现在人工智能很火,各大高校都开展了人工智能的学习课程
既然如此,让我们开始试试人工智能的程序实现与设计-MFC实现
一.A*算法的实现与设计
首先要明确一下什么是A*算法和八数码问题?
A*(A-Star)算法是一种静态路网中求解最短路径最有效的直接搜索方法也是一种启发性的算法,也是解决许多搜索问题的有效算法。算法中的距离估算值与实际值越接近,最终搜索速度越快。启发中的估价是用估价函数表示的,如:
f(n) = g(n) + h(n) 其中f(n) 是节点n的估价函数,g(n)实在状态空间中从初始节点到n节点的实际代价,h(n)是从n到目 标节点最佳路径的估计代价。其中最重要的是h(n)函数,要求
h(n)<h'(n) 其中h'(n)为实际中当前状态要到达目标状态的步骤数。
八数码问题就是在一个3*3的矩阵中摆放1-8一共八个数字,还有一个空余的位置用于移动来改变当前的位置来达到最终的状态。如下图
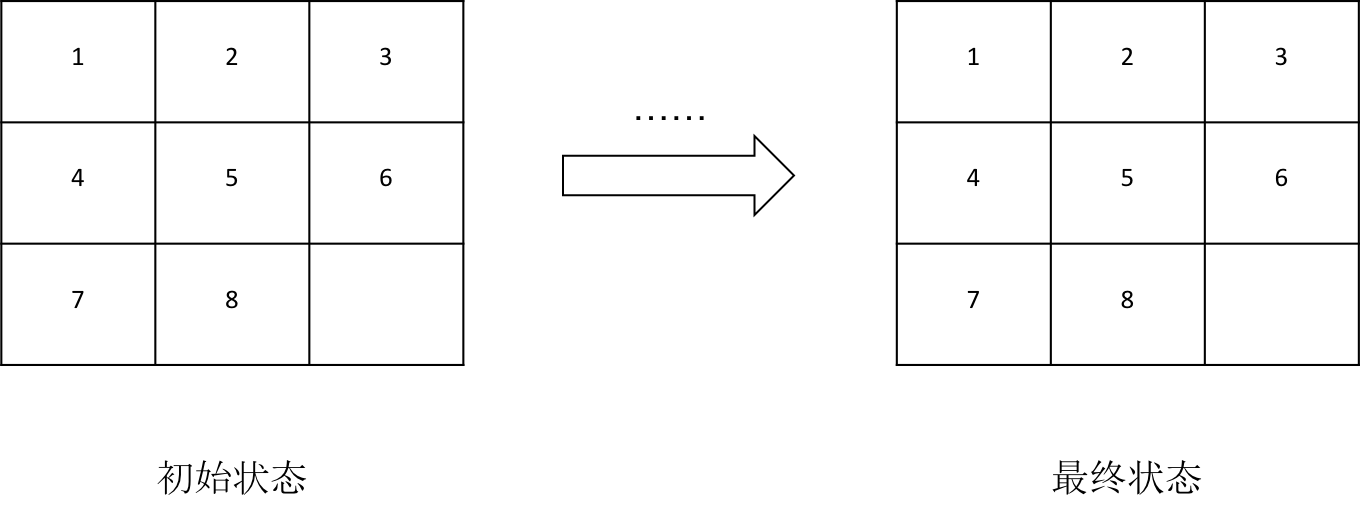
既然明白了,让我们动手试试吧
实验一:
A算法程序设计
本程序用于实现例3.3中的10 x 10个方格中从指定起点到指定终点的最短路径,其中 可以在任意方格中放置障碍。对于10 x 10个方格使用二维数组m_a[10] [10]表示,每个 方格用数组元素表示。
寻路代码:
// AStarPathFinding.cpp: implementation of the AStarPathFinding class.
