结构

1.lt rb我觉得不是很合适 正确来说是lb rt 因为比较出来的都是左下和右上坐标
比如前两个,都是max出来的 选两个box左下坐标中最大的, 后两个则是右上坐标中最小的 那也就形成了交集面积
但是代码中仍然是lt rb我也就直接这样说
而算出lt和rb之后 算他们差可以算出高宽,只要没有交集 w或者h必定为负,可以画图验证一下
后面就是普通的iou算法
def compute_iou(self, bbox1, bbox2):
""" Compute the IoU (Intersection over Union) of two set of bboxes, each bbox format: [x1, y1, x2, y2].
Args:
bbox1: (Tensor) bounding bboxes, sized [N, 4].
bbox2: (Tensor) bounding bboxes, sized [M, 4].
Returns:
(Tensor) IoU, sized [N, M].
"""
N = bbox1.size(0)
M = bbox2.size(0)
# Compute left-top coordinate of the intersections
lt = torch.max(
bbox1[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N, 2] -> [N, 1, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
bbox2[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2) # [M, 2] -> [1, M, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
)
# Conpute right-bottom coordinate of the intersections
rb = torch.min(
bbox1[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N, 2] -> [N, 1, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
bbox2[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2) # [M, 2] -> [1, M, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
)
# Compute area of the intersections from the coordinates
wh = rb - lt # width and height of the intersection, [N, M, 2]
wh[wh < 0] = 0 # clip at 0
inter = wh[:, :, 0] * wh[:, :, 1] # [N, M]
# Compute area of the bboxes
area1 = (bbox1[:, 2] - bbox1[:, 0]) * (bbox1[:, 3] - bbox1[:, 1]) # [N, ]
area2 = (bbox2[:, 2] - bbox2[:, 0]) * (bbox2[:, 3] - bbox2[:, 1]) # [M, ]
area1 = area1.unsqueeze(1).expand_as(inter) # [N, ] -> [N, 1] -> [N, M]
area2 = area2.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(inter) # [M, ] -> [1, M] -> [N, M]
# Compute IoU from the areas
union = area1 + area2 - inter # [N, M, 2]
iou = inter / union # [N, M, 2]
return iou
2.比较难的部分也就是重头戏
coord_mask = target_tensor[..., 4] > 0 #三个点自动判断维度 自动找到最后一维 用4找出第五个 也就是置信度,为什么30维 第二个框是怎么样的 等下再看
#没有目标的张量[n_batch, S, S]
noobj_mask = target_tensor[..., 4] == 0
#扩展维度的布尔值相同,[n_batch, S, S] -> [n_batch, S, S, N]
coord_mask = coord_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor)
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor)
target中具有真实的置信度 有就是1没有就是0 而不是训练时的train值 train值是从0-1模糊的与网络输出值
而这里的置信度赋值是从voc的encode方法中赋值的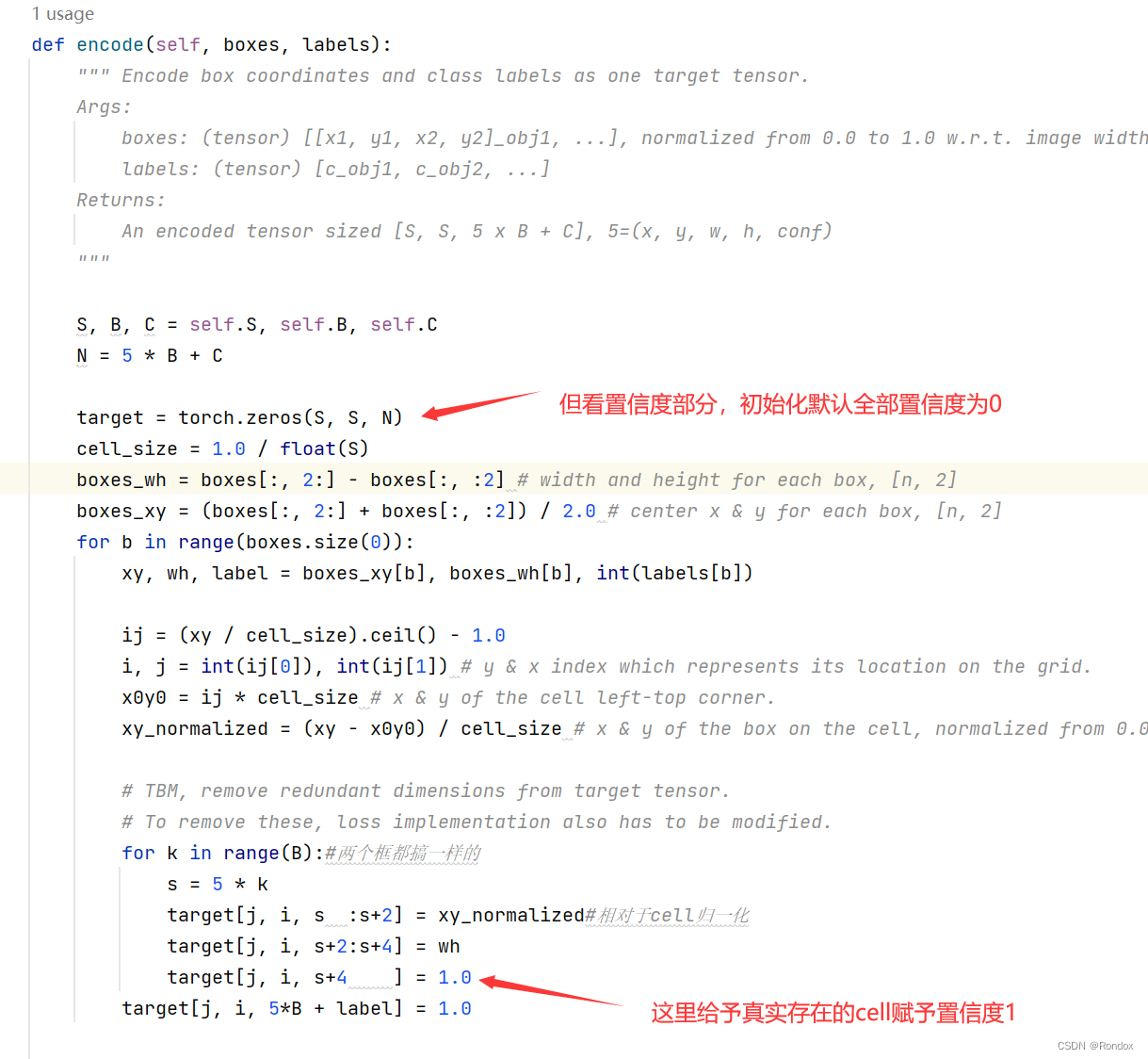
这里筛选出存在物体与不存在物体的部分分别为coord_mask和noobj_mask,大小也分别为(batch_size,S,S) 意思是这个batch批次中,这个像素是否存在物体, 值为True False
