1.Introduction
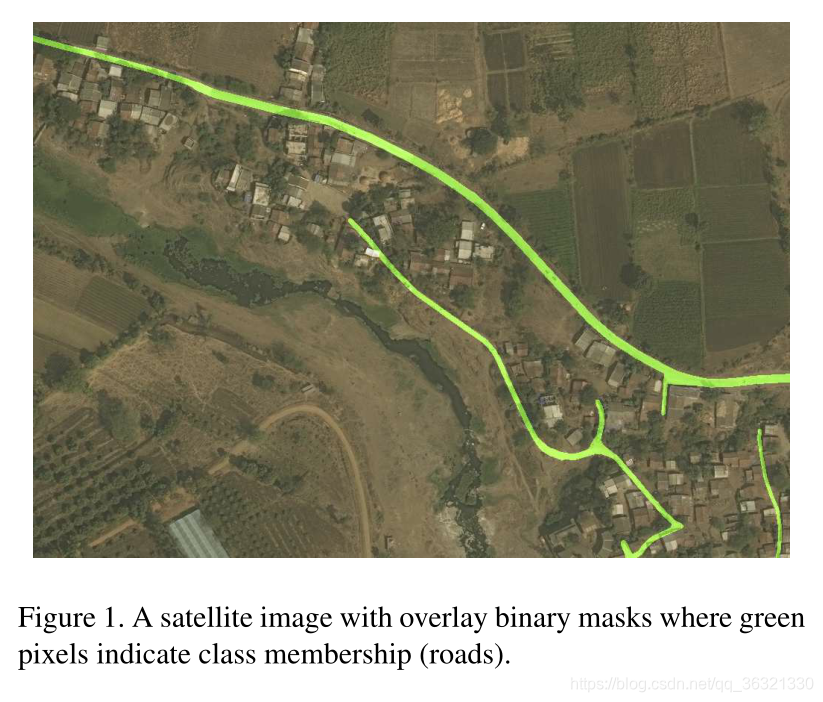

2. Model
我们对原始的U-Net网络进行了改进,使用了类似的网络和类似的编码器,使用预训练的ResNet-34网络作为编码器。卷积核的大小是7x7,stride=2,在每个residual block中,第一个卷积的步长是2,剩下的卷积操作步长都为1。
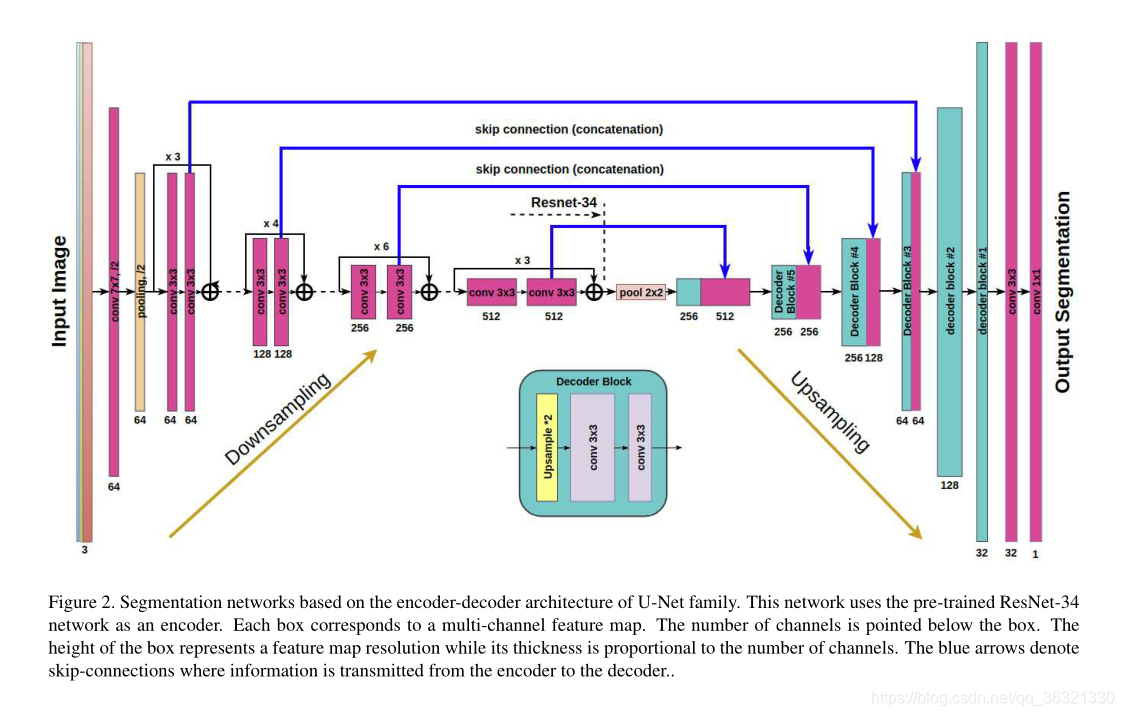
3. Training
使用Jaccard index(IOU)作为评价指标
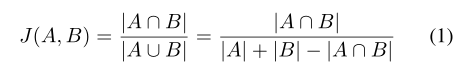
离散公式:(分别为像素i的 二值和 预测概率)
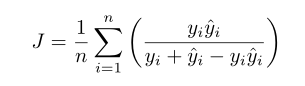
损失函数(H:BCE):
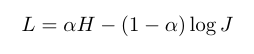
最小化L,相当于最小化H,并且最大化J
经过测试,α=0.7
使用Adam 优化器,IOU的预测值在迭代之间变化比较显著,使用了Dropout(0.3),使用了TTA(test time augmentation),即将图像进行90度的旋转得到四张图像,预测然后取平均值。
References
[1] http://deepglobe.org/.
[2] http://ods.ai/.
[3] I. Demir, K. Koperski, D. Lindenbaum, G. Pang, J. Huang,S. Basu, F. Hughes, D. Tuia, and R. Raskar. Deepglobe 2018:A challenge to parse the earth through satellite images. arXiv preprint arXiv:1805.06561, 2018.
[4] M. Everingham, S. A. Eslami, L. V an Gool, C. K. Williams,J. Winn, and A. Zisserman. The pascal visual object classes challenge: A retrospective. International journal of com-puter vision, 111(1):98–136, 2015.
[5] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages
770–778, 2016.
[6] V . Iglovikov, S. Mushinskiy, and V . Osin. Satellite imagery feature detection using deep convolutional neural network: A kaggle competition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.06169, 2017.