//
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "astar.h"
#include "AStarPathFinding.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[]=__FILE__;
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#endif
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Construction/Destruction
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int MaxDistance = 9999;
AStarPathFinding::AStarPathFinding():m_steps(0)
{
}
AStarPathFinding::~AStarPathFinding()
{
//千万不能有这句代码,因为startNode已加入OPEN表,会在释放OPEN表
//的时候释放,否则会造成重复释放,出现bug
//delete startNode;
delete endNode;
////释放迷宫布局数组:注意多维数组空间释放
for (int i = 0;i < m_rows;++i)
{
delete[] m_maze[i];
}
delete[] m_maze;
for (i = 0;i < m_rows;++i)
{
delete[] m_path[i];
}
delete[] m_path;
//释放OPEN表以及CLOSED表内存空间
clear();
}
void AStarPathFinding::clear()
{
vector<Node*>::iterator iter;
for (iter = OPENTable.begin();iter != OPENTable.end();++iter)
{
delete (*iter);
}
OPENTable.clear();
vector<Node*>::iterator iter2;
for (iter2 = CLOSEDTable.begin();iter2 != CLOSEDTable.end();++iter2)
{
delete (*iter2);
}
CLOSEDTable.clear();
}
void AStarPathFinding::init(CPoint st,CPoint ed,int **mapinfo)
{
dx[0] =dx[4] = dx[5] = -1;
dx[1] =dx[3] = 0;
dx[2] =dx[6] = dx[7] = 1;
dy[3] = dy[4] = dy[7] = -1;
dy[0] =dy[2] = 0;
dy[1] =dy[5] = dy[6] = 1;
readMap(st,ed,mapinfo);
//分配空间
m_path = new int *[m_rows];
for (int i = 0;i < m_rows;++i)
{
m_path[i] = new int[m_cols];
}
startNode = new Node;
startNode->x = m_startX;
startNode->y = m_startY;
startNode->g = 0;
startNode->h = judge(startNode->x,startNode->y);
startNode->f = startNode->g + startNode->h;
startNode->father = NULL;
endNode = new Node;
endNode->x = m_endX;
endNode->y = m_endY;
endNode->father = NULL;
}
int AStarPathFinding::pathFinding()
{
//判断起始点和目标点是否是同一点
if (m_startX == m_endX && m_startY == m_endY)
{
return 1;
}
OPENTable.push_back(startNode);//起始点装入OPEN表
//对vector中元素进行排序:将最后一个元素加入原本已序的heap内
push_heap(OPENTable.begin(),OPENTable.end(),HeapCompare_f());
Node *tempNode = new Node;
//开始遍历
for (;;)
{
if (OPENTable.empty())//判断OPEN表是否为空
{
return 2;
}
tempNode = OPENTable.front();//注意:OPEN表为空会导致未定义行为
++m_steps;
//将第一个元素移到最后,并将剩余区间重新排序,组成新的heap
pop_heap(OPENTable.begin(),OPENTable.end(),HeapCompare_f());
OPENTable.pop_back();//删除最后一个元素
//判断是否已经搜寻到目标节点
if (tempNode->x == m_endX && tempNode->y == m_endY)
{
endNode->g = tempNode->g;
endNode->h = tempNode->h;
endNode->f = tempNode->f;
endNode->father = tempNode->father;
generatePath();
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0;i < 8;++i)//针对每个子节点
{
int nextX = tempNode->x + dx[i];
int nextY = tempNode->y + dy[i];
if (isIllegle(nextX,nextY))
{
//注意:障碍物角落不能直接通过
if (1 == *(*(m_maze + tempNode->x) + nextY) ||
1 == *(*(m_maze + nextX) + tempNode->y))
{
continue;
}
//计算此子节点的g值
int newGVal;
if (!dx[i] && !dy[i])//位于对角线上
{
newGVal = tempNode->g + 14;
}
else
newGVal = tempNode->g + 10;
//搜索OPEN表,判断此点是否在OPEN表中
vector<Node*>::iterator OPENTableResult;
for (OPENTableResult = OPENTable.begin();
OPENTableResult != OPENTable.end();++OPENTableResult)
{
if ((*OPENTableResult)->x == nextX &&
(*OPENTableResult)->y == nextY)
{
break;
}
}
//此子节点已经存在于OPEN表中
if (OPENTableResult != OPENTable.end())
{
//OPEN表中节点的g值已经是最优的,则跳过此节点
if ((*OPENTableResult)->g <= newGVal)
{
continue;
}
}
//搜索CLOSED表,判断此节点是否已经存在于其中
vector<Node*>::iterator CLOSEDTableResult;
for (CLOSEDTableResult = CLOSEDTable.begin();
CLOSEDTableResult != CLOSEDTable.end();++CLOSEDTableResult)
{
if ((*CLOSEDTableResult)->x == nextX &&
(*CLOSEDTableResult)->y == nextY)
{
break;
}
}
//此节点已经存在于CLOSED表中
if (CLOSEDTableResult != CLOSEDTable.end())
{
//CLOSED表中的节点已经是最优的,则跳过
if ((*CLOSEDTableResult)->g <= newGVal)
{
continue;
}
}
//此节点是迄今为止的最优节点
Node *bestNode = new Node;
bestNode->x = nextX;
bestNode->y = nextY;
bestNode->father = tempNode;
bestNode->g = newGVal;
bestNode->h = judge(nextX,nextY);