扩充维数,使之对应(batch_size,S,S,30) 30维度
而负责的话这30维全为true或者不负责全为false
下一部分
#预测值里含有目标的张量取出来,[n_coord, N] view类似于reshape 这里可以当作reshape看 就是变形
coord_pred = pred_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N)
#提取bbox和C,[n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
bbox_pred = coord_pred[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5) #防止内存不连续报错
# 预测值的分类信息[n_coord, C]
class_pred = coord_pred[:, 5*B:]
#含有目标的标签张量,[n_coord, N]
coord_target = target_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N)
#提取标签bbox和C,[n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
bbox_target = coord_target[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5)
#标签的分类信息
class_target = coord_target[:, 5*B:]
从网络中输出的预测张量中,这里叫他预测值(但这只是训练网络输出的预测值,而不是detect的预测值),我们在target中所有的含有物体的像素的地方,从预测中取出来,叫coord_pred
coord_pred也就是对应着真实存在的像素的张量,下面把他分割出bbox和class出来。
target也分割出bbox和class出来用于待会比较 切成10和20长度
ps:coord_pred的是取出结果后将前面三个维度拉平了, 只留最后一个维度N也就是30,
以整体来看pred_tensor.view(-1, N) 形状是(batch_size*S*S,N) coord_pred就是取出来之后的类比于这个形状的张量 (所有batch中各自对应的图片中所有含有物体的像素的cell,N),人话来说就是所有batch中真实框个数总和
#没有目标的处理
#找到预测值里没有目标的网格张量[n_noobj, N],n_noobj=SxS-n_coord
noobj_pred = pred_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
#标签的没有目标的网格张量 [n_noobj, N]
noobj_target = target_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
noobj_conf_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(noobj_pred.size()).fill_(0) # [n_noobj, N]
for b in range(B):
noobj_conf_mask[:, 4 + b*5] = 1 # 没有目标置信度置1,noobj_conf_mask[:, 4] = 1; noobj_conf_mask[:, 9] = 1 目标是下面把置信度拿出来再并排
noobj_pred_conf = noobj_pred[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj x 2=len([conf1, conf2])] 这里目标是
noobj_target_conf = noobj_target[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj x 2=len([conf1, conf2])]
#计算没有目标的置信度损失 加法》? #如果 reduction 参数未指定,默认值为 'mean',表示对所有元素的误差求平均值。
#loss_noobj=F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf,)*len(noobj_pred_conf)
loss_noobj = F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf, reduction='sum')
这里是取出所有不含物体的预测张量的部分,那个for循环是提前把位置赋予1标出来 后面用来提取找出这部分。
找出对应两个部分置信度之后做mse,平方差损失得到 不负责物体的像素置信度的损失,实际上是(0-预测出来的置信度)^2 论文中还要带个权重, 原因是不负责的像素太多了为了公平性,基于比较低的权重
coord_response_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(0) # [n_coord x B, 5]
coord_not_response_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(1)# [n_coord x B, 5]
