1. 遍历目标路径下的所有子文件及文件
函数定义:vector<SubfolderInfo> listFiles(const char * dir, bool flag = false);
函数功能:递归遍历指定目录下所有子文件夹,文件夹信息保存至结构体SubfolderInfo中,最终返回一个vector<SubfolderInfo>,其中包含指定目录下所有子目录的信息
传入参数:
const char* dir:目标路径bool flag:是否清空函数中的static变量,第二次及以后调用时需为true
返回示例:

#include <iostream>
#include <io.h>
using namespace std;
struct SubfolderInfo
{
string folder_name; //存放该子目录名称
vector<string> file_names; //存放该子目录下的文件名称
};
vector<SubfolderInfo> listFiles(const char * dir, bool flag = false)
{
char dirNew[200];
strcpy_s(dirNew, dir);
strcat_s(dirNew, "\\*.*"); // 在目录后面加上"\\*.*"进行第一次搜索
static vector<SubfolderInfo> sub_dirs; //加static防止该变量被优化掉导致内存错误
static size_t folder_counter = 0;
if (flag)
{
sub_dirs.clear();
folder_counter = 0;
}
intptr_t handle;
_finddata_t findData;
handle = _findfirst(dirNew, &findData);
if (handle == -1) // 检查是否成功
return sub_dirs;
do
{
SubfolderInfo subfolder;
if (findData.attrib & _A_SUBDIR) //子文件夹
{
if (strcmp(findData.name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(findData.name, "..") == 0) //过滤.和..文件夹
continue;
//cout << findData.name << "\t<dir>\n";
subfolder.folder_name = string(findData.name);
folder_counter++;
sub_dirs.push_back(subfolder);
// 在目录后面加上"\\"和搜索到的目录名进行下一次搜索
strcpy_s(dirNew, dir);
strcat_s(dirNew, "\\"); //后加"\\"
strcat_s(dirNew, findData.name);
listFiles(dirNew);
}
else
{
sub_dirs[folder_counter-1].file_names.push_back(string(findData.name));
}
//cout << findData.name << "\t" << findData.size << " bytes.\n";
} while (_findnext(handle, &findData) == 0);
_findclose(handle); // 关闭搜索句柄
return sub_dirs;
}
//使用示例
int main()
{
char* id_path = "D:\\Desktop\\working\\ruiyanSDK\\293_id";
char* camera_path = "D:\\Desktop\\working\\ruiyanSDK\\293_camera";
vector<SubfolderInfo> id_lists = listFiles(id_path);
vector<SubfolderInfo> camera_lists = listFiles(camera_path, true); //第二次调用时添加参数true来清空函数中的static变量
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
2. 生成不重复的随机数
函数定义:size_t * rand_numbers(size_t total_size, size_t get_size);
函数功能:从0--total_size-1(含0和total_size-1)的范围中生成get_size个互不相同的随机整数,并以数组的形式返回
传入参数:
size_t total_size:取值范围0--total_size中的整数size_t get_size:取值个数get_size个
注意:
- 使用
rand()函数之前,要在主函数中调用srand(time(0))根据时间产生一个数,确保每次运行产生的随机数不同 - time()精度低,
srand(time(0))不能写在循环内部,否则每次生成的随机数仍一样
返回示例:
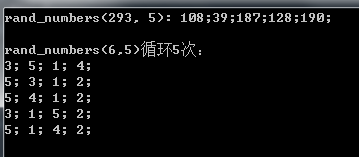
注意:函数返回的为动态数组,使用完毕后需要delete[]。
相似函数:random_shuffle()用来对一个元素序列进行重新排序(随机的)
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
size_t * rand_numbers(size_t total_size, size_t get_size)
{
if (get_size > total_size)
{
cout << endl << "In rand_numbers: input error (get_size > total_size)" << endl;
return NULL;
}
size_t* total_array = new size_t[total_size];
for (size_t i = 0; i < total_size; ++i) //生成0到total_size个顺序排列的数
total_array[i] = i;
for (size_t i = total_size - 1; i >= 1; --i)
swap(total_array[i], total_array[rand() % i]); //将顺序数组打乱
size_t* get_array = new size_t[get_size];
memcpy(get_array, total_array, get_size * sizeof(size_t));
delete[] total_array;
return get_array;
}
//函数测试
int main(void)
{
srand(size_t(time(0))); //根据时间产生一个数,确保每次运行产生的随机数不同;注意:time()精度低,这句话不能写在循环内部,否则每次生成的随机数仍一样
size_t* rand_array = rand_numbers(293, 5);
cout << "rand_numbers(293, 5): ";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << rand_array[i] << ";";
delete[] rand_array;
