注意!!!
此教程是基于《【SpringMVC】7.REST风格的CRUD实战(一)之前期工作》来讲解的,在阅读前请务必查阅此文章。
一、前情提要
在之前的第一篇文章《【SpringMVC】7.REST风格的CRUD实战(一)之前期工作》中,我们明确了API接口要求
修改操作
- 显示修改页面
- URI:emp/{id}
- 请求方式:GET
- 显示效果:回显表单。
修改员工信息
- URI:emp
- 请求方式:PUT
- 显示效果:完成修改,重定向到 list 页面
- 注意:lastName不能被修改
二、具体步骤
1.在EmployeeHandler编写相关的Handler方法
input方法适用于表单回显
update方法用于更新数据库的内容
getEmployee方法使用了@ModelAttribute是为了更新数据库时,如果只更新了一项,不会让employee的其他属性都为null,@ModelAttribute的解释请看《【SpringMVC】5.处理模型数据》
package com.springmvc.crud.handlers;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.springmvc.crud.dao.DepartmentDao;
import com.springmvc.crud.dao.EmployeeDao;
import com.springmvc.crud.entities.Employee;
@Controller
public class EmployeeHandler {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@Autowired
private DepartmentDao departmentDao;
@ModelAttribute
public void getEmployee(@RequestParam(value="id",required=false) Integer id,Map<String,Object> map){
if(id != null){
map.put("employee", employeeDao.get(id));
}
}
@RequestMapping(value="/emp",method=RequestMethod.PUT)
public String update(Employee employee){
employeeDao.save(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
@RequestMapping(value="emp/{id}",method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String input(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,Map<String, Object> map){
map.put("employee", employeeDao.get(id));
map.put("departments", departmentDao.getDepartments());
return "input";
}
}
2.input.jsp的相关代码
这里使用了SpringMVC所 提供的表单标签,为能能够更快地回显表单,减少工作量。
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form"%>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
<html>
<head>
<title>My JSP 'input.jsp' starting page</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--
为什么使用form标签呢?
1.因为可以更快速地开发出表单页面,而且可以更方便地进行表单值的回显
2.注意
可以通过modelAttribute 属性指定绑定的模型属性,
若没有指定该属性,则默认从request 域对象中读取command的表单bean,
如果也不存在,则报错java.lang.IllegalStateException: Neither BindingResult nor plain target object for bean name 'command' available as request attribute。
-->
<form:form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/emp" method="POST" modelAttribute="employee">
<c:if test="${employee.id == null }">
<!-- path属性对应html表单标签的name -->
LastName:<form:input path="lastName" />
<br>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${employee.id != null }">
<form:hidden path="id"/>
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT">
<%--
对于_method 不能使用form:hidden 标签,因为ModelAttribute 对应的bean中没有 _method 属性--%>
<%-- <form:hidden path="_method"/> --%>
<br>
</c:if>
Email:<form:input path="email" />
<br>
<%
Map<String, String> genders = new HashMap<String, String>();
genders.put("1", "Male");
genders.put("0", "Female");
request.setAttribute("genders", genders);
%>
Gender:<form:radiobuttons path="gender" items="${genders }" />
<br>
Department:<form:select path="department.id" items="${departments }"
itemLabel="departmentName" itemValue="id"></form:select>
<br />
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form:form>
</body>
</html>
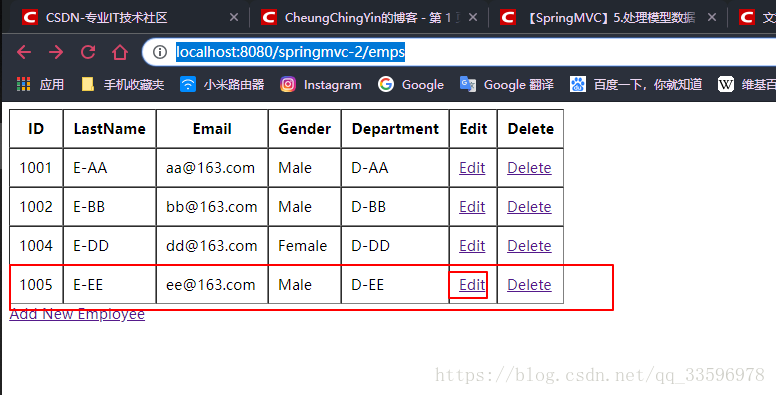
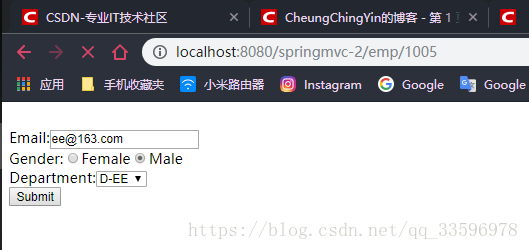
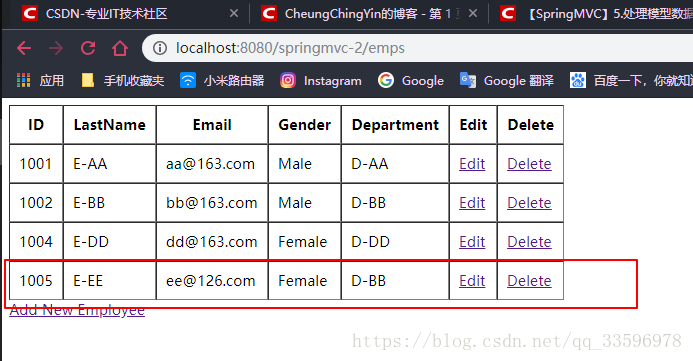
3.效果展示
启动tomcat,访问 http://localhost:8080/springmvc-2/emps























 1657
1657

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