bbox_target_iou = torch.zeros(bbox_target.size()).cuda() # [n_coord x B, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
初始化下面循环需要用到的变量
for i in range(0, bbox_target.size(0), B):
pred = bbox_pred[i:i+B] # predicted bboxes at i-th cell, [B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
pred_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(pred.size())) # [B, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=pred[:, 2] and (w,h)=pred[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
pred_xyxy[:, :2] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
pred_xyxy[:, 2:4] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
target = bbox_target[i] # target bbox at i-th cell. Because target boxes contained by each cell are identical in current implementation, enough to extract the first one.
target = bbox_target[i].view(-1, 5) # target bbox at i-th cell, [1, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
target_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(target.size())) # [1, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=target[:, 2] and (w,h)=target[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
target_xyxy[:, :2] = target[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
target_xyxy[:, 2:4] = target[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
iou = self.compute_iou(pred_xyxy[:, :4], target_xyxy[:, :4]) # [B, 1]
max_iou, max_index = iou.max(0)
max_index = max_index.data.cuda()
coord_response_mask[i+max_index] = 1
coord_not_response_mask[i+max_index] = 0
# "we want the confidence score to equal the intersection over union (IOU) between the predicted box and the ground truth"
# from the original paper of YOLO.
bbox_target_iou[i+max_index, torch.LongTensor([4]).cuda()] = (max_iou).data.cuda()
训练是进行预测框中每两个循环一次的比较,
预测值两个框是独立不一样的,而真实值target中在voc我们给予两个框一样的值。
pred_xyxy[:, :2] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
pred_xyxy[:, 2:4] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]但是这里除以S,我也没搞懂 我就先跳了
这里preds和target数量是一一对应的
而pred和target中坐标分别为 中心x和y还有w和h,target这四个都是相对图片归一化的 可以从voc解析中知道,而pred则是网络预测的随机值
iou需要传入的参数是左上,右下坐标 这里需要计算
于是在某次循环中,得出最大iou,将那个iou的索引,也就是iou最大是第几个框拿出来在coord_response_mask 和coord_notresponse_mask,这两个变量形状完全与bbox相同
bbox_target_iou在gpu存下结果,用于下面计算损失,循环结束
下面是循环外内容
bbox_target_iou = Variable(bbox_target_iou).cuda()
