1.Atomic原子操作类
- 题目
public class Atomic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
System.out.println(atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
System.out.println(atomicInteger.get());
}
}
- 输出
1
2
- 掌握知识
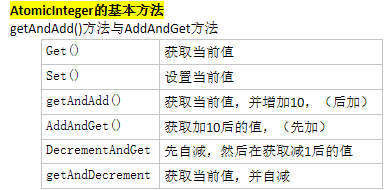
1.对于Java中的运算操作,例如自增或自减,若没有进行额外的同步操作,在多线程环境下就是线程不安全的。同步:多线程并发访问共享数据时,保证共享数据再同一时刻只被一个或一些线程使用。
2.那什么叫做非阻塞同步呢?在并发环境下,某个线程对共享变量先进行操作,如果没有其他线程争用共享数据那操作就成功;如果存在数据的争用冲突,那就才去补偿措施,比如不断的重试机制,直到成功为止,因为这种乐观的并发策略不需要把线程挂起,也就把这种同步操作称为非阻塞同步(操作和冲突检测具备原子性)
3.incrementAndGet()方法在一个无限循环体内,不断尝试将一个比当前值大1的新值赋给自己,如果失败则说明在执行"获取-设置"操作的时已经被其它线程修改过了,于是便再次进入循环下一次操作,直到成功为止.
4.参考链接:原子操作类AtomicInteger详解
2.子类不能重写父类的静态方法
- 题目
public class Scratch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fruit apple = new Apple();
apple.name();
apple.realName();
}
static class Fruit {
public static void name() {
System.out.println("Fruit");
}
public void realName() {
System.out.println("Fruit");
}
}
static class Apple extends Fruit {
public static void name() {
System.out.println("Apple");
}
public void realName() {
System.out.println("Apple");
}
}
}
- 输出
Fruit
Apple
- 掌握知识
1.子类不能重写父类的静态方法
2. 注意编译器也会进行告警
3. 构造方法和getset
- 题目
public class Robin {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Key, String> aa = new HashMap<>();
Key c=new Key(30,10);
aa.put(c, "Robin");
System.out.println(aa.get(c)); // Robin
c.setFst(30);
System.out.println(aa.get(c)); // Robin
c.setFst(10);
System.out.println(aa.get(c)); // Robin
}
public static class Key {
private int fst;
private int scn;
public Key(int fst, int scn) {
this.fst = fst;
this.scn = scn;
}
public int getFst() {
return fst;
}
public void setFst(int fst) {
this.fst = fst;
}
public int getScn() {
return scn;
}
public void setScn(int scn) {
this.scn = scn;
}
}
}
- 输出
Robin
Robin
Robin
- 掌握知识
1.构造方法:给对象数据进行初始化
2.要注意:在静态方法中没有this关键字(静态是随着类的加载而加载,this是随着对象的创建而存在,静态比对象先存在) ; 静态方法只能访问静态;非静态方法都可以访问
4.线程的interrupt
- 题目
public class Sys extends Thread{
boolean stop = false;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Sys thread = new Sys();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
thread.interrupt();
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println("Stopping application...");
}
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
System.out.println("Thread is running...");
}
System.out.println("Thread exiting under request...");
}
}
- 输出
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
Thread is running...
...
- 掌握知识
1.thread.interrupt() 给目标线程发送中断信号,目标线程中断标记置为true
2.thread.isInterrupted() 返回目标线程的中断标记
3.thread.interrupted() 返回目标线程的中断标记,并将其置为false
4.注意:该题将中断标志置为false,但是没有逻辑去处理该中断,所以线程会一直执行。
5.switch顺序
- 题目
public class SwitchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
switch (5) {
default:
System.out.println(5);
case 0:
System.out.println(0);
case 1:
System.out.println(1);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println(2);
break;
}
}
}
- 输出
5
0
1
- 掌握知识
1.switch可以处理int、short、byte、char类型的值,但是不能处理long、String等类型
2.如果case后面没有break或者return语句,会紧接着执行其后的语句
3.switch进来就会找对应的case,找不到找default。该题找到了default直接往后执行,在1跳出。
6.三元表达式比较
- 题目
public class CompareDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char alpha = 'A';
int foo = 65;
boolean trueExp = true;
System.out.println(trueExp ? alpha : 0);
System.out.println(trueExp ? alpha : foo);
}
}
- 输出
A
65
- 掌握知识
1.三元表达式中的表达式1和表达式2为同种类型。所以与char比较返回char,与int比较返回int。
7.this关键字
- 题目
public class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void setLocation(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point p1 = new Point(0, 0);
Point p2 = new Point(0, 0);
modifyPoint(p1, p2);
System.out.println("[" + p1.x + "," + p1.y + "],[" + p2.x + "," + p2.y + "]");
}
private static void modifyPoint(Point p1, Point p2) {
Point tmpPoint = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = tmpPoint;
p1.setLocation(5, 5);
p2 = new Point(5, 5);
}
}
- 输出
[0,0],[5,5]
- 掌握知识
1.可以使用this关键字调用重载构造方法。避免相同的初始化代码,只能在构造方法中用,并且必须位于构造方法的第一句。并且,除了构造器之外,编译器禁止在其他任何方法中调用构造器。
2.this代表当前对象的一个引用
3.this只能在方法内部使用
4.this不能用于静态方法
8.父子类的成员变量成员方法
- 题目
class Parent {
int a = 100;
public int f() {
return 10;
}
}
public class Son extends Parent {
int a = 200;
public int f() {
return 20;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent parent = new Son();
System.out.println(parent.f() + " " + parent.a);
}
}
- 输出
20 100
- 掌握知识
1.如果在多态,即Parent c = new Child(),子类重载父类方法,则c.方法( ) 调用的是子类的方法,改变的子类变量数据,c.变量 显示的是父类数据,还是未改变的。
9.封装类型比较
- 题目
public class ComDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Comparator<Integer> df = new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 > o2 ? 1 : (o1 == o2) ? 0 : -1;
}
};
System.out.println(df.compare(new Integer(1), new Integer(1)));
}
}
- 输出
-1
- 掌握知识
1.o1==o2比较的是是否为同一对象,即内存地址相同,所以输出-1
10.数组和list的协变
- 题目
public class ListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arrayList1 = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList1.add(new String());
ArrayList<Object> arrayList2 = arrayList1;
System.out.println(arrayList2.size());
}
}
- 输出
编译错误
- 掌握知识
1.数组是协变的,而集合不是协变的。
11.volatile
- 题目
public class SysDemo extends Thread {
private boolean isRunning = true;
public boolean isRunning() {
return isRunning;
}
public void setRunning(boolean isRunning) {
this.isRunning = isRunning;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("begin");
while (isRunning) {
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SysDemo thread = new SysDemo();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.setRunning(false);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 输出
begin
- 掌握知识
1.因为isRunning不是volatile,导致线程里面的isRunning一直无法获取最新的值,所以一直处理死循环内部。
12.getclass
- 题目
public class ListDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> stringList = new ArrayList<String>();
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
System.out.println(stringList.getClass().equals(integerList.getClass()));
}
}
- 输出
true
- 掌握知识
1.两个都是class java.util.ArrayList.
13.Integer
- 题目
public class InteDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer fst = 1;
Integer snd = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(fst == snd);
System.out.println(new Integer(1) == snd);
System.out.println(fst == Integer.valueOf(1));
Integer trd = 256;
System.out.println(trd == Integer.valueOf(256));
}
}
- 输出
false
false
true
false
- 掌握知识
java8中,Integer缓存池的大小默认为-128~127。
- 题目
- 输出
- 掌握知识






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








