我们设定四种路线情况(按顺序0~3编号):
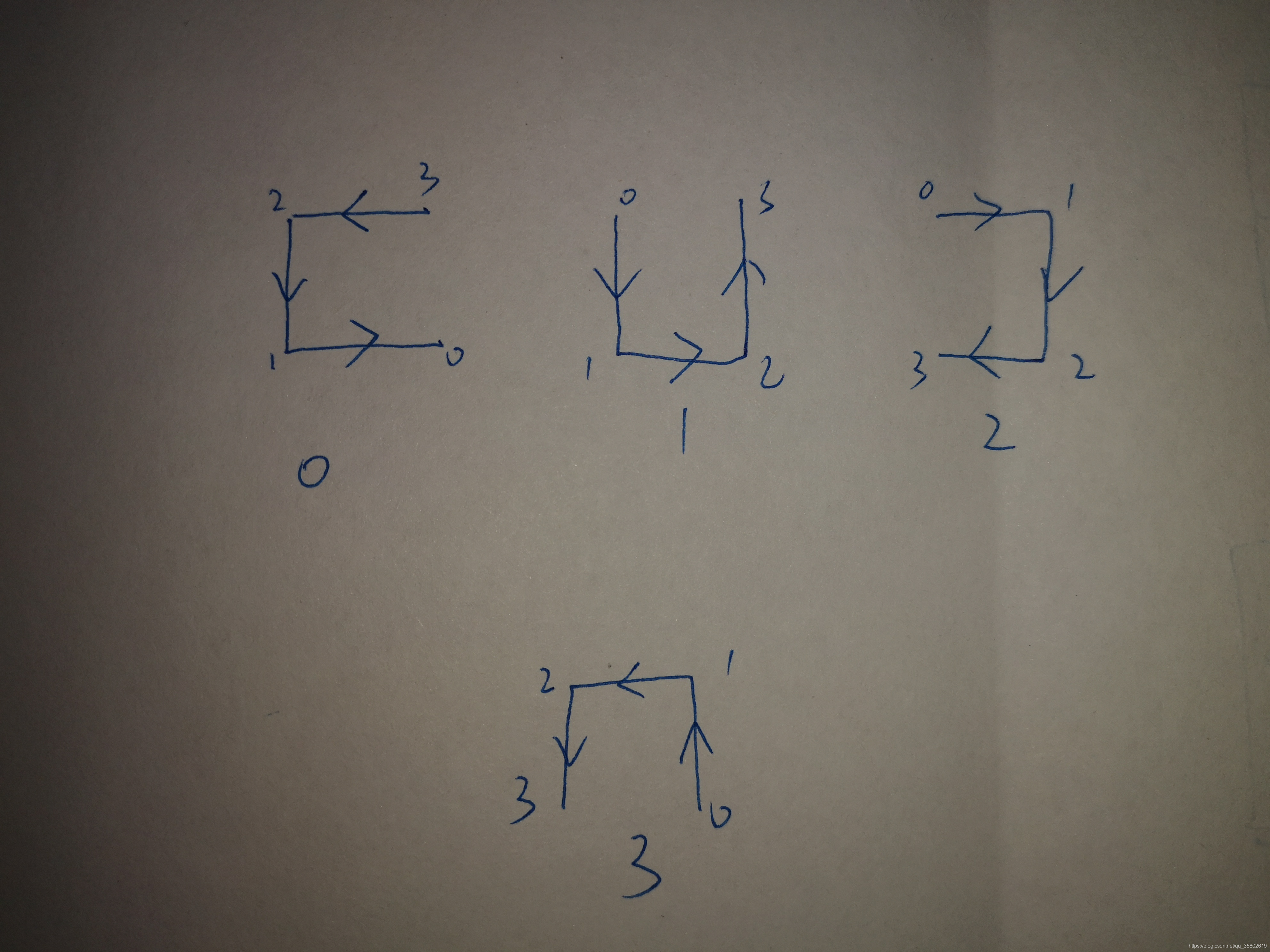
这样我们在想下一层递归分治时,就看出变化:例如1状态的0号位置下一层会变成2。我们每次看比较两坐标,如果不在一个区间块,我们就得出了它们的大小(按图中标定的顺序)。如果在一个区间块,就向下递归寻找。
下面是ac代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
//#include <conio.h>
#include <queue>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int tt[4][4] = {{2,1,0,3},{0,1,2,3},{0,3,2,1},{2,3,0,1}};//储存4种路径的顺序信息
struct Node
{
ll x, y;
}su[1000005];
bool che(Node a, Node b, int k, int gg)
{
// cout << k <<" " <<gg <<endl;
// cout << a.x <<" " << a.y << endl;
// cout << b.x <<" " <<b.y <<endl;
k--;
int ga, gb;//储存a,b在那个区间块
if (a.x <= (1<<k) && a.y <= (1<<k))
{
ga = tt[gg][0];
goto to1;//在左上角
}
else if (a.x > (1<<k) && a.y <= (1<<k))
{
ga = tt[gg][1];
a.x -= (1<<k);
goto to1;//在左下
}
else if (a.x > (1<<k) && a.y > (1<<k))
{
ga = tt[gg][2];
a.x -= (1<<k);
a.y -= (1<<k);
goto to1;//依次类推
}
else if (a.x <= (1<<k) && a.y > (1<<k))
{
ga = tt[gg][3];
a.y -= (1<<k);
goto to1;
}
to1:
if (b.x <= (1<<k) && b.y <= (1<<k))
{
gb = tt[gg][0];
goto to;
}
else if (b.x > (1<<k) && b.y <= (1<<k))
{
gb = tt[gg][1];
b.x -= (1<<k);
goto to;
}
else if (b.x > (1<<k) && b.y > (1<<k))
{
gb = tt[gg][2];
b.x -= (1<<k);
b.y -= (1<<k);
goto to;
}
else if (b.x <= (1<<k) && b.y > (1<<k))
{
gb = tt[gg][3];
b.y -= (1<<k);
goto to;
}
to:
// cout << ga <<" " <<gb <<endl;