# BBox location/size and objectness loss for the response bboxes.
bbox_pred_response = bbox_pred[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5]
bbox_target_response = bbox_target[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5], only the first 4=(x, y, w, h) are used
target_iou = bbox_target_iou[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
loss_xy = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, :2], bbox_target_response[:, :2], reduction='sum')
loss_wh = F.mse_loss(torch.sqrt(bbox_pred_response[:, 2:4]), torch.sqrt(bbox_target_response[:, 2:4]), reduction='sum')
loss_obj = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, 4], target_iou[:, 4], reduction='sum')
################################################################################
# Class probability loss for the cells which contain objects.
loss_class = F.mse_loss(class_pred, class_target, reduction='sum')
# Total loss
loss = self.lambda_coord * (loss_xy + loss_wh) + loss_obj + self.lambda_noobj * loss_noobj + loss_class
loss = loss / float(batch_size)
负责物体部分的损失
xy坐标求损失,因为含物体的像素少,论文中给予权重5加大损失倾向,
wh求损失,因为大框和小框之间差会非常大,容易造成损失,所以论文中加入根号,使之差不会过于太大,(大框差的值加在小框上是好几倍甚至几十倍这是无法容忍的),这里也因为像素少,给予权重5
置信度损失,此处网络输出出来的预测值是随机的,论文的想法是应该逼近她所应该位于的值,也就是真实的置信度。他位置在哪就应该给予在哪的置信度。这里体现在与真实框的iou交并比。但是yolov3中将这个与真实框的iou交并比的标签值换成了1,不懂这里也不用纠结。
这里是单纯计算损失 计算方法保持论文中提到的要求,mse_loss也是默认参数不给的话会自动求平均,加个参数sum单纯求平方差的和
返回的loss最终是除以batch_size的一个平均值
def forward(self, pred_tensor, target_tensor):#target_tensor[2,0,0,:]
""" Compute loss for YOLO training. #
Args:
pred_tensor: (Tensor) predictions, sized [n_batch, S, S, Bx5+C], 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf]).
target_tensor: (Tensor) targets, sized [n_batch, S, S, Bx5+C].
Returns:
(Tensor): loss, sized [1, ].
"""
# TODO: Romove redundant dimensions for some Tensors.
#获取网格参数S=7,每个网格预测的边框数目B=2,和分类数C=20
S, B, C = self.S, self.B, self.C
N = 5 * B + C # 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf],N=30
#批的大小
batch_size = pred_tensor.size(0)
#有目标的张量[n_batch, S, S]
coord_mask = target_tensor[..., 4] > 0 #三个点自动判断维度 自动找到最后一维 用4找出第五个 也就是置信度,为什么30维 第二个框是怎么样的 等下再看
#没有目标的张量[n_batch, S, S]
noobj_mask = target_tensor[..., 4] == 0
#扩展维度的布尔值相同,[n_batch, S, S] -> [n_batch, S, S, N]
coord_mask = coord_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor)
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor)
#int8-->bool
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.bool() #不是已经bool了?
coord_mask = coord_mask.bool()
##################################################
#预测值里含有目标的张量取出来,[n_coord, N]
coord_pred = pred_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N)
#提取bbox和C,[n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
bbox_pred = coord_pred[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5) #防止内存不连续报错
# 预测值的分类信息[n_coord, C]
class_pred = coord_pred[:, 5*B:]
#含有目标的标签张量,[n_coord, N]
coord_target = target_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N)
#提取标签bbox和C,[n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
bbox_target = coord_target[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5)
#标签的分类信息
class_target = coord_target[:, 5*B:]
######################################################
# ##################################################
#没有目标的处理
#找到预测值里没有目标的网格张量[n_noobj, N],n_noobj=SxS-n_coord
noobj_pred = pred_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
#标签的没有目标的网格张量 [n_noobj, N]
noobj_target = target_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
noobj_conf_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(noobj_pred.size()).fill_(0) # [n_noobj, N]
for b in range(B):
noobj_conf_mask[:, 4 + b*5] = 1 # 没有目标置信度置1,noobj_conf_mask[:, 4] = 1; noobj_conf_mask[:, 9] = 1 目标是下面把置信度拿出来再并排
noobj_pred_conf = noobj_pred[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj x 2=len([conf1, conf2])] 这里目标是
noobj_target_conf = noobj_target[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj x 2=len([conf1, conf2])]
#计算没有目标的置信度损失 加法》? #如果 reduction 参数未指定,默认值为 'mean',表示对所有元素的误差求平均值。
#loss_noobj=F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf,)*len(noobj_pred_conf)
loss_noobj = F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf, reduction='sum')
#################################################################################
#################################################################################