bestNode->f = bestNode->g + bestNode->h;
//如果已经存在于CLOSED表中,将其移除
if (CLOSEDTableResult != CLOSEDTable.end())
{
delete (*CLOSEDTableResult);
CLOSEDTable.erase(CLOSEDTableResult);
}
//如果已经存在于OPEN表,更新
if (OPENTableResult != OPENTable.end())
{
delete (*OPENTableResult);
OPENTable.erase(OPENTableResult);
//重新建堆,实现排序。注意不能用sort_heap,因为如果容器为空的话会出现bug
make_heap(OPENTable.begin(),OPENTable.end(),HeapCompare_f());
}
OPENTable.push_back(bestNode);//将最优节点放入OPEN表
push_heap(OPENTable.begin(),OPENTable.end(),HeapCompare_f());//重新排序
}
}
CLOSEDTable.push_back(tempNode);
}
return 3;
}
void AStarPathFinding::generatePath()
{
Node *nodeChild = endNode;
Node *nodeParent = endNode->father;
do
{
*(*(m_path + nodeChild->x) + nodeChild->y) = NODE_PATH;//标记为路径上的点
nodeChild = nodeParent;
nodeParent = nodeParent->father;
} while (nodeChild != startNode);
*(*(m_path + startNode->x) + startNode->y) = NODE_PATH;//标记为路径上的点
}
void AStarPathFinding::printPath(int **result)
{
CFile fin("result.txt",CFile::modeCreate|CFile::modeWrite);
for (int i = 0;i < m_rows;++i)
{
for (int j = 0;j < m_cols;++j)
{
if (NODE_PATH == *(*(m_path + i) + j))
{
result[i][j]=1;
}
else
result[i][j]=0;
CString s;
s.Format("%d ",*(*(m_path + i) + j));
fin.Write(s,2);
}
fin.Write("\r\n",2);
}
fin.Flush();
fin.Close();
}
bool AStarPathFinding::readMap(CPoint st,CPoint ed,int **mapinfo)
{
//从文本文件读取迷宫布局信息
CFile fin(("map.txt"),CFile::modeWrite|CFile::modeCreate);
m_rows=20;
m_cols=40;
//多维数组空间分配
m_maze = new int *[m_rows];
for (int i = 0;i < m_rows;++i)
{
m_maze[i] = new int[m_cols];
}
m_startY=st.x;
m_startX=st.y;
m_endY=ed.x;
m_endX=ed.y;
for (i = 0;i < m_rows;++i)
{
for (int j = 0;j < m_cols;++j)
{
*(*(m_maze + i) + j)=mapinfo[i][j];
CString s;
s.Format("%d ",*(*(m_maze + i) + j));
fin.Write(s,2);
}
fin.Write("\r\n",2);
}
fin.Flush();
fin.Close();
return true;
}
int AStarPathFinding::judge(int x, int y)
{
return (10 * (abs(m_endX - x) + abs(m_endY - y)));
}
bool AStarPathFinding::isIllegle(int x, int y)
{
if (x >= 0 && x < m_rows &&
y >= 0 && y < m_cols &&
*(*(m_maze + x) + y) == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}实在不行,详细工程打包见文末下载
二,产生式系统反向推理算法
产生式规则
简称产生式。它是指形如α─→β或IFαTHENβ或其等价形式的一条规则,其中α称为产生式的左部或前件;β称为产生式的右部或后件。①如果α、β分别代表需要注视的一组条件及其成立时需要采取的行动,那么称为条件-行动型产生式;②如果α、β分别代表前提及其相应的结论,那么称为前提-结论型产生式。人工智能中的推理很多是建立在直观经验基础上的不精确推理,而产生式在表示和运用不精确知识方面具有灵活性,因此许多专家系统采用产生式系统为体系结构。
折叠编辑本段组成
一个产生式系统由下列3部分组成:
一个总数据库(global database),它含有与具体任务有关的信息;随着应用情况的不同,这些数据库可能像数字矩阵那样简单,也可能像检索文件结构那样复杂。
一套规则,它对数据库进行操作运算。每条规则由左右两部分组成,左部鉴别规则的适用性或先决条件,右部描述规则应用时所完成的动作。应用规则来改变数据库。
一个控制策略,它确定应该采用哪一条适用规则,而且当数据库的终止条件满足时,就停止计算
实验二:一、实验目的及要求
1.理解产生式系统的结构原理与实际应用。
2.掌握产生式规则表示及规则库组建的实现方法。
3.理解推理机的算法原理并掌握其编程实现方法。
4.熟悉和掌握产生式系统的运行机制,掌握基于规则推理的基本
方法。
二、实验内容与要求
运用所学知识,设计包含 15 条规则的规则库,并编程实现一个简
单的产生式系统,实现反向推理。要求所开发的系统能识别老虎,金钱豹,斑马,长颈鹿,企鹅,鸵鸟等 6 种动物,并能通过反向推理得
到正确的动物识别结果。
三、实验原理
反向推理:从目标出发,反向使用规则进行推理,朝初始事实/
数据方向前进。又称为反向推理、目标驱动的推理。反向推理算法如
下:
步 1.将初始事实/数据置入动态数据库,将目标条件置入目标链。
步 2.若目标链为空,推理成功,结束。
步3.取出目标链中第一个目标,用动态数据库中的事实同其匹配,
若匹配成功,转步 2。
步 4.用规则集中的各规则同该目标匹配,若匹配成功,则将第一
个匹配成功且未用过的规则的前提作为新的目标,并取代原来的父目标加入目标链,转步 3。
步 5.若该目标是初始目标,则推理失败,退出。
步 6.将该目标的父目标移回目标链,取代该目标及其兄弟目标,
转步 3。
代码:
// 产生式系统Dlg.cpp : implementation file
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "产生式系统.h"
#include "产生式系统Dlg.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
#endif
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CAboutDlg dialog used for App About
class CAboutDlg : public CDialog
{
public:
CAboutDlg();
// Dialog Data
//{{AFX_DATA(CAboutDlg)
enum { IDD = IDD_ABOUTBOX };
//}}AFX_DATA
// ClassWizard generated virtual function overrides
//{{AFX_VIRTUAL(CAboutDlg)
protected:
virtual void DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX); // DDX/DDV support
//}}AFX_VIRTUAL
// Implementation
protected:
//{{AFX_MSG(CAboutDlg)
//}}AFX_MSG
DECLARE_MESSAGE_MAP()
};
