Code:YaqiLYU/AANAP
Paper:Adaptive As-Natural-As-Possible Image Stitching
1、加载并显示图片
加载两幅图片:img1、img2,把img2大小resize为img1大小。
%% Global options
% 0 - Bilinear interpolation, implementation by MATLAB锛宻lower but better-->双线性插值
% 1 - Nearest neighbor interpolation,implementation by C++, Faster but worse---->最邻近插值
fast_stitch = 1;
img_n = 2; % only support two image stitching
in_name = cell(img_n,1);
in_name{1} = 'images/case26/img04.JPG';
in_name{2} = 'images/case26/img05.JPG';
img_n = size(in_name, 1);
gamma = 0;
sigma = 12.5;
%% load and preprocessing
I = cell(img_n, 1);
for i = 1 : img_n
I{i} = imread(in_name{i});
end
max_size = 1000 * 1000;
imgw = zeros(img_n, 1);
imgh = zeros(img_n, 1);
for i = 1 : img_n
if numel(I{i}(:, :, 1)) > max_size
I{i} = imresize(I{i}, sqrt(max_size / numel(I{i}(:, :, 1))));
end
imgw(i) = size(I{i}, 2);
imgh(i) = size(I{i}, 1);
end
img1 = I{1};
img2 = I{2};
img2 = imresize(img2,size(img1,1)/size(img2,1));
figure(4),
imshow(img1,[]);
pause(0.3);
figure(5),
imshow(img2,[]);
pause(0.3);
2、变量初始化
%% User defined parameters for APAP
clear global;
global fitfn resfn degenfn psize numpar
fitfn = 'homography_fit'; %计算Global H
resfn = 'homography_res';
degenfn = 'homography_degen';
psize = 4;
numpar = 9;
M = 500;
thr_g = 0.1; %RANSAC threshold
if fast_stitch
C1 = 100; %C1,C2为分块大小
C2 = 100;
else
C1 = 200;
C2 = 200;
end
3、SIFT特征检测与匹配
[ kp1,ds1 ] = vl_sift(single(rgb2gray(img1)),'PeakThresh', 0,'edgethresh',500);
[ kp2,ds2 ] = vl_sift(single(rgb2gray(img2)),'PeakThresh', 0,'edgethresh',500);
[match_idxs, scores] = vl_ubcmatch(ds1,ds2);
f1 = kp1(:,match_idxs(1,:));
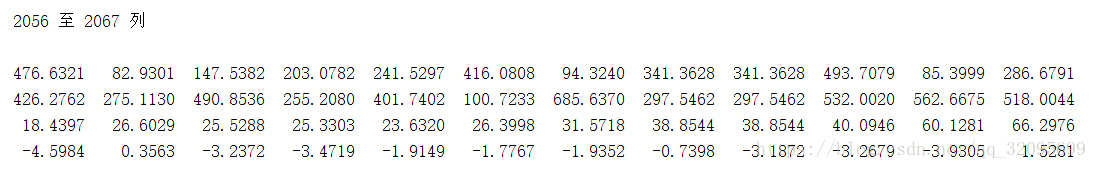
f2 = kp2(:,match_idxs(2,:));kp1:img1的特征点(本例中kp1:4x2067,既找到了2067个特征点)
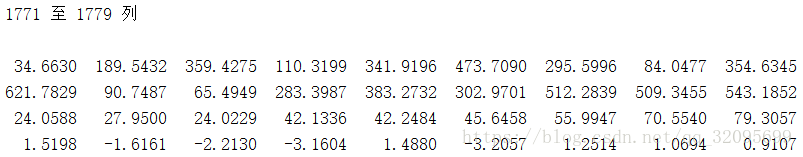
kp2:img2的特征点(本例中kp2:4x1779,既找到了1779个特征点)
match_idxs:img1,img2匹配的特征点的索引:(本例中match_idxs:2x534,既找到了534个匹配对)
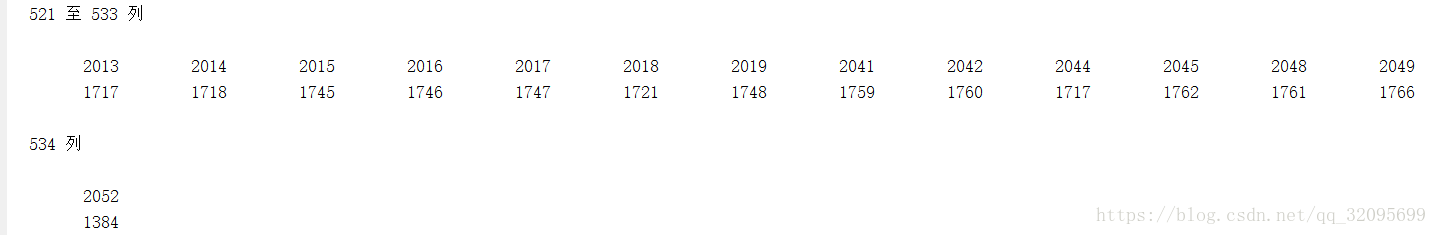
[F,D] = VL_SIFT(I)
F为特征点,D为描述子。
% Each column of F is a feature frame and has the format [X;Y;S;TH], where
% X,Y is the (fractional) center of the frame, S is the scale and TH is
% the orientation (in radians).