# Compute loss for the cells with objects.
coord_response_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(0) # [n_coord x B, 5]
coord_not_response_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(1)# [n_coord x B, 5]
bbox_target_iou = torch.zeros(bbox_target.size()).cuda() # [n_coord x B, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
# Choose the predicted bbox having the highest IoU for each target bbox.
for i in range(0, bbox_target.size(0), B):
pred = bbox_pred[i:i+B] # predicted bboxes at i-th cell, [B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
pred_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(pred.size())) # [B, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=pred[:, 2] and (w,h)=pred[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
pred_xyxy[:, :2] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
pred_xyxy[:, 2:4] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
target = bbox_target[i] # target bbox at i-th cell. Because target boxes contained by each cell are identical in current implementation, enough to extract the first one.
target = bbox_target[i].view(-1, 5) # target bbox at i-th cell, [1, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
target_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(target.size())) # [1, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=target[:, 2] and (w,h)=target[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
target_xyxy[:, :2] = target[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
target_xyxy[:, 2:4] = target[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
iou = self.compute_iou(pred_xyxy[:, :4], target_xyxy[:, :4]) # [B, 1]
max_iou, max_index = iou.max(0)
max_index = max_index.data.cuda()
coord_response_mask[i+max_index] = 1
coord_not_response_mask[i+max_index] = 0
# "we want the confidence score to equal the intersection over union (IOU) between the predicted box and the ground truth"
# from the original paper of YOLO.
bbox_target_iou[i+max_index, torch.LongTensor([4]).cuda()] = (max_iou).data.cuda()
bbox_target_iou = Variable(bbox_target_iou).cuda()
# BBox location/size and objectness loss for the response bboxes.
bbox_pred_response = bbox_pred[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5]
bbox_target_response = bbox_target[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5], only the first 4=(x, y, w, h) are used
target_iou = bbox_target_iou[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
loss_xy = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, :2], bbox_target_response[:, :2], reduction='sum')
loss_wh = F.mse_loss(torch.sqrt(bbox_pred_response[:, 2:4]), torch.sqrt(bbox_target_response[:, 2:4]), reduction='sum')
loss_obj = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, 4], target_iou[:, 4], reduction='sum')
################################################################################
# Class probability loss for the cells which contain objects.
loss_class = F.mse_loss(class_pred, class_target, reduction='sum')
# Total loss
loss = self.lambda_coord * (loss_xy + loss_wh) + loss_obj + self.lambda_noobj * loss_noobj + loss_class
loss = loss / float(batch_size)
return loss

总的
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.autograd import Variable
class Loss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, feature_size=7, num_bboxes=2, num_classes=20, lambda_coord=5.0, lambda_noobj=0.5):
""" Constructor.
Args:
feature_size: (int) size of input feature map.
num_bboxes: (int) number of bboxes per each cell.
num_classes: (int) number of the object classes.
lambda_coord: (float) weight for bbox location/size losses.
lambda_noobj: (float) weight for no-objectness loss.
"""
super(Loss, self).__init__()
self.S = feature_size
self.B = num_bboxes
self.C = num_classes
self.lambda_coord = lambda_coord
self.lambda_noobj = lambda_noobj
def compute_iou(self, bbox1, bbox2):
""" Compute the IoU (Intersection over Union) of two set of bboxes, each bbox format: [x1, y1, x2, y2].
Args:
bbox1: (Tensor) bounding bboxes, sized [N, 4].
bbox2: (Tensor) bounding bboxes, sized [M, 4].
Returns:
(Tensor) IoU, sized [N, M].
