单继承中没有虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather
{
public:
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CSon : public CFather
{
};
int main()
{
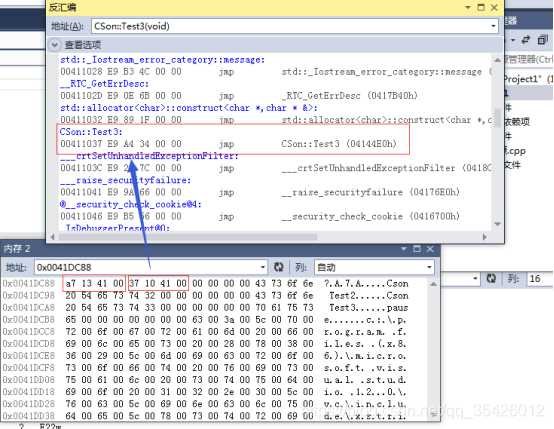
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
内存如下图
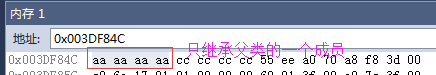
单继承中有虚函数
注意:如果子类有虚函数,父类没有虚函数,子类自己会生成一个虚指针,如果父类有虚指针,子类继承了的话子类写了多个虚函数是不会生成虚指针的,
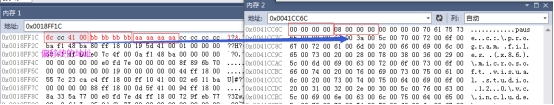
如下代码内存中只有一个虚指针
1子类没有重写虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather
{
public:
virtual void Test()
{
cout << "CFather" << endl;
}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CSon : public CFather
{
public:
virtual void Test2()
{
cout << "Cson Test2" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
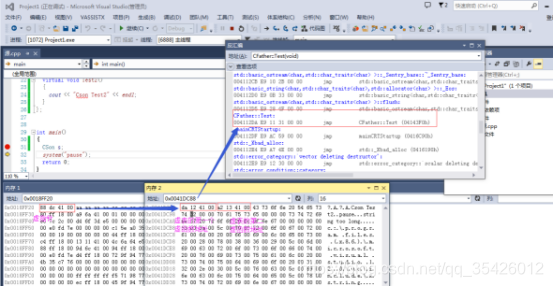
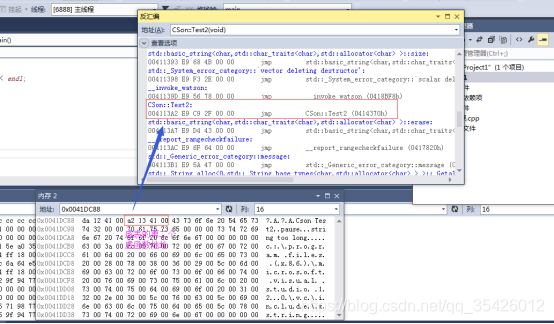
2子类重写虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather
{
public:
virtual void Test()
{
cout << "CFather" << endl;
}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CSon : public CFather
{
public:
virtual void Test()
{
cout << "CSon" << endl;
}
virtual void Test2()
{
cout << "Cson Test2" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
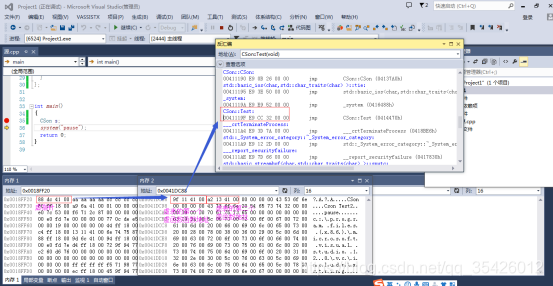
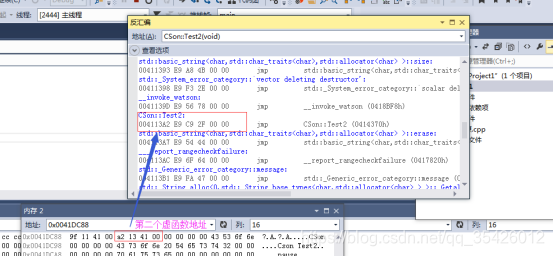
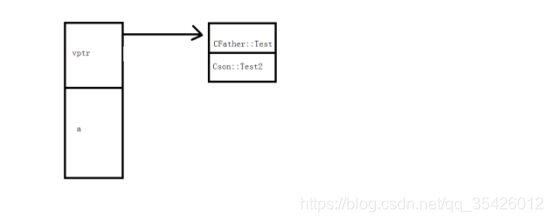
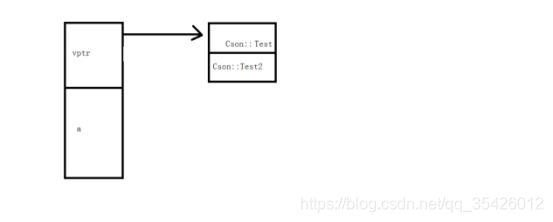
内容简易图如下
多重继承
1多重继承无虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather1
{
public:
void Test()
{
cout << "CFather" << endl;
}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CFather2
{
public:
void Test()
{
cout << "CFather" << endl;
}
int a = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
class CSon : public CFather1,public CFather2
{
public:
void Test2()
{
cout << "Cson Test2" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
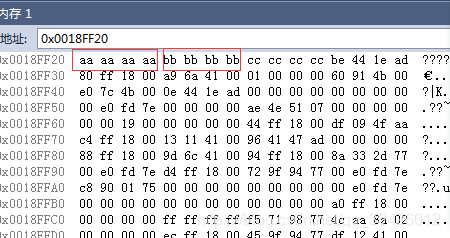
