一、布局
1. 盒子模型的宽度如何计算?
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>盒模型</title> <style> #box1 { width: 100px; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid #000; margin: 10px; background-color: yellow; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="box1">box1</div> </body> </html>
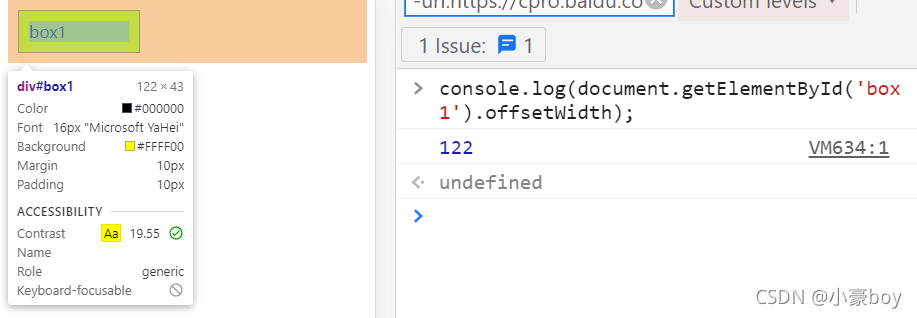
- offsetWidth = ( 内容宽度 + 内边距 + 边框 ),无外边距。
- 这里的offsetWidth是 122px。
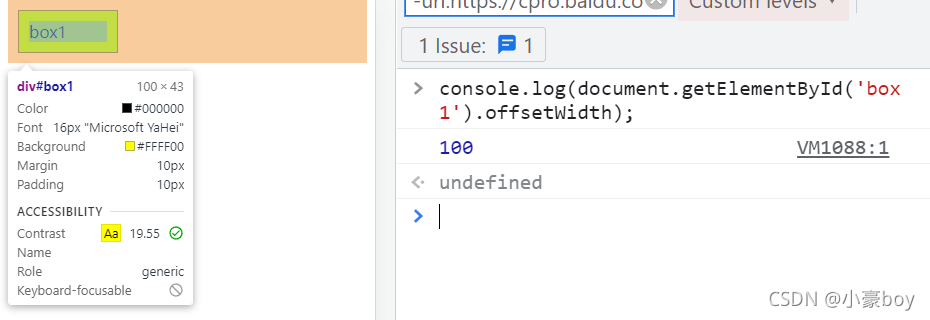
- 补充:如果让 offsetWidth 等于 100px ,该如何做?
- 添加: box-sizing: border-box;
2. margin 纵向重叠的问题
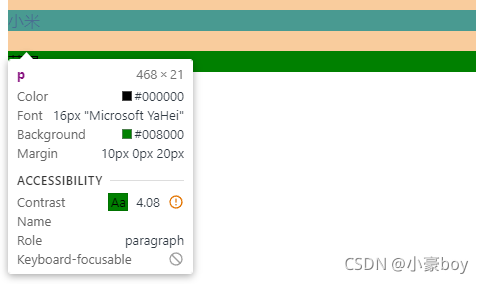
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>margin 纵向重叠</title> <!-- 小米和苹果之间的距离是多少? --> <style> p { background-color: green; margin-top: 10px; margin-bottom: 20px; } </style> </head> <body> <p>小米</p> <p></p> <p></p> <p></p> <p>苹果</p> </body> </html>
总结:
- 相邻元素的 margin-top 和 margin-bottom 会发生重叠,取两者的最大值作为它们之间的距离,故这里小米与苹果的距离为 20 px。
- 空白内容的 <p></p> 也会重叠。
3. margin 负值的问题
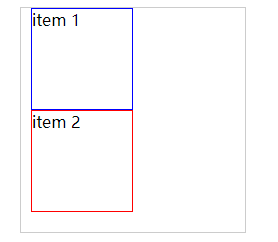
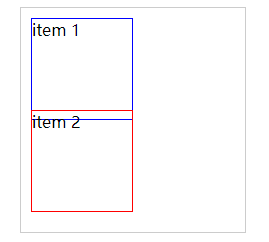
3.1 测试 margin top bottom 的负数情况
- 没有添加margin时:
- 若给 item 1 添加 margin-top: -10px;
- 若给 item 1 添加 margin-bottom: -10px;
3.2 测试 margin left right 的负数情况
- 没有添加margin时:
- 若给 item 1 添加 margin-left: -10px;
- 若给 item 1 添加 margin-right: -10px;
总结:
- margin-top 和 margin-left 负值,元素向上、向左移动。
- margin-right 设置负值不会产生位移,只会减小元素供CSS读取的宽度。
- margin-bottom 设置负值不会产生位移,只会减小元素供CSS读取的高度。
4. BFC 理解和应用
4.1 什么是 BFC?如何应用?
