
这一题有了前面的积累,就是把前面写过的并集和交集结合起来即可。
至于时间复杂度,前面实现的都是与链表长度成正比,所以这里自然也就满足了。
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct node
{
int data;
struct node * next;
}Node;
typedef struct list
{
Node* head;
Node* tail;
}List;
void Init_list(List* L)
{
Node* first = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(!first)
printf("wrong!\n");
first -> data = 0;
first -> next = NULL;
L->head = L->tail = first;
int length;
printf("please enter list length: ");
scanf("%d",&length); //scanf里面不能写类似于printf中打印字符串的语句
for(int i = 0; i< length; i++)
{
Node* new = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
scanf("%d",&new -> data); //这个语句注意一下
new -> next = NULL;
L->tail -> next = new;
L->tail = new;
}
}
void jiaoji(List* l2,List l3)
{
Node *p, *q,*save,*prev;
prev = l2->head;
p = l2->head -> next; q = l3.head -> next;
//用l1来存储新的链表
while(p)
{
if(q->data == p->data)
{
prev = p;
p = p->next;
q = q->next;
}
else
{
save = q; //保留q最初的地方
if(q->data > p->data) //找不到就删除节点
{
p = p->next;
prev -> next = p;
q = save;
}
else
{
q = q->next;
if(q == NULL)
{
prev -> next = NULL;
break; //找遍了也找不到的话,就后面都不用比较了
}
}
}
}
}
void bingji(List* l1,List l2)
{
Node *p, *q,*save,*prev;
p = l1->head->next; q = l2.head->next; prev = l1->head;
//用l1来存储新的链表
while(p && q)
{
if(p->data < q->data)
{
prev = p;
p = p->next;
}
else if(p->data > q->data)
{
save = q;
q = q->next;
prev->next = save;
save->next = p;
prev = prev -> next;
}
else
{
prev = p;
p = p -> next;
q = q-> next;
}
}
//将最后一个元素归到链表中
if(q == NULL)
;
else
{
prev -> next = q;
}
}
void print_list(List L)
{
Node* p;
p = L.head->next;
while(p != NULL)
{
printf("%d ",p->data);
p = p -> next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
List l1,l2,l3;
Init_list(&l1);
Init_list(&l2);
Init_list(&l3);
jiaoji(&l2,l3);
bingji(&l1,l2);
printf("After opertion: ");
print_list(l1);
return 0;
}
```
运行截图:
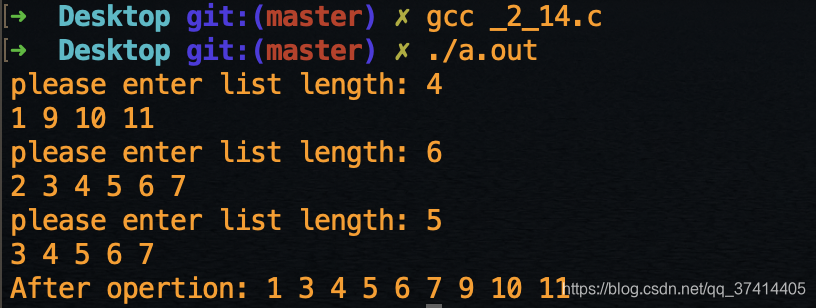




 本文介绍了一种使用链表实现交集和并集的算法,通过遍历两个链表并比较节点数据,实现了两个链表的交集和并集运算。代码示例展示了如何初始化链表、进行交集和并集操作,并最终打印结果。
本文介绍了一种使用链表实现交集和并集的算法,通过遍历两个链表并比较节点数据,实现了两个链表的交集和并集运算。代码示例展示了如何初始化链表、进行交集和并集操作,并最终打印结果。

















 1338
1338

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










