本系列博客汇总在这里:Java系列_汇总
一、简介

- 打印流:只做输出没有输入。
- 打印流分为字节打印流和字符打印流。
- PrintWriter:字符打印流。
特点
- 可以打印各种数据类型。
- 封装了字符输出流,还可以字符流和字节流的转换。
- 可以使用自动刷新,则只有在调用 println、printf 或 format 的其中一个方法时才可能完成此操作。
- 可以直接向文件中写数据。
二、范例:使用打印流向文件中打印数据
- 示例
public static void main(String[] args) { PrintWriter pw = null; try { pw = new PrintWriter("b.txt"); pw.print(true); pw.print('c'); pw.print(new char[] { 'd', 'g', 'g' }); pw.print(123l); pw.print(12f); pw.print(1); pw.print(45); pw.println("张三"); pw.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(pw != null) { pw.close(); } } }
三、范例:从文件中读取数据并且打印在控制台
- 示例
public static void main(String[] args) { //定义缓冲区输入流对象 BufferedReader br = null; PrintWriter pw = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt")); //pw = new PrintWriter(System.out); //设置自动刷新的打印流,就不需要flush了 pw = new PrintWriter(System.out,true); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { pw.println(line); //pw.flush(); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (pw != null) { pw.close(); } try { if (br != null) { br.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
四、范例:使用打印流来复制文本文件
- 示例
public static void main(String[] args) { BufferedReader br = null; PrintWriter pw = null; System.out.println(); try { br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("a.txt")); pw = new PrintWriter("c.txt"); String line = null; while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { pw.println(line); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if (pw != null) { pw.close(); } if (br != null) { br.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }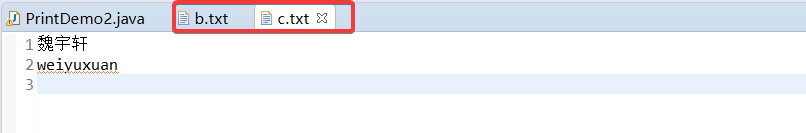
如有错误,欢迎指正!





 本文深入探讨Java中的打印流概念,包括字节打印流和字符打印流,并通过实例演示如何使用PrintWriter进行数据输出,从文件读取数据并显示在控制台,以及复制文本文件。文章覆盖打印流的特点及其在不同场景下的应用。
本文深入探讨Java中的打印流概念,包括字节打印流和字符打印流,并通过实例演示如何使用PrintWriter进行数据输出,从文件读取数据并显示在控制台,以及复制文本文件。文章覆盖打印流的特点及其在不同场景下的应用。
















 521
521

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