- Block format context ,块级格式化上下文。
- 一块独立渲染区域,内部元素的渲染不会影响边界以外的元素。
4.2 形成 BFC 的常见条件
- float 不是 none。
- position 是 absolute 或 fixed。
- overflow 不是 visible。
- display 是 flex inline-block 等。
4.3 BFC 的常见应用
- 清除浮动
详细解释:BFC的形成条件和特性分析 - 简书,BFC 形成条件 - 孟繁贵 - 博客园
5. float 布局的问题,以及 clearfix
5.1 圣杯布局和双飞翼布局的目的:
- 三栏布局,中间一栏最先加载和渲染(内容最重要)
- 两侧内容固定,中间内容随着宽度自适应
- 一般用于 PC 网页
5.2 如何实现圣杯布局和双飞翼布局
圣杯布局:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-sacle=1.0"> <title>圣杯布局</title> <style> body { min-width: 550px; } #header { text-align: center; background-color: #f1f1f1; } #container { padding-left: 200px; padding-right: 150px; } #container .column { float: left; } #center { width: 100%; background-color: #ccc; } #left { position: relative; width: 200px; background-color: aqua; /* 相对父容器宽度的 100% */ margin-left: -100%; right: 200px; } #right { width: 150px; background-color: blueviolet; margin-right: -150px; } #footer { text-align: center; background-color: #f1f1f1; } /* 清除浮动 */ .clearfix:after { content: ''; display: table; clear: both; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="header">header</div> <div id="container" class="clearfix"> <div id="center" class="column">center</div> <div id="left" class="column">left</div> <div id="right" class="column">right</div> </div> <div id="footer">footer</div> </body> </html>
双飞翼布局:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>双飞翼布局</title> <style> body { min-width: 550px; } .col { float: left; } #main { width: 100%; height: 200px; background-color: #ccc; } #main-wrap { margin: 0 190px; } #left { width: 190px; height: 200px; background-color: rgb(0, 255, 64); margin-left: -100%; } #right { width: 190px; height: 200px; background-color: #f00; margin-left: -190px; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="main" class="col"> <div id="main-wrap"> main </div> </div> <div id="left" class="col">left</div> <div id="right" class="col">right</div> </body> </html>
5.3 圣杯布局和双飞翼布局的技术总结
- 使用 float 布局。
- 两侧使用 margin 负值,以便和中间内容横向重叠。
- 防止中间内容被两侧覆盖,一个用 padding 一个用 margin。
5.4 手写 clearfix
/* 手写 clearfix */ .clearfix:after { content: ''; display: table; clear: both; } .clearfix { /* 兼容 IE 低版本 */ *zoom: 1; }
- :after/::after的异同:
:after/::after和:before/::before的异同-优快云博客
- 关于使用 display:block与display:table 的区别:
6. flex 布局的问题
6.1 常用语法回顾
- 容器属性:flex-direction(决定主轴的方向)、justify-content(主轴上的对齐)、flex-wrap(是否换行)、align-items(交叉轴上如何对齐)。
- 项目属性:align-self(该项目在交叉轴的对齐方式)。
- 详细介绍地址:flex布局--入门_小豪boy的博客-优快云博客
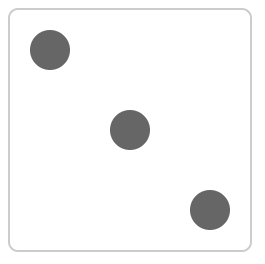
6.2 flex 实现一个三点的色子
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>flex 画骰子</title> <style> .box { width: 200px; height: 200px; border: 2px solid #ccc; border-radius: 10px; padding: 20px; /* flex 布局 */ display: flex; /* 两端对齐 */ justify-content: space-between; } .item { /* 点的样式 */ display: block; width: 40px; height: 40px; border-radius: 50%; background-color: #666; } .item:nth-child(2) { /* 第二项居中对齐 */ align-self: center; } .item:nth-child(3) { /* 第三项尾对齐 */ align-self: flex-end; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box"> <span class="item"></span> <span class="item"></span> <span class="item"></span> </div> </body> </html>
二、定位
1. absolute 和 relative 分别依据什么定位?
- relative 依据自身定位。
- absolute 依据最近一层的定位元素定位。
- 定位元素:
- absolute relative fixed
- body
2. 居中对齐有哪些实现方式?
