队列
队列是常见的数据结构之一,队列是“操作受限”的线性表,具有先进先出的特性,在STL中,queue可以通过封装deque来实现,同时也可以通过list来实现,一般来说链表的实现可以分为顺序队列,链式队列和循环队列
顺序队列
要点
- 入队时,当末尾指针tail到达数组容量时,且头指针head != 0,表示数组中还有空间,可以进行数据搬移,否则表示队列满了
- 出队时要进行判空操作
代码实现
#include <assert.h>
//基于数组实现的队列
class MyQueue
{
public:
MyQueue(int capacity)
{
this->capacity = capacity;
items = new int[capacity];
n = capacity;
head = 0;
tail = 0;
}
~MyQueue()
{
if(items != NULL)
{
delete [] items;
items = nullptr;
}
}
//入队
bool enqueue(int val)
{
//表示整个队列都满了
if(tail == n && head == 0)
{
return false;
}
//没有空间,进行数据搬移
if(tail == n)
{
for(int i = head;i < tail;i++)
items[i-head] = items[i];
//搬移之后重新更新head和tail
tail -= head;
head = 0;
}
items[tail] = val;
tail++;
return true;
}
//出队
bool dequeue()
{
if(head == tail)
return false;
head++;
return true;
}
int front()
{
assert(head != tail);
int ret = items[head];
return ret;
}
private:
int* items
int capacity;
int head;
int tail;
int n;
};
基于链表的队列
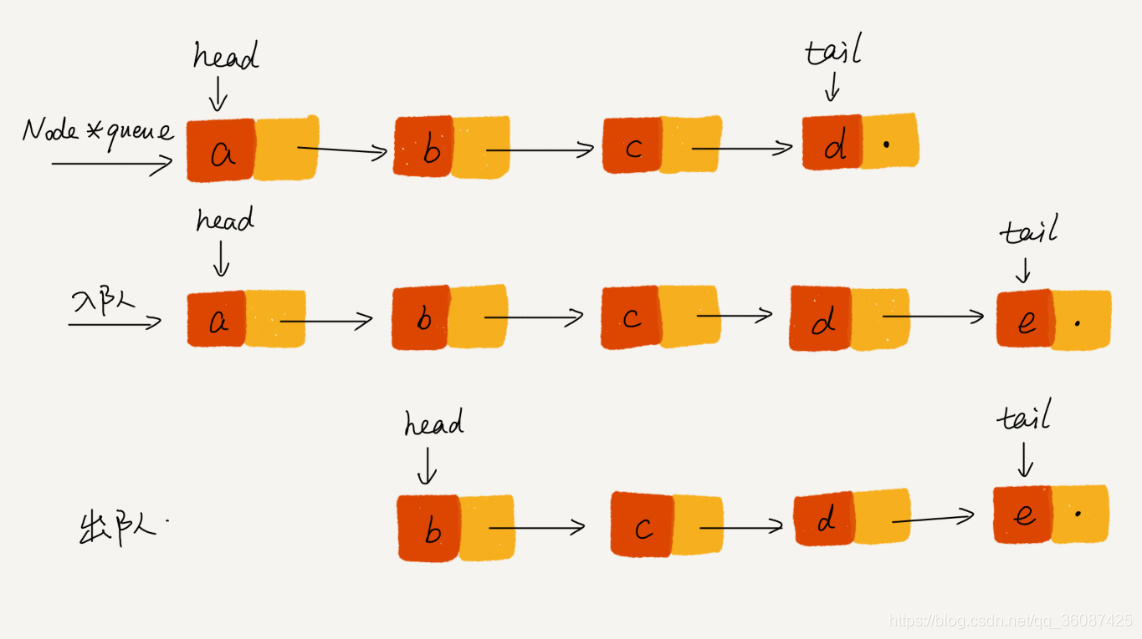
代码实现
#include <assert.h>
class ListNode
{
public:
int val;
ListNode* next;
ListNode(int val):val(val),next(NULL)
{}
};
class MyQueue
{
public:
MyQueue():head(NULL),tail(NULL)
{}
~MyQueue()
{
while(head)
{
ListNode* p = head->next;
delete head;
head = p;
}
}
//入队
void enqueue(int val)
{
if(tail == NULL)
{
ListNode* newNode = new ListNode(val);
head = newNode;
tail = newNode;
}
else
{
tail->next = new ListNode(val);
tail = tail->next;
}
}
//出队
void dequeue()
{
if(head == NULL)
return NULL;
head = head->next;
if(head == NULL)
tail = NULL;
}
int front()
{
assert(head != NULL);
return head->val;
}
private:
ListNode* head;
ListNode* tail;
};
循环队列
这里简单给出循环队列的入队和出队操作,大部分逻辑和以上两个相同
//循环队列的入队出队
bool enqueue(int val)
{
//队列满了
if((tail+1)%n == head)
return false;
items[tail] = val;
tail = (tail+1)%n;
return true;
}
//循环队列的出队
void dequeue()
{
if(head == tail)
return NULL;
head = (head+1)%n;
}





 博客介绍了队列这一常见数据结构,它是操作受限的线性表,有先进先出特性。在STL中可通过封装deque或list实现。还阐述了顺序队列入队、出队要点及代码实现,基于链表的队列代码实现,也简单提及循环队列的入队和出队操作。
博客介绍了队列这一常见数据结构,它是操作受限的线性表,有先进先出特性。在STL中可通过封装deque或list实现。还阐述了顺序队列入队、出队要点及代码实现,基于链表的队列代码实现,也简单提及循环队列的入队和出队操作。
















 13万+
13万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








