绪论
学习文档,笔记整理。
多线程这里我还有本书没怎么看,这些日子抽时间看一下,把相关内容也整理上来。
正文
进程: 程序(任务)的执行过程,持有资源(共享内存、文件)和线程动态性,载体。
线程: 系统中最小的执行单元,共享进程资源,同一进程有多个线程。
交互方式: 互斥,同步。
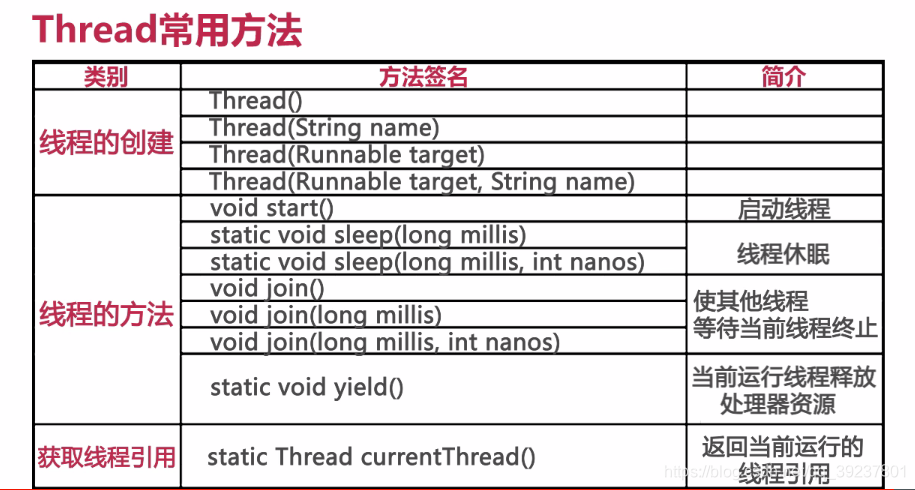
实现方式: 继承Thread类或实现Runnable接口。
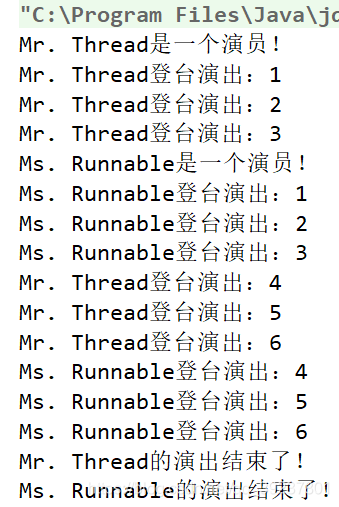
举个例子:
public class Actor extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println(getName() + "是一个演员!");
int count = 0;
boolean keepRunning = true;
while (keepRunning) {
System.out.println(getName() + "登台演出:" + (++count));
if (count == 6) {
keepRunning = false;
}
if (count % 3 == 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(getName() + "的演出结束了!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread actor = new Actor();
actor.setName("Mr. Thread");
actor.start();
Thread actressThread = new Thread(new Actress(), "Ms. Runnable");
actressThread.start();
}
}
class Actress implements Runnable {
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "是一个演员!");
int count = 0;
boolean keepRunning = true;
while (keepRunning) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "登台演出:" + (++count));
if (count == 6) {
keepRunning = false;
}
if (count % 3 == 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "的演出结束了!");
}
}
结果:
线程的正确停止: stop()方法不正确,会造成突然强行停止线程。一般是把对象中的布尔属性更改,使线程停止。
争用条件: 当多个线程同时共享访问同一数据(内存区域)时,每个线程都尝试操作该数据,从而导致数据被破坏(会造成损失)。为了避免造成损失,引入同步和互斥,互斥关键字(synchronized)。
(若有什么错误,请留言指正,3Q)





 本文深入探讨了多线程的基础概念,包括进程与线程的区别,以及如何通过继承Thread类或实现Runnable接口来创建线程。通过一个演员登台演出的例子,展示了线程的运行与停止机制,同时讨论了争用条件下的数据破坏问题及同步互斥的解决方案。
本文深入探讨了多线程的基础概念,包括进程与线程的区别,以及如何通过继承Thread类或实现Runnable接口来创建线程。通过一个演员登台演出的例子,展示了线程的运行与停止机制,同时讨论了争用条件下的数据破坏问题及同步互斥的解决方案。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