2.1 水平居中
文本水平居中:
- 文本内容居中:text-align: center;
div水平居中:
- 有固定宽度:margin: 0 auto;
- absolute 定位,知道元素宽度:left: 50% ;margin-left:负宽度的一半;
- absolute 定位,元素宽度未知:left: 50%;transform:translateX(-50%);
- absolute 定位:left: 0; right: 0; margin: 0 auto;
- flex布局:justify-content: center;
2.2 垂直居中
文本垂直居中:
- 设置行高等于所在区域的高度:height: 200px; line-height: 200px;
- vertical-align实现文本的垂直居中:display:table-cell; vertical-align:middle;
div垂直居中:
- absolute 定位,知道元素高度:top: 50%;margin-top:负高度的一半;
- absolute 定位,元素高度未知:top: 50%;transform: translateY(-50%);
- absolute 定位:top: 0; bottom: 0; margin: auto 0;
- flex布局:align-items:center;
2.3 水平垂直居中
文本水平垂直居中:
- text-align: center;height: 200px; line-height: 200px;
- text-align: center;display:table-cell; vertical-align:middle;
div水平垂直居中:
- absolute 定位,知道元素宽高:left: 50% ;margin-left:负宽度的一半;top: 50%;margin-top:负高度的一半;
- absolute 定位,元素宽高未知:left: 50%; top: 50%;transform: translate(-50%,-50%);
- absolute 定位:left: 0; right: 0; top: 0; bottom: 0; margin: auto;
- flex布局:justify-content: center; align-items:center;
三、图文样式
1. line-height 如何继承?
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>line-height 如何继承</title> <!-- 如下代码,p 标签的行高将会是多少? --> <style> body { font-size: 20px; line-height: 200%; } p { font-size: 16px; } </style> </head> <body> <p>666</p> </body> </html>
- 写具体数值,如 30px ,则继承该值(比较好理解)。
- 写比例,如 2 ,则继承该比例(如这里p标签的font-size:16px,所以line-height为16*2=32px)
- 写百分比,如 200% ,则继承计算出来的值,即 20*200%=40px(考点)
四、响应式
1. rem 是什么?
- rem 是一个长度单位。
- em ,相对长度单位,相对于父元素,不常用。
- px ,绝对长度单位,最常用。
- rem ,相对长度单位,相对于根元素,常用于响应式布局。
2. 响应式布局的常见方案?
- media-query,根据不同的屏幕宽度设置根元素 font-size。
- rem,基于根元素的相对单位。
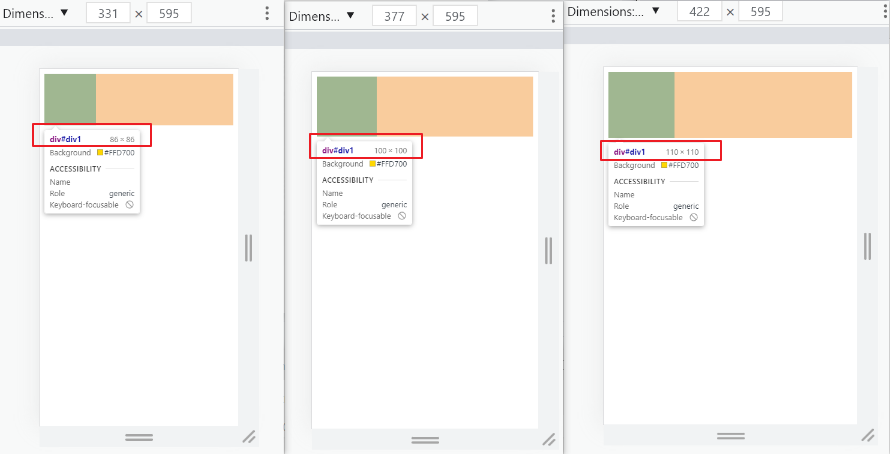
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>响应式布局</title> <style> @media only screen and (max-width: 374px) { /* iphone5 或者更小的尺寸,以 iphone5 的宽度(320px)比例设置 font-size */ html { font-size: 86px; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 375px) and (max-width: 413px) { /* iphone6/7/8 和 iphone x */ html { font-size: 100px; } } @media only screen and (min-width: 414px) { /* iphone6p 或者更大的尺寸,以 iphone6p 的宽度(414px)比例设置 font-size */ html { font-size: 110px; } } body { font-size: 0.16rem; } #div1 { width: 1rem; height: 1rem; background-color: gold; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="div1"></div> </body> </html>
- rem的弊端: “阶梯” 性。
网页视口尺寸:
- window.screen.height // 屏幕高度
- window.innerHeight // 网页视口高度
- document.body.clientHeight // body 高度
- vw 网页视口宽度的1/100。
- vh 网页视口高度的1/100。
- vmax 取两者(vw/vh)最大值;vmin 取两者最小值。































 874
874

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








