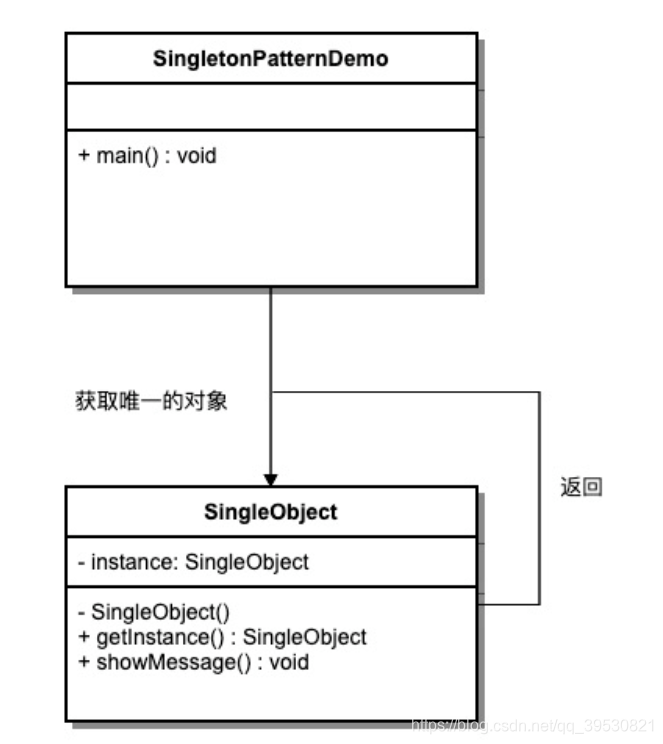
public class SingleObject {
private static SingleObject instance = new SingleObject();
private SingleObject() {
}
public static SingleObject getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public void showMessage() {
System.out.println(instance);
}
}
public class SingletonPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
SingleObject instance = SingleObject.getInstance();
instance.showMessage();
}
}
}
输出结果是一样的,表明是同个对象。
com.freedom.pattern.singleton.SingleObject@47089e5f
com.freedom.pattern.singleton.SingleObject@47089e5f
com.freedom.pattern.singleton.SingleObject@47089e5f
2. 单例模式特点
- 只有一个实例;
- 构造函数必须私有,即其他对象不能通过new创建;
- 自身必须提供获得实例的方法。
3. 延伸阅读
- https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/singleton
- https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/singleton-pattern.html
- https://design-patterns.readthedocs.io/zh_CN/latest/creational_patterns/singleton.html
4. 几种单例写法
4.1 饿汉式1
/**
* 饿汉式
* <p>
* 类加载的时候就实例化,保证线程安全, 简单实用。 缺点:如果不用也实例化,占内存。
* </p>
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton01 {
private static Singleton01 INSTANCE = new Singleton01();
private Singleton01() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
public static Singleton01 getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton01 instance = Singleton01.getInstance();
instance.doSomething();
Singleton01 instance2 = Singleton01.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance == instance2);
}
}
4.2 饿汉式2
/**
* 饿汉式,跟Singleton01一样
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton02 {
private static Singleton02 INSTANCE;
static {
INSTANCE = new Singleton02();
}
private Singleton02() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
public static Singleton02 getInstance() {
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Singleton02 instance = Singleton02.getInstance();
instance.doSomething();
Singleton02 instance2 = Singleton02.getInstance();
System.out.println(instance == instance2);
}
}
4.3 懒汉1
/**
* 懒汉式,实现了按需加载,但是线程不安全
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton03 {
private static Singleton03 INSTANCE;
private Singleton03() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
public static Singleton03 getInstance() {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
// 模拟创建对象比较慢
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
INSTANCE = new Singleton03();
}
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Singleton03.getInstance().hashCode())).start();
}
}
}
4.4 懒汉2
/**
* 懒汉式,实现了按需加载,线程是安全了,但是获得实例对象的操作都是
* 串行化,影响性能
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton04 {
private static Singleton04 INSTANCE;
private Singleton04() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
/**
* synchronize修饰静态方法,它的锁就是当前的类对象,相当于synchronized(Singleton04.class)
*/
public static synchronized Singleton04 getInstance() {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
// 模拟创建对象比较慢
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
INSTANCE = new Singleton04();
}
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Singleton04.getInstance().hashCode())).start();
}
}
}
4.5 懒汉3
/**
* 懒汉式,实现了按需加载,获得实例对象的操作不都是串行化,
* 提升性能,但是线程不安全,编译优化有可能让还未初始化的INSTANCE返回,
* 其他线程因此拿到实例调用报空指针异常
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton05 {
private static Singleton05 INSTANCE;
private Singleton05() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
public static Singleton05 getInstance() {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
synchronized (Singleton05.class) {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
// 模拟创建对象比较慢
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
INSTANCE = new Singleton05();
}
}
}
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Singleton05.getInstance().hashCode())).start();
}
}
}
4.6 懒汉4
/**
* 懒汉式,实现了按需加载,获得实例对象的操作不都是串行化,
* 提升性能,volatile保证变量可见性。比较理想的写法。
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton06 {
private static volatile Singleton06 INSTANCE;
private Singleton06() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
public static Singleton06 getInstance() {
// 双重检查
if (INSTANCE == null) {
synchronized (Singleton06.class) {
if (INSTANCE == null) {
// 模拟创建对象比较慢
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
INSTANCE = new Singleton06();
}
}
}
return INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Singleton06.getInstance().hashCode())).start();
}
}
}
4.7 内部静态类
/**
* 内部静态类方式,JVM保证单例。加载外部类时不加载器静态内部类
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public class Singleton07 {
private Singleton07() {
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
private static class InnerHolder{
private static final Singleton07 INSTANCE = new Singleton07();
}
public static Singleton07 getInstance() {
return InnerHolder.INSTANCE;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Singleton07.getInstance().hashCode())).start();
}
}
}
4.8 枚举类实现
/**
* 枚举实现方式:线程安全,不被反序列化
*
* @author tobebetter9527
* @create 2021/07/24 11:08
*/
public enum Singleton08 {
INSTANCE;
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("Do something");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
new Thread(() -> System.out.println(Singleton08.INSTANCE.hashCode())).start();
}
}
}





 本文深入探讨了单例模式的设计原则,包括其唯一实例的特点、构造函数的私有化及实例获取方法。通过多个实例代码,详细讲解了饿汉式、懒汉式、内部静态类及枚举类等不同实现方式,帮助读者全面理解单例模式。
本文深入探讨了单例模式的设计原则,包括其唯一实例的特点、构造函数的私有化及实例获取方法。通过多个实例代码,详细讲解了饿汉式、懒汉式、内部静态类及枚举类等不同实现方式,帮助读者全面理解单例模式。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








