转自:http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/emplace/ template <class... Args> iterator emplace (const_iterator position, Args&&... args);
vector::emplace
在position位置插入一个元素
转自:http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/push_back/
http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/push_back/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4303513/push-back-vs-emplace-back
Construct and insert element
The container is extended by inserting a new element at position. This new element is constructed in place using argsas the arguments for its construction.
This effectively increases the container size by one.
Because vectors use an array as their underlying storage, inserting elements in positions other than the vector endcauses the container to shift all the elements that were after position by one to their new positions. This is generally an inefficient operation compared to the one performed by other kinds of sequence containers (such as list or forward_list). See emplace_back for a member function that extends the container directly at the end.
在position位置插入一个元素后,原position后的元素都要一次后移一个位置
Return value
An iterator that points to the newly emplaced element. 返回指向新插入元素的迭代器
Member type iterator is a random access iterator type that points to an element.
Example
// vector::emplace
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main ()
{
std::vector<int> myvector = {10,20,30};
auto it = myvector.emplace ( myvector.begin()+1, 100 );
myvector.emplace ( it, 200 );
myvector.emplace ( myvector.end(), 300 );
std::cout << "myvector contains:";
for (auto& x: myvector)
std::cout << ' ' << x;
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}Outputs:
myvector contains: 10 200 100 20 30 300
emplace_back vs push_back
std::vector::emplace_back
template <class... Args> void emplace_back (Args&&... args);
std::vector::push_back
void push_back (const value_type& val); void push_back (value_type&& val);
emplace_back 传递的是参数列表, push_back传递的是value_type
Optimization for emplace_back can be demonstrated in next example.
For emplace_back constructor A (int x_arg) will be called. And for push_back A (int x_arg) is called first and move A (A &&rhs) is called afterwards.
push_back()会调用一次构造函数+一次拷贝构造函数
emplace_back()只调用一次构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class A
{
public:
A (int x_arg) : x (x_arg) { std::cout << "A (x_arg)\n"; }
A () { x = 0; std::cout << "A ()\n"; }
A (const A &rhs) noexcept { x = rhs.x; std::cout << "A (A &)\n"; }
A (A &&rhs) noexcept { x = rhs.x; std::cout << "A (A &&)\n"; }
private:
int x;
};
int main ()
{
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call emplace_back:\n";
a.emplace_back (0);
}
{
std::vector<A> a;
std::cout << "call push_back:\n";
a.push_back (1);
}
return 0;
}输出:
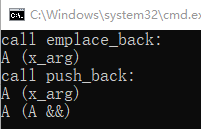
One more in case of lists:
// constructs the elements in place.
emplace_back("element");//It will create new object and then copy(or move) its value of arguments. push_back(explicitDataType{"element"});
emplace_back() vs push_back()
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/emplace-vs-insert-c-stl/
When we use push_back(), we create an object and then insert it into the vector. With emplace_back(), the object is constructed in-place and saves an unnecessary copy. Please see emplace vs insert in C++ STL for details.
|
|
Output :
a 24 b 25

Output:
a 24 b 25





 博客主要介绍了C++中vector容器的emplace操作,在position位置插入元素会使后续元素后移。重点对比了emplace_back和push_back,push_back传递value_type,会调用一次构造和一次拷贝构造;emplace_back传递参数列表,仅调用一次构造,可避免不必要的拷贝。
博客主要介绍了C++中vector容器的emplace操作,在position位置插入元素会使后续元素后移。重点对比了emplace_back和push_back,push_back传递value_type,会调用一次构造和一次拷贝构造;emplace_back传递参数列表,仅调用一次构造,可避免不必要的拷贝。
















 723
723

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