CAboutDlg::CAboutDlg() : CDialog(CAboutDlg::IDD)
{
//{{AFX_DATA_INIT(CAboutDlg)
//}}AFX_DATA_INIT
}
void CAboutDlg::DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX)
{
CDialog::DoDataExchange(pDX);
//{{AFX_DATA_MAP(CAboutDlg)
//}}AFX_DATA_MAP
}
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CAboutDlg, CDialog)
//{{AFX_MSG_MAP(CAboutDlg)
// No message handlers
//}}AFX_MSG_MAP
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CMyDlg dialog
CMyDlg::CMyDlg(CWnd* pParent /*=NULL*/)
: CDialog(CMyDlg::IDD, pParent)
{
//{{AFX_DATA_INIT(CMyDlg)
m_r = _T("");
m_s = _T("");
m_t = FALSE;
m_f = _T("");
m_g = _T("");
//}}AFX_DATA_INIT
// Note that LoadIcon does not require a subsequent DestroyIcon in Win32
m_hIcon = AfxGetApp()->LoadIcon(IDR_MAINFRAME);
}
void CMyDlg::DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX)
{
CDialog::DoDataExchange(pDX);
//{{AFX_DATA_MAP(CMyDlg)
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT1, m_r);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT2, m_s);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT3, m_t);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT4, m_f);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT5, m_g);
//}}AFX_DATA_MAP
}
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CMyDlg, CDialog)
//{{AFX_MSG_MAP(CMyDlg)
ON_WM_SYSCOMMAND()
ON_WM_PAINT()
ON_WM_QUERYDRAGICON()
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON1, OnButton1)
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON2, OnButton2)
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON5, OnButton5)
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON3, OnButton3)
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON4, OnButton4)
ON_EN_CHANGE(IDC_EDIT1, OnChangeEdit1)
ON_EN_CHANGE(IDC_EDIT2, OnChangeEdit2)
ON_EN_CHANGE(IDC_EDIT3, OnChangeEdit3)
ON_EN_CHANGE(IDC_EDIT4, OnChangeEdit4)
ON_EN_CHANGE(IDC_EDIT5, OnChangeEdit5)
//}}AFX_MSG_MAP
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CMyDlg message handlers
BOOL CMyDlg::OnInitDialog()
{
CDialog::OnInitDialog();
// Add "About..." menu item to system menu.
// IDM_ABOUTBOX must be in the system command range.
ASSERT((IDM_ABOUTBOX & 0xFFF0) == IDM_ABOUTBOX);
ASSERT(IDM_ABOUTBOX < 0xF000);
CMenu* pSysMenu = GetSystemMenu(FALSE);
if (pSysMenu != NULL)
{
CString strAboutMenu;
strAboutMenu.LoadString(IDS_ABOUTBOX);
if (!strAboutMenu.IsEmpty())
{
pSysMenu->AppendMenu(MF_SEPARATOR);
pSysMenu->AppendMenu(MF_STRING, IDM_ABOUTBOX, strAboutMenu);
}
}
// Set the icon for this dialog. The framework does this automatically
// when the application's main window is not a dialog
SetIcon(m_hIcon, TRUE); // Set big icon
SetIcon(m_hIcon, FALSE); // Set small icon
// TODO: Add extra initialization here
return TRUE; // return TRUE unless you set the focus to a control
}
void CMyDlg::OnSysCommand(UINT nID, LPARAM lParam)
{
if ((nID & 0xFFF0) == IDM_ABOUTBOX)
{
CAboutDlg dlgAbout;
dlgAbout.DoModal();
}
else
{
CDialog::OnSysCommand(nID, lParam);
}
}
// If you add a minimize button to your dialog, you will need the code below
// to draw the icon. For MFC applications using the document/view model,
// this is automatically done for you by the framework.
void CMyDlg::OnPaint()
{
if (IsIconic())
{
CPaintDC dc(this); // device context for painting
SendMessage(WM_ICONERASEBKGND, (WPARAM) dc.GetSafeHdc(), 0);
// Center icon in client rectangle
int cxIcon = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXICON);
int cyIcon = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYICON);
CRect rect;
GetClientRect(&rect);
int x = (rect.Width() - cxIcon + 1) / 2;
int y = (rect.Height() - cyIcon + 1) / 2;
// Draw the icon
dc.DrawIcon(x, y, m_hIcon);
}
else
{
CDialog::OnPaint();
}
}
// The system calls this to obtain the cursor to display while the user drags
// the minimized window.