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "rand_numbers(6,5)循环5次:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
size_t* rand_array1 = rand_numbers(6, 5);
for (int j = 0; j < 5 - 1; j++)
{
if (rand_array1[j] == 0)
swap(rand_array1[j], rand_array1[4]);
cout << rand_array1[j] << "; ";
}
cout << endl;
delete[] rand_array1;
}
std::cin.get();
return 0;
}
3. 用户输入数字
返回示例:
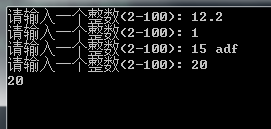
注意:函数调用时num_min和num_max不可使用负数,且num_max>num_min
#include <iostream>
using namspace std;
bool isint(string &str)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
if (!isdigit(str[i]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
size_t input_integer(size_t num_min = 0, size_t num_max = 999, string note = "Please input a number")
{
string input_num_temp;
size_t input_num;
bool input_num_flag = false;
while (!input_num_flag)
{
cout << note << "(" << num_min << "-" << num_max << "): ";
getline(cin, input_num_temp);//read a line into string
if (isint(input_num_temp))
{
input_num = stoi(input_num_temp); //string to int
if ((input_num >= num_min) && (input_num <= num_max))
input_num_flag = true;
}
}
return input_num;
}
int main(void)
{
size_t input_num = input_integer(2, 100, "请输入一个整数");
cout << input_num << endl;
return 0;
}
4.用户输入路径
返回示例:
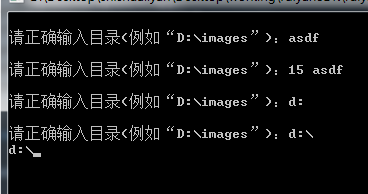
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
string input_dir()
{
string inputPath = "";
char *cstr_inputPath = (char*)(inputPath.c_str()); //const char *cstr_inputPath = inputPath.c_str();
//char *cstr_inputPath = inputPath.c_str();
while (_access(cstr_inputPath, 0) == -1 || inputPath.find_last_of(":") == inputPath.size() - 1) //判断输入的目录是否存在 且 最后一个字符不能是":"
{
cout << endl << "请正确输入目录(例如“D:\\images”):";
//读入string
//cin >> inputPath; //read a word 遇到空格结束 若输入包含空格,将视作多次输入
getline(cin, inputPath);//read a line 遇到\n结束
size_t pos_last_space = inputPath.find_last_of(" "); //修改2:通过while循环删除用户输入字符串中尾部所有空格
while (pos_last_space == inputPath.size() - 1)
{
inputPath.replace(pos_last_space, 1, "");
pos_last_space = inputPath.find_last_of(" ");
}
//inputPath = inputPath.replace(" ", "");
cstr_inputPath = (char*)inputPath.c_str(); //********
}
return cstr_inputPath;
}
int main()
{
string inputDir = input_dir();
cout << inputDir;
return 0;
}
5. 创建文件夹
#include <io.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void create_dir(string baseDir, string mkDir)
{
string folderPath = baseDir + "\\" + mkDir;
string command;
if (_access(folderPath.c_str(), 0)) //判断文件夹是否存在
{
command = "md " + folderPath;
system(command.c_str()); //windows命令行cmd中运行该命令
cout << "\"" << folderPath << "\"文件夹创建成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "\"" << folderPath << "\"文件夹已存在" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
create_dir("D:", "testdir"); //创建D:\testdir文件夹
create_dir(".", "testdir"); //在当前目录下创建文件夹
return 0;
}
函数原型: int _access(const char *filename, int mode);
所属头文件:io.h
filename:可以填写文件夹路径或者文件路径
mode:0 (F_OK) 只判断是否存在
2 (R_OK) 判断写入权限
4 (W_OK) 判断读取权限
6 (X_OK) 判断执行权限
用于判断文件夹是否存在的时候,mode取0,判断文件是否存在的时候,mode可以取0、2、4、6。 若存在或者具有权限,返回值为0;不存在或者无权限,返回值为-1。





 本文介绍了五个C++实用函数,包括遍历目标路径下所有子文件及文件,生成不重复的随机数,获取用户输入的数字和路径,以及创建文件夹。这些函数涵盖了文件操作、随机数生成和用户交互等常见场景。
本文介绍了五个C++实用函数,包括遍历目标路径下所有子文件及文件,生成不重复的随机数,获取用户输入的数字和路径,以及创建文件夹。这些函数涵盖了文件操作、随机数生成和用户交互等常见场景。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