// cout << "--------" << endl;
//_getch();
if (ga != gb) return ga < gb;//不在一个区间块,就输出顺序
//否则进行下一层递归
if(gg == 0)
{
if (ga == 0) return che(a, b, k, 3);
else if (ga == 3) return che(a, b, k, 1);
return che(a, b, k, 0);
}
else if (gg == 1)
{
if (ga == 0) return che(a, b, k, 2);
else if (ga == 3) return che(a, b, k, 0);
return che(a, b, k, 1);
}
else if (gg == 2)
{
if (ga == 0) return che(a, b, k, 1);
else if (ga == 3) return che(a, b, k, 3);
return che(a, b, k, 2);
}
else
{
if (ga == 0) return che(a, b, k, 0);
else if (ga == 3) return che(a, b, k, 2);
return che(a, b, k, 3);
}
}
int n, k;
bool cmp(const Node &a, const Node &b)
{
return che(a, b, k, 1);//递归比较a,b顺序
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &k);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &su[i].x, &su[i].y);
sort(su, su + n, cmp);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%lld %lld\n", su[i].x, su[i].y);
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了一种基于递归分治策略的算法实现,通过四种路径情况的设定,对坐标进行比较和排序。该算法首先判断两个坐标是否位于同一区间块,若不在,则直接得出它们的相对顺序;若在同一区间块,则进一步递归处理。代码中使用了C++实现,包括预定义的路径顺序信息、节点结构体和比较函数。
本文介绍了一种基于递归分治策略的算法实现,通过四种路径情况的设定,对坐标进行比较和排序。该算法首先判断两个坐标是否位于同一区间块,若不在,则直接得出它们的相对顺序;若在同一区间块,则进一步递归处理。代码中使用了C++实现,包括预定义的路径顺序信息、节点结构体和比较函数。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








