ReentrantLock
1.什么是可重入锁?
即一个线程持有某个对象的锁时,再次去获取这个对象的锁可以成功的。
ReentrantLock是个典型的独占模式AQS,同步状态为0时表示空闲。当有线程获取到空闲的同步状态时,它会将同步状态加1,将同步状态改为非空闲,于是其他线程挂起等待。在修改同步状态的同时,并记录下自己的线程,作为后续重入的依据,即一个线程持有某个对象的锁时,再次去获取这个对象的锁是可以成功的。
2.ReentrantLock的特点
ReentrantLock锁相对于Synchronized锁的高级功能,
- 等待可中断:指当前持有所得线程长期不释放锁的时候,等待的线程可以选择放弃等待,改为处理其他事情。
将lockInterruptibly() 放到代码块中,调用interrupt方法进行中断时,lockInterruptibly()会立即响应。
@ReservedStackAccess
final void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!initialTryLock())
acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
- 公平锁:指多个线程在等待同一锁时,当锁可用时,必须按照申请锁的时间顺序来依次获取锁。
- 锁绑定多个条件:相对于synchronized 的object.notify() , object.notifyAll() 只能随机唤醒一个,或者全部唤醒。
ReentrantLock唤醒线程时可以有选择的唤醒。
public void threadDemo2() {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition c1 = lock.newCondition();
Condition c2 = lock.newCondition();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
lock.lock();
for (int i = 'A'; i < 'K'; i++) {
while (state != 1) {
try {
c1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print((char) i + " ");
state = 2;
c2.signal();
}
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
lock.lock();
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++) {
while (state != 2) {
try {
c2.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.print( i + " ");
state = 1;
c1.signal();
}
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
}
3.公平锁和非公平锁是什么?有什么区别?
公平锁:就是当锁可用时,等待锁时间最长的线程获得锁。
非公平锁:当锁可用时,随机分配使用权
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
- 当使用的是非公平锁时,只要CAS操作成功,即获取锁
/**
* Acquire for non-reentrant cases after initialTryLock prescreen
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
if (getState() == 0 && compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
- 当使用非公平锁时,在进行CAS操作之前,还判断当前线程是否有前驱节点,有的话返回false
/**
* Acquires only if thread is first waiter or empty
*/
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
if (getState() == 0 && !hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
4. 加锁流程
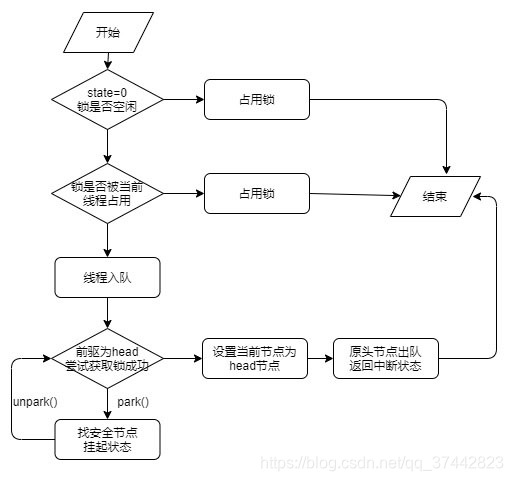
- 首先调用lock()加锁,
- 执行初始加锁,initialTryLock()
2.1 如果state = 0,并且CAS操作成功,那么设置保存当前线程号,加锁成功,
2.2 否则看当前拥有锁的线程是否是自己,是的话,state++,即重入
2.3 否则加锁失败,调用acquire(1); 执行入队流程 - 队列中的线程自旋尝试再次获取锁时,tryAcquire();
3.1 使用公平锁,非公平锁时的判断条件不一样,如上所示
1.ReentrantLock:
public void lock() {
sync.lock();
}
2. sync
final void lock() {
if (!initialTryLock())
acquire(1);
}
3. FairSync/NonfairSync
final boolean initialTryLock() {
.....