HCURSOR CMyDlg::OnQueryDragIcon()
{
return (HCURSOR) m_hIcon;
}
void CMyDlg::OnChangeEdit1()
{
UpdateData(true);
}
void CMyDlg::OnChangeEdit2()
{
UpdateData(true);
}
void CMyDlg::OnChangeEdit3()
{
UpdateData(true);
}
void CMyDlg::OnChangeEdit4()
{
UpdateData(true);
}
void CMyDlg::OnChangeEdit5()
{
UpdateData(true);
}
void CMyDlg::OnButton1() //建初始规则
{
int i;
rule[0].reason=_T("有奶");
rule[0].result=_T("哺乳动物");
rule[0].t=false;
rule[1].reason=_T("哺乳动物,吃肉");
rule[1].result=_T("食肉动物");
rule[1].t=false;
rule[2].reason=_T("哺乳动物,有蹄");
rule[2].result=_T("有蹄动物");
rule[2].t=false;
rule[3].reason=_T("食肉动物,黄褐色,有黑色条纹");
rule[3].result=_T("老虎");
rule[3].t=true;
rule[4].reason=_T("食肉动物,黄褐色,有黑色斑点");
rule[4].result=_T("金钱豹");
rule[4].t=true;
rule[5].reason=_T("有蹄动物,长腿,长脖子,黄褐色,有暗斑点");
rule[5].result=_T("长颈鹿");
rule[5].t=true;
rule[6].reason=_T("有蹄动物,白色,有黑色条纹");
rule[6].result=_T("斑马");
rule[6].t=true;
rule[7].reason=_T("鸟,不会飞,长腿,长脖子,黑白色");
rule[7].result=_T("鸵鸟");
rule[7].t=true;
rule[8].reason=_T("鸟,不会飞,会游泳,黑白色");
rule[8].result=_T("企鹅");
rule[8].t=true;
//rule[9].reason=_T("鸟,擅飞,不怕风浪");
//rule[9].result=_T("海燕");
//rule[9].t=true;
rule[10].reason=_T("有毛");
rule[10].result=_T("哺乳动物");
rule[10].t=false;
rule[11].reason=_T("有羽毛");
rule[11].result=_T("鸟");
rule[11].t=false;
rule[12].reason=_T("会飞,生蛋");
rule[12].result=_T("鸟");
rule[12].t=false;
rule[13].reason=_T("哺乳动物,有爪,有犬齿,目盯前方,吃肉");
rule[13].result=_T("食肉动物");
rule[13].t=false;
num=14;
CDC *pDC=GetDlgItem(IDC_RULE)->GetDC();
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
{
pDC->TextOut(5,i*20,rule[i].reason);
pDC->TextOut(310,i*20,rule[i].result);
}
}
void CMyDlg::OnButton2() //退出
{
}
void CMyDlg::OnButton5() //添加
{
rule[num].reason=m_r;
rule[num].result=m_s;
rule[num].t=m_t;
CDC *pDC=GetDlgItem(IDC_RULE)->GetDC();
pDC->TextOut(5,num*20+5,rule[num].reason);
pDC->TextOut(410,num*20+5,rule[num].result);
num++;
MessageBox("成功添加!");
}
BOOL com(CString str1[],int n,CString str2)
{
char s1[50],*s2;
CString str[100];
strcpy(s1,str2);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
int m=0;
while(s2!=NULL)
{
str[m++].Format("%s",s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}
int t=0;
for(int j=0;j<m;j++)
{ for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(str1[i]==str[j])
{t=1;break;}
if(t==0) return(false);
t=0;
}
return(true);
}
void CMyDlg::OnButton3() //正向推理
{
CDC *pDC=GetDlgItem(IDC_RESULT)->GetDC();
if(rule[0].reason=="")
{
MessageBox("没有规则库!");
return;
}
CString db[50];
RULE wait[50];
CString str;
char s1[50],*s2;
int n=0;
strcpy(s1,m_f);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
while(s2!=NULL)
{
db[n++].Format("%s",s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}
int k=0,t=1;
BOOL bz[100]={100*0};
while(t)
{
for(int i=0;i<num;i++)
if(com(db,n,rule[i].reason)&&rule[i].t)
{
pDC->TextOut(10,15,"推理结果:");