"""
N = bbox1.size(0)
M = bbox2.size(0)
# Compute left-top coordinate of the intersections
lt = torch.max(
bbox1[:, :2].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N, 2] -> [N, 1, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
bbox2[:, :2].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2) # [M, 2] -> [1, M, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
)
# Conpute right-bottom coordinate of the intersections
rb = torch.min(
bbox1[:, 2:].unsqueeze(1).expand(N, M, 2), # [N, 2] -> [N, 1, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
bbox2[:, 2:].unsqueeze(0).expand(N, M, 2) # [M, 2] -> [1, M, 2] -> [N, M, 2]
)
# Compute area of the intersections from the coordinates
wh = rb - lt # width and height of the intersection, [N, M, 2]
wh[wh < 0] = 0 # clip at 0
inter = wh[:, :, 0] * wh[:, :, 1] # [N, M]
# Compute area of the bboxes
area1 = (bbox1[:, 2] - bbox1[:, 0]) * (bbox1[:, 3] - bbox1[:, 1]) # [N, ]
area2 = (bbox2[:, 2] - bbox2[:, 0]) * (bbox2[:, 3] - bbox2[:, 1]) # [M, ]
area1 = area1.unsqueeze(1).expand_as(inter) # [N, ] -> [N, 1] -> [N, M]
area2 = area2.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(inter) # [M, ] -> [1, M] -> [N, M]
# Compute IoU from the areas
union = area1 + area2 - inter # [N, M, 2]
iou = inter / union # [N, M, 2]
return iou
def forward(self, pred_tensor, target_tensor):#target_tensor[2,0,0,:]
""" Compute loss for YOLO training. #
Args:
pred_tensor: (Tensor) predictions, sized [n_batch, S, S, Bx5+C], 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf]).
target_tensor: (Tensor) targets, sized [n_batch, S, S, Bx5+C].
Returns:
(Tensor): loss, sized [1, ].
"""
# TODO: Romove redundant dimensions for some Tensors.
#获取网格参数S=7,每个网格预测的边框数目B=2,和分类数C=20
S, B, C = self.S, self.B, self.C
N = 5 * B + C # 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf],N=30
#批的大小
batch_size = pred_tensor.size(0)
#有目标的张量[n_batch, S, S]
coord_mask = target_tensor[..., 4] > 0 #三个点自动判断维度 自动找到最后一维 用4找出第五个 也就是置信度,为什么30维 第二个框是怎么样的 等下再看
#没有目标的张量[n_batch, S, S]
noobj_mask = target_tensor[..., 4] == 0
#扩展维度的布尔值相同,[n_batch, S, S] -> [n_batch, S, S, N]
coord_mask = coord_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor)
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand_as(target_tensor)
#int8-->bool
noobj_mask = noobj_mask.bool() #不是已经bool了?
coord_mask = coord_mask.bool()
##################################################
#预测值里含有目标的张量取出来,[n_coord, N]
coord_pred = pred_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N)
#提取bbox和C,[n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
bbox_pred = coord_pred[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5) #防止内存不连续报错
# 预测值的分类信息[n_coord, C]
class_pred = coord_pred[:, 5*B:]
#含有目标的标签张量,[n_coord, N]
coord_target = target_tensor[coord_mask].view(-1, N)
#提取标签bbox和C,[n_coord x B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
bbox_target = coord_target[:, :5*B].contiguous().view(-1, 5)
#标签的分类信息
class_target = coord_target[:, 5*B:]
######################################################
# ##################################################
#没有目标的处理
#找到预测值里没有目标的网格张量[n_noobj, N],n_noobj=SxS-n_coord
noobj_pred = pred_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
#标签的没有目标的网格张量 [n_noobj, N]
noobj_target = target_tensor[noobj_mask].view(-1, N)
noobj_conf_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(noobj_pred.size()).fill_(0) # [n_noobj, N]
for b in range(B):
noobj_conf_mask[:, 4 + b*5] = 1 # 没有目标置信度置1,noobj_conf_mask[:, 4] = 1; noobj_conf_mask[:, 9] = 1 目标是下面把置信度拿出来再并排
noobj_pred_conf = noobj_pred[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj x 2=len([conf1, conf2])] 这里目标是
noobj_target_conf = noobj_target[noobj_conf_mask] # [n_noobj x 2=len([conf1, conf2])]
#计算没有目标的置信度损失 加法》? #如果 reduction 参数未指定,默认值为 'mean',表示对所有元素的误差求平均值。
#loss_noobj=F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf,)*len(noobj_pred_conf)
loss_noobj = F.mse_loss(noobj_pred_conf, noobj_target_conf, reduction='sum')
#################################################################################
#################################################################################