[7] V . Iglovikov and A. Shvets. Ternausnet: U-net with vgg11 encoder pre-trained on imagenet for image segmentation.arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.05746, 2018.
[8] D. P . Kingma and J. Ba. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.6980, 2014.
[9] J. Long, E. Shelhamer, and T. Darrell. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 3431–3440, 2015.
[10] O. Ronneberger, P . Fischer, and T. Brox. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In International Conference on Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pages 234–241, 2015.
[11] W. Wang, N. Y ang, Y . Zhang, F. Wang, T. Cao, and P . Eklund. A review of road extraction from remote sensing images. Journal of Traffic and TransportationEngineering (English Edition), 3(3):271–282, 2016.
[12] Z. Zhang, Q. Liu, and Y . Wang. Road extraction by deep residual u-net. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018.
[13] Z. Zhong, J. Li, W. Cui, and H. Jiang. Fully convolutional networks for building and road extraction: preliminary results. In Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), 2016 IEEE International, pages 1591–1594.IEEE, 2016.





 本文介绍了一种改进的U-Net网络,用于从卫星图像中精确提取道路。通过使用预训练的ResNet-34作为编码器,并结合Dropout和TTA技术,实现了对道路特征的有效检测。实验结果显示,该模型在Jaccard指数上表现优秀。
本文介绍了一种改进的U-Net网络,用于从卫星图像中精确提取道路。通过使用预训练的ResNet-34作为编码器,并结合Dropout和TTA技术,实现了对道路特征的有效检测。实验结果显示,该模型在Jaccard指数上表现优秀。
















 1802
1802

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