pDC->TextOut(100,15,rule[i].result);
t=0;
}
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
if(com(db,n,rule[i].reason)&&!bz[i])
{
wait[k].reason=rule[i].reason;
wait[k++].result=rule[i].result;
bz[i]=1;
}
if(k==0)
{
pDC->TextOut(10,10,"推理失败!");
t=0;
}
for(i=0;i<k;i++)
db[i+n]=wait[i].result;
n+=k;
k=0;
}
}
void CMyDlg::OnButton4() //反向推理
{
CDC *pDC=GetDlgItem(IDC_RESULT)->GetDC();
if(rule[0].reason=="")
{
MessageBox("没有规则库!");
return;
}
CString db[50];
RULE goal[50];
CString str,g[50];
char s1[50],*s2;
int n=0,t=1;
strcpy(s1,m_f);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
while(s2!=NULL)
{
db[n++].Format("%s",s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}
int k=-1,k1=-1;
goal[++k].reason=m_g;
goal[k].result=m_g;
g[++k1]=m_g;
while(t)
{
if(k==-1)
{
pDC->TextOut(10,15,"推理结果:");
pDC->TextOut(100,15,m_g);
t=0;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(goal[k].reason==db[i])
break;
if(i<n)
{
k--;continue;
}
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
if(rule[i].result==goal[k].reason)
{
for(int j=0;j<k1;j++)
if(g[j]==rule[i].reason&&g[j]!=m_g) break;
if(j==k1)
{
g[++k1]=rule[i].reason;
strcpy(s1,rule[i].reason);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
k--;
while(s2!=NULL)
{
str.Format("%s",s2);
goal[++k].reason=str;
goal[k].result=rule[i].result;
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}
}
else continue;
break;
}
if(i==num)
if(goal[k].reason==m_g)
{
pDC->TextOut(10,10,"推理失败!");
t=0;
}
else
{
str=goal[k].result;
for(i=k;i>=0;i--)
if(goal[k].result!=str) break;
k=i+1;
goal[k].reason=str;
}
}
}
三,BP神经网络算法设计与实现
传统的BP算法简述
BP算法是一种有监督式的学习算法,其主要思想是:输入学习样本,使用反向传播算法对网络的权值和偏差进行反复的调整训练,使输出的向量与期望向量尽可能地接近,当网络输出层的误差平方和小于指定的误差时训练完成,保存网络的权值和偏差。具体步骤如下:
(1)初始化,随机给定各连接权[w],[v]及阀值θi,rt。
(2)由给定的输入输出模式对计算隐层、输出层各单元输出
bj=f(■wijai-θj) ct=f(■vjtbj-rt)
式中:bj为隐层第j个神经元实际输出;ct为输出层第t个神经元的实际输出;wij为输入层至隐层的连接权;vjt为隐层至输出层的连接权。
dtk=(ytk-ct)ct(1-ct) ejk=[■dtvjt] bj(1-bj)
(3)选取下一个输入模式对返回第2步反复训练直到网络设输出误差达到要求结束训练。
传统的BP算法,实质上是把一组样本输入/输出问题转化为一个非线性优化问题,并通过负梯度下降算法,利用迭代运算求解权值问题的一种学习方法,但其收敛速度慢且容易陷入局部极小,为此提出了一种新的算法,即高斯消元法。
折叠改进的BP网络算法
2.1 改进算法概述
此前有人提出:任意选定一组自由权,通过对传递函数建立线性方程组,解得待求权。本文在此基础上将给定的目标输出直接作为线性方程等式代数和来建立线性方程组,不再通过对传递函数求逆来计算神经元的净输出,简化了运算步骤。没有采用误差反馈原理,因此用此法训练出来的神经网络结果与传统算法是等效的。其基本思想是:由所给的输入、输出模式对通过作用于神经网络来建立线性方程组,运用高斯消元法解线性方程组来求得未知权值,而未采用传统BP网络的非线性函数误差反馈寻优的思想。
2.2 改进算法的具体步骤
对给定的样本模式对,随机选定一组自由权,作为输出层和隐含层之间固定权值,通过传递函数计算隐层的实际输出,再将输出层与隐层间的权值作为待求量,直接将目标输出作为等式的右边建立方程组来求解。
现定义如下符号(见图1):x (p)输入层的输入矢量;y (p)输入层输入为x (p)时输出层的实际输出矢量;t (p)目标输出矢量;n,m,r分别为输入层、隐层和输出层神经元个数;W为隐层与输入层间的权矩阵;V为输出层与隐层间的权矩阵。具体步骤如下:
(1)随机给定隐层和输入层间神经元的初始权值wij。
(2)由给定的样本输入xi(p)计算出隐层的实际输出aj(p)。为方便起见将图1网络中的阀值写入连接权中去,令:隐层阀值θj=wnj,x(n)=-1,则:
aj(p)=f(■wijxi(p)) (j=1,2…m-1)。
(3)计算输出层与隐层间的权值vjr。以输出层的第r个神经元为对象,由给定的输出目标值tr(p)作为等式的多项式值建立方程,用线性方程组表示为:
a0(1)v1r+a1(1)v2r+…+am(1)vmr=tr(1)a0(2)v1r+a1(2)v2r+…+am(2)vmr=tr(2) ……a0(p)v1r+a1(p)v2r+…+am(p)vmr=tr(p) 简写为: Av=T