# Compute loss for the cells with objects.
coord_response_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(0) # [n_coord x B, 5]
coord_not_response_mask = torch.cuda.BoolTensor(bbox_target.size()).fill_(1)# [n_coord x B, 5]
bbox_target_iou = torch.zeros(bbox_target.size()).cuda() # [n_coord x B, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
# Choose the predicted bbox having the highest IoU for each target bbox.
for i in range(0, bbox_target.size(0), B):
pred = bbox_pred[i:i+B] # predicted bboxes at i-th cell, [B, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
pred_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(pred.size())) # [B, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=pred[:, 2] and (w,h)=pred[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
pred_xyxy[:, :2] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
pred_xyxy[:, 2:4] = pred[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * pred[:, 2:4]
target = bbox_target[i] # target bbox at i-th cell. Because target boxes contained by each cell are identical in current implementation, enough to extract the first one.
target = bbox_target[i].view(-1, 5) # target bbox at i-th cell, [1, 5=len([x, y, w, h, conf])]
target_xyxy = Variable(torch.FloatTensor(target.size())) # [1, 5=len([x1, y1, x2, y2, conf])]
# Because (center_x,center_y)=target[:, 2] and (w,h)=target[:,2:4] are normalized for cell-size and image-size respectively,
# rescale (center_x,center_y) for the image-size to compute IoU correctly.
target_xyxy[:, :2] = target[:, :2]/float(S) - 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
target_xyxy[:, 2:4] = target[:, :2]/float(S) + 0.5 * target[:, 2:4]
iou = self.compute_iou(pred_xyxy[:, :4], target_xyxy[:, :4]) # [B, 1]
max_iou, max_index = iou.max(0)
max_index = max_index.data.cuda()
coord_response_mask[i+max_index] = 1
coord_not_response_mask[i+max_index] = 0
# "we want the confidence score to equal the intersection over union (IOU) between the predicted box and the ground truth"
# from the original paper of YOLO.
bbox_target_iou[i+max_index, torch.LongTensor([4]).cuda()] = (max_iou).data.cuda()
bbox_target_iou = Variable(bbox_target_iou).cuda()
# BBox location/size and objectness loss for the response bboxes.
bbox_pred_response = bbox_pred[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5]
bbox_target_response = bbox_target[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5], only the first 4=(x, y, w, h) are used
target_iou = bbox_target_iou[coord_response_mask].view(-1, 5) # [n_response, 5], only the last 1=(conf,) is used
loss_xy = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, :2], bbox_target_response[:, :2], reduction='sum')
loss_wh = F.mse_loss(torch.sqrt(bbox_pred_response[:, 2:4]), torch.sqrt(bbox_target_response[:, 2:4]), reduction='sum')
loss_obj = F.mse_loss(bbox_pred_response[:, 4], target_iou[:, 4], reduction='sum')
################################################################################
# Class probability loss for the cells which contain objects.
loss_class = F.mse_loss(class_pred, class_target, reduction='sum')
# Total loss
loss = self.lambda_coord * (loss_xy + loss_wh) + loss_obj + self.lambda_noobj * loss_noobj + loss_class
loss = loss / float(batch_size)
return loss




 这段代码详细展示了YOLO(YouOnlyLookOnce)目标检测模型中的损失函数计算过程,包括有目标和无目标的像素处理,以及预测框与真实框的IoU计算,用于优化网络训练。主要涉及坐标计算、交并比、平方差损失(MSE)以及损失加权等概念。
这段代码详细展示了YOLO(YouOnlyLookOnce)目标检测模型中的损失函数计算过程,包括有目标和无目标的像素处理,以及预测框与真实框的IoU计算,用于优化网络训练。主要涉及坐标计算、交并比、平方差损失(MSE)以及损失加权等概念。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