没有虚函数内存中不会生成虚指针
2多重继承有两个父类都有虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather1
{
public:
virtual void Test1()
{
cout << "CFather1" << endl;
}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CFather2
{
public:
virtual void Test2()
{
cout << "CFather2" << endl;
}
int a = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
class CSon : public CFather1,public CFather2
{
public:
virtual void Test1()
{
cout << "Cson Test1" << endl;
}
virtual void Test2()
{
cout << "Cson Test2" << endl;
}
virtual void Test3()
{
cout << "Cson Test3" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
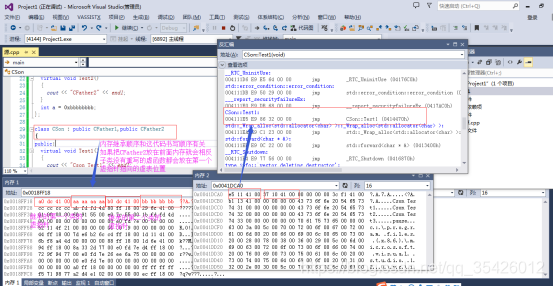
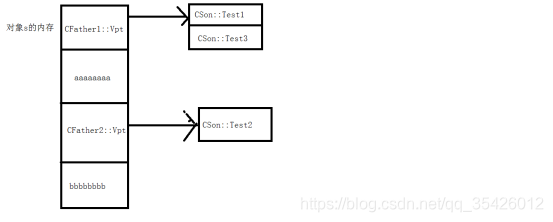
内存结构图如下
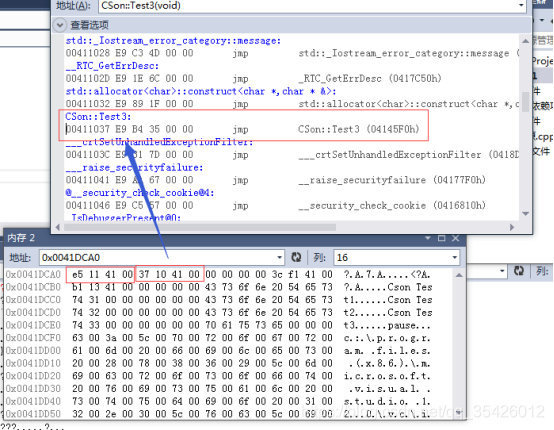
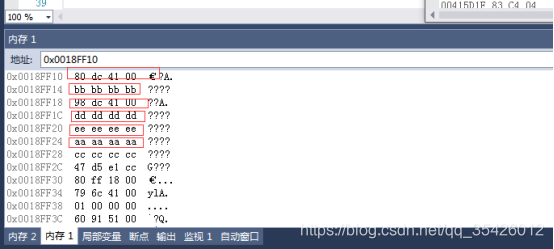
3多重继承有只有一个父类有虚函数
这时候是有虚函数的父类的内存位于最上面,子类的虚函数挂靠到这个父类的虚表中
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather1
{
public:
void Test1()
{
cout << "CFather1" << endl;
}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CFather2
{
public:
virtual void Test2()
{
cout << "CFather2" << endl;
}
int a = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
class CSon : public CFather1,public CFather2
{
public:
virtual void Test2()
{
cout << "Cson Test2" << endl;
}
virtual void Test3()
{
cout << "Cson Test3" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
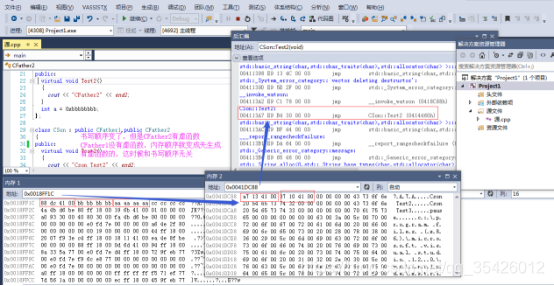
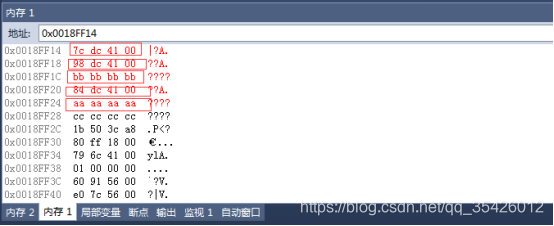
虚继承
1单重虚继承无虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather1
{
public:
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CSon : virtual public CFather1
{
public:
int b = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
虚基类位于内存的末尾,内存首地址存储着偏移块指针,偏移块大小为8个字节,第二个四字节保存了虚基类到内存首地址的偏移
2单重虚继承有虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CFather
{
public:
