MySQL☞自连接
自连接:一张表中根据自身列之间的关联关系,自己跟自己链接。
A、创建一个user表,且插入数据,数据如下:

B、分析: 把user表看成两张表,一张员工表,一张领导表,发现员工表中lead(领导编号)等于领导表中id(员工的编号)员工表和领导表中之间的关联关系: 员工表.lead=领导表.id
案例:
1、查询user表中员工的编号,姓名,以及领导的编号,姓名

2、查询user表中员工的编号,姓名,职位,以及领导的编号,姓名,职位
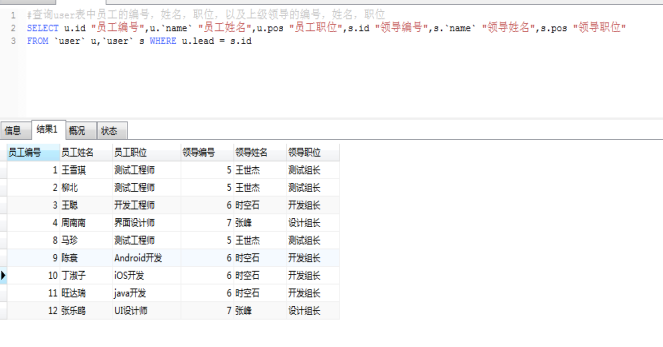
3、查询user表中员工的编号,姓名,职位,工资,以及领导的编号,姓名,职位,工资, 最后根据员 工的工资进行升序排列

4、查询工资在3000~6000之间,并且名字中不包含汉字王 的员工的编号,姓名,工资以及领导的编号, 姓名,工资,根据员工的编号进行降序排列。





















 1815
1815

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