为了使该方程组有唯一解,方程矩阵A为非奇异矩阵,其秩等于其增广矩阵的秩,即:r(A)=r(A┊B),且方程的个数等于未知数的个数,故取m=p,此时方程组的唯一解为: Vr=[v0r,v2r,…vmr](r=0,1,2…m-1)
(4)重复第三步就可以求出输出层m个神经元的权值,以求的输出层的权矩阵加上随机固定的隐层与输入层的权值就等于神经网络最后训练的权矩阵。
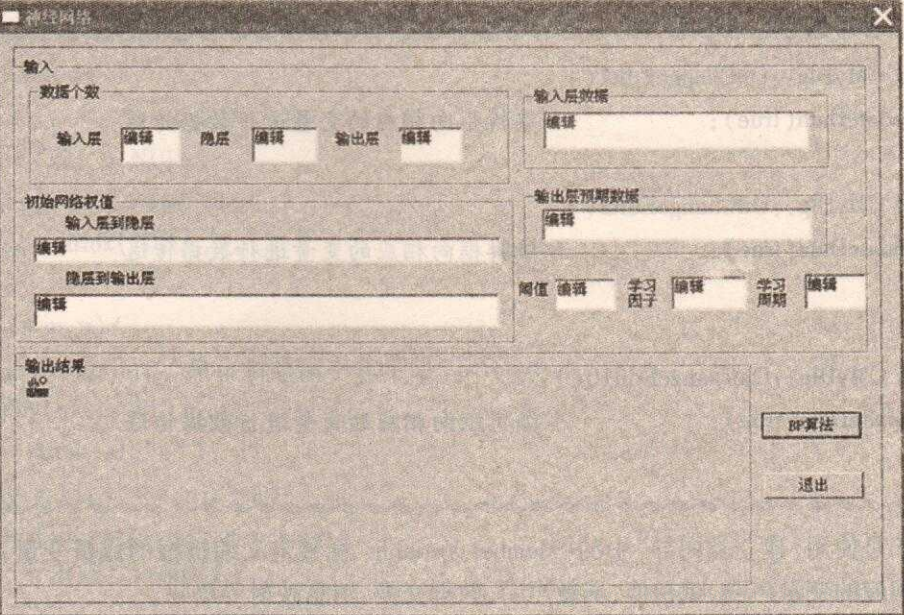
BP算法程序设计
代码:
// test3Dlg.cpp : implementation file
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "test3.h"
#include "test3Dlg.h"
#include "math.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#define new DEBUG_NEW
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
#endif
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CTest3Dlg dialog
CTest3Dlg::CTest3Dlg(CWnd* pParent /*=NULL*/)
: CDialog(CTest3Dlg::IDD, pParent)
{
//{{AFX_DATA_INIT(CTest3Dlg)
m_n = 3;
m_u = 4;
m_m = 3;
m_in = _T("0.3,0.8,0.1");
m_out = _T("1,0,0");
m_w1 = _T("0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25");
m_w2 = _T("0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25,0.25");
m_y = 0.1f;
m_x = 0.8f;
m_t = 1.0f;
//}}AFX_DATA_INIT
// Note that LoadIcon does not require a subsequent DestroyIcon in Win32
m_hIcon = AfxGetApp()->LoadIcon(IDR_MAINFRAME);
}
void CTest3Dlg::DoDataExchange(CDataExchange* pDX)
{
CDialog::DoDataExchange(pDX);
//{{AFX_DATA_MAP(CTest3Dlg)
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT1, m_n);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT2, m_u);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT3, m_m);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT4, m_in);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT5, m_out);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT6, m_w1);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT7, m_w2);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT8, m_y);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT9, m_x);
DDX_Text(pDX, IDC_EDIT10, m_t);
//}}AFX_DATA_MAP
}
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CTest3Dlg, CDialog)
//{{AFX_MSG_MAP(CTest3Dlg)
ON_WM_PAINT()
ON_WM_QUERYDRAGICON()
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON1, OnButton1)
ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_BUTTON2, OnButton2)
//}}AFX_MSG_MAP
END_MESSAGE_MAP()
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// CTest3Dlg message handlers
BOOL CTest3Dlg::OnInitDialog()
{
CDialog::OnInitDialog();
// Set the icon for this dialog. The framework does this automatically
// when the application's main window is not a dialog
SetIcon(m_hIcon, TRUE); // Set big icon
SetIcon(m_hIcon, FALSE); // Set small icon
// TODO: Add extra initialization here
return TRUE; // return TRUE unless you set the focus to a control
}
// If you add a minimize button to your dialog, you will need the code below
// to draw the icon. For MFC applications using the document/view model,
// this is automatically done for you by the framework.