}
4. sync
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
acquire(null, arg, false, false, false, 0L);
}
5. FairSync/NonfairSync
//自旋获取锁,
//这一个方法FairSync/NonfairSync的不同重写,体现了Fair、NoFair的特点
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
......
}
6.sync
//主要的请求方法,等待队列的管理,node入队的操作。。。
final int acquire(Node node, int arg, boolean shared,
boolean interruptible, boolean timed, long time) {
.......
}
总结
- ReentrantLock与Synchrionized的区别
- 底层实现上来说,
- synchronized 是JVM层面的锁,是Java关键字,通过monitor对象来完成(monitorenter与monitorexit),锁的竞争其实就是对monitor对象的竞争。
synchronized 的实现涉及到锁的升级,具体为无锁、偏向锁、轻量级锁、重量级锁。- ReentrantLock 是API层面的锁,ReentrantLock实现则是通过利用CAS(CompareAndSwap)保证线程操作的原子性,volatile保证数据可见性以实现锁的功能。
- 加锁对象上来说,
- synchronized 锁的是对象,锁信息保存在对象头中
- ReentrantLock锁的是线程,锁的信息保存在AQS 的state标识,以及ownerThread字段。
- 使用上来说
- synchronized 可以用来修饰方法,代码块。由Jvm自动释放锁
- ReentrantLock只能修饰代码块。需要手动释放锁
- 功能上来说 ReentrantLock 相对 synchronized 多了三中功能:1)等待可中断,2)公平锁,3)可绑定多个条件,实现有选择的唤醒等待
- ReentrantLock 的关键代码
//ReentrantLock中有一个抽象类Sync,它继承了AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private final Sync sync;
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
......
}
}
// 根据构造方法的Boolean参数,实例化Sync的不同实现类
//FairSync, NonfairSync
//AbstractOwnableSynchronizer,有一个volatile修饰的state,以及
//AbstractOwnableSynchronizer类中的字段exclusiveOwnerThread,还有一个Node类,作为等待队列,封装了等待线程
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer
implements java.io.Serializable {
private volatile int state;
private transient Thread exclusiveOwnerThread; //AbstractOwnableSynchronizer类中的字段
private transient volatile Node head;
private transient volatile Node tail;
/** CLH Nodes */
abstract static class Node {
volatile Node prev; // initially attached via casTail
volatile Node next; // visibly nonnull when signallable
Thread waiter; // visibly nonnull when enqueued
volatile int status; // written by owner, atomic bit ops by others
.......
}
- ReentrantLock 的等待可中断是怎么实现的
使用 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 加锁。其会响应 threadB.interrupt();
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
.........
final void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
if (!initialTryLock())
acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
}
- ReentrantLock 的绑定多个条件是怎么实现的
1. ReentrantLock
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
2.Sync
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
3.AQS
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L;
/** First node of condition queue. */
private transient ConditionNode firstWaiter;
/** Last node of condition queue. */
private transient ConditionNode lastWaiter;
//将当前线程封装为一个conditionObject,入队阻塞
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
....
}
//将条件队列中的首节点,加入到同步(等待)队列中
public final void signal() {
.....
}
}
static final class ConditionNode extends Node
implements ForkJoinPool.ManagedBlocker {
ConditionNode nextWaiter; // link to next waiting node
*/
public final boolean isReleasable() {
return status <= 1 || Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
}
public final boolean block() {
while (!isReleasable()) LockSupport.park();
return true;
}
}





 本文详细介绍了Java中的可重入锁ReentrantLock,包括它的可重入特性、与synchronized的区别、公平锁与非公平锁的概念,以及加锁流程。ReentrantLock提供了等待可中断、公平锁选择和绑定多个条件等高级功能。
本文详细介绍了Java中的可重入锁ReentrantLock,包括它的可重入特性、与synchronized的区别、公平锁与非公平锁的概念,以及加锁流程。ReentrantLock提供了等待可中断、公平锁选择和绑定多个条件等高级功能。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