virtual void Test1(){}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CSon:virtual public CFather
{
public:
virtual void Test2(){}
public:
int b = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//子类的内存
/*
子类的虚表指针
偏移块指针
子类的数据
虚基类的虚表指针
虚基类的数据
*/
//偏移块的数据
/*
+0 保留‐‐ 猜测为偏移块与内存首地址的偏移
+4 虚基类与偏移块指针的偏移
*/
多重虚继承(菱形继承)
1多重虚继承无虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class GrandFather
{
public:
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CFather1 :virtual public GrandFather
{
public:
int b = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
class CFather2 :virtual public GrandFather
{
public:
int d = 0xdddddddd;
};
class CSon :public CFather1, public CFather2
{
public:
int e = 0xeeeeeeee;
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//子类的内存
/*
第一顺位父类的偏移块指针
第一顺位父类的数据
第二顺位父类的偏移块指针
第二顺位父类的数据
子类的数据
虚基类的数据
*/
2多重虚继承无虚函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class GrandFather
{
public:
virtual void Test1(){}
int a = 0xaaaaaaaa;
};
class CFather1 :virtual public GrandFather
{
public:
virtual void Test1(){}
virtual void Test2(){}//虚继承如果有自己的虚函数会生成一个虚指针(父类有虚函数的话也会继承一个父类的虚指针)
int b = 0xbbbbbbbb;
};
class CFather2 :virtual public GrandFather
{
public:
int d = 0xdddddddd;
};
class CSon :public CFather1, public CFather2
{
public:
int e = 0xeeeeeeee;
};
int main()
{
CSon s;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
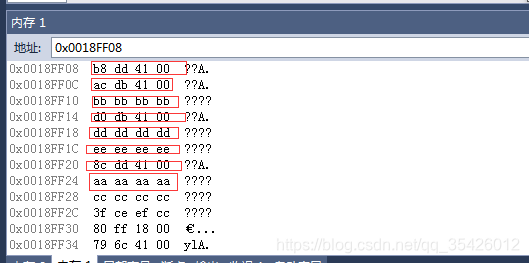
//子类的内存
/*
第一顺位父类的虚表的指针
第一顺位父类的偏移块指针
第一顺位父类的数据
第二顺位父类的偏移块指针
第二顺位父类的数据
子类的数据
虚基类的虚表指针
虚基类的数据
*/
子类(CSon)新加新添加的虚函数挂靠到第一顺位父类的虚表中





 博客主要分析了不同继承方式下有无虚函数时的内存结构。包括单继承、多重继承和虚继承,详细阐述了子类有无重写虚函数、不同父类有无虚函数等情况对虚指针生成和内存布局的影响,如多重继承中虚函数父类内存位置、虚继承中虚基类位置等。
博客主要分析了不同继承方式下有无虚函数时的内存结构。包括单继承、多重继承和虚继承,详细阐述了子类有无重写虚函数、不同父类有无虚函数等情况对虚指针生成和内存布局的影响,如多重继承中虚函数父类内存位置、虚继承中虚基类位置等。
















 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