void CTest3Dlg::OnPaint()
{
if (IsIconic())
{
CPaintDC dc(this); // device context for painting
SendMessage(WM_ICONERASEBKGND, (WPARAM) dc.GetSafeHdc(), 0);
// Center icon in client rectangle
int cxIcon = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CXICON);
int cyIcon = GetSystemMetrics(SM_CYICON);
CRect rect;
GetClientRect(&rect);
int x = (rect.Width() - cxIcon + 1) / 2;
int y = (rect.Height() - cyIcon + 1) / 2;
// Draw the icon
dc.DrawIcon(x, y, m_hIcon);
}
else
{
CDialog::OnPaint();
}
}
// The system calls this to obtain the cursor to display while the user drags
// the minimized window.
HCURSOR CTest3Dlg::OnQueryDragIcon()
{
return (HCURSOR) m_hIcon;
}
void CTest3Dlg::OnButton1()
{
// TODO: Add your control notification handler code here
UpdateData(true);
CDC *p=GetDlgItem(IDC_OUT)->GetDC();
int n,m,u;
float x[10],y[10],w1[10][10],w2[10][10];
char s1[80],*s2;
CString s,S;
strcpy(s1,m_in);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
int i=1;
while(s2!=NULL){
x[i++]=atof(s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}
if(i<m_n){
MessageBox("输入层数据个数不够");
return ;
}
x[0]=-1;
strcpy(s1,m_out);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
i=1;
while(s2!=NULL){
y[i++]=atof(s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}
if(i<m_m){
MessageBox("输出层数据个数不够");
return ;
}
strcpy(s1,m_w1);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
for(i=1;i<=m_n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m_u;j++){
if(s2!=NULL){
w1[i][j]=atof(s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}else{
MessageBox("权值数据个数不够");
return ;
}
}
for(int j=1;j<=m_u;j++)
w1[0][j]=m_y;
strcpy(s1,m_w2);
s2=strtok(s1,",");
for(i=1;i<=m_u;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=m_m;j++){
if(s2!=NULL){
w2[i][j]=atof(s2);
s2=strtok(NULL,",");
}else{
MessageBox("权值数据个数不够");
return ;
}
}
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++)
w2[0][j]=m_y;
float a[10]={10*0},O1[10],O2[10];
int kmax=100,kk=0;
while(kk++<m_t){
x[0]=-1;
for(int j=1;j<=m_u;j++){
a[j]=0;
for(i=0;i<=m_n;i++)
a[j]=a[j]+x[i]*w1[i][j];
O1[j]=1.0/(1+exp(-a[j]));
}
O1[0]=-1;
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++){
a[j]=0;
for(i=0;i<=m_u;i++)
a[j]=a[j]+w2[i][j]*O1[i];
O2[j]=1.0/(1+exp(-a[j]));
}
float c[10],C[10];
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++)
c[j]=O2[j]*(1-O2[j])*(y[j]-O2[j]);
for(j=1;j<=m_u;j++){
C[j]=0;
for(int k=1;k<=m_m;k++)
C[j]=C[j]+c[k]*w2[j][k];
C[j]=C[j]*O1[j]*(1-O1[j]);
}
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++)
for(i=1;i<=m_u;i++)
w2[i][j]=w2[i][j]+m_x*c[j]*O1[i];
for(j=1;j<=m_u;j++)
for(i=1;i<=m_n;i++)
w1[i][j]=w1[i][j]+m_x*C[j]*x[i];
}
float err=0;
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++)
err=err+(y[j]-O2[j])*(y[j]-O2[j]);
err=err/2.0;
s.Format("%f",err);
p->TextOut(10,10,"误差为:"+s);
p->TextOut(10,30,"结果为:");
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++){
s.Format("%f",O2[j]);
p->TextOut(j*100,30,s);
}
p->TextOut(10,70,"输入层到隐层权值为:");
S="";
for(i=1;i<=m_n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=m_u;j++){
s.Format("%5.3f",w1[i][j]);
S=S+s+" ";
}
p->TextOut(10,90,S);
p->TextOut(10,110,"隐层到输出层权值为:");
S="";
for(i=1;i<=m_u;i++)
for(j=1;j<=m_m;j++){
s.Format("%5.3f",w2[i][j]);
S=S+s+" ";
}
p->TextOut(10,130,S);
}
void CTest3Dlg::OnButton2()
{
// TODO: Add your control notification handler code here
exit(0);
}
程序下载:
实验一:1
实验二:2
实验三:3
实验四:





















 768
768

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