% [F,D] = VL_SIFT(I) computes the SIFT descriptors [1] as well. Each
% column of D is the descriptor of the corresponding frame in F. A
% descriptor is a 128-dimensional vector of class UINT8.4、匹配点归一化,用门限值 thr_g = 0.1 删除RANSAC的Outliner
%% Normalise point distribution and Outlier removal with Multi-GS RANSAC.
% (x1;y1;1;x2;y2;1)
data_orig = [ kp1(1:2,match_idxs(1,:)) ; ones(1,size(match_idxs,2)) ;
kp2(1:2,match_idxs(2,:)) ; ones(1,size(match_idxs,2)) ];
[ dat_norm_img1,T1 ] = normalise2dpts(data_orig(1:3,:));
[ dat_norm_img2,T2 ] = normalise2dpts(data_orig(4:6,:));
data_norm = [ dat_norm_img1 ; dat_norm_img2 ];
% Multi-GS
% rng(0);
[ ~,res,~,~ ] = multigsSampling(100,data_norm,M,10);
con = sum(res<=thr_g);
[ ~, maxinx ] = max(con);
inliers = find(res(:,maxinx)<=thr_g);%找到匹配度最高的特征点序列,inliers存的是匹配对的索引data_orig:齐次坐标下所有匹配特征点的组合。(本例中data_orig:6x534,对应534个匹配对的坐标–>x1,y1,1;x2,y2,1)
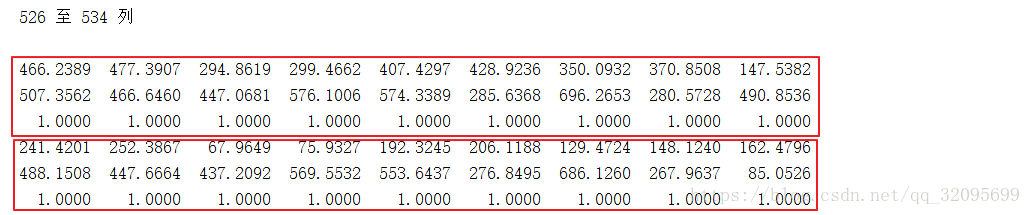
[newpts, T] = normalise2dpts(pts):归一化函数
作用:把一系列的齐次坐标[x y 1]归一化,使得这些点以原点为中心,距离原点均值为sqrt(2)。
function [newpts, T] = normalise2dpts(pts)
if size(pts,1) ~= 3
error('pts must be 3xN');
end
% Find the indices of the points that are not at infinity
finiteind = find(abs(pts(3,:)) > eps);%找出非无穷远点的序号
if length(finiteind) ~= size(pts,2)
disp('Some points are at infinity');
end
% For the finite points ensure homogeneous coords have scale of 1
pts(1,finiteind) = pts(1,finiteind)./pts(3,finiteind);
pts(2,finiteind) = pts(2,finiteind)./pts(3,finiteind);
pts(3,finiteind) = 1;
c = mean(pts(1:2,finiteind)')'; % Centroid of finite points (找出所有点的中值)
% c =
%368.3553
%434.4607
newp(1,finiteind) = pts(1,finiteind)-c(1); % Shift origin to centroid.
newp(2,finiteind) = pts(2,finiteind)-c(2); % 其他特征点到中值点的偏移量
dist = sqrt(newp(1,finiteind).^2 + newp(2,finiteind).^2);%其他特征点到中值点的距离
meandist = mean(dist(:)); % Ensure dist is a column vector for Octave 3.0.1其他特征点到中值点的平均距离
scale = sqrt(2)/meandist;
T = [scale 0 -scale*c(1)
0 scale -scale*c(2)
0 0 1 ];
newpts = T*pts;
endT的作用相当于:
x’ = scale(x-c(1));
y’ = scale(y- c(2));
data_norm :归一化后的匹配点矩阵
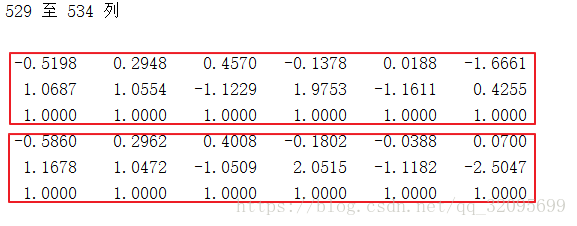
inliers:最佳匹配对索引:(本例中inliers:511x1,对应511个内点的索引)
RANSAC算法流程:

详情看slids:
Advances in Computer Vision
Lecture 9
Mid level vision:
Stereo, Homographies, RANSAC
5、通过内点计算Global H
%% Global homography (H) again.
[ Hl,A,D1,D2 ] = feval(fitfn,data_norm(:,inliers));
Hg = T2\(reshape(Hl,3,3)*T1);
Hg = Hg / Hg(3,3)
Hg =
1.3326 0.0151 -314.6591
0.2190 1.2556 -104.2045
0.0006 0.0000 1.0000
6、求Global similarity transformation—->S
%% Compute Global similarity
S = ransac_global_similarity(data_norm(:,inliers),data_orig(:,inliers),img1,img2);
S = T2\(S*T1)先看看相似变换:图像的等距变换,相似变换,仿射变换,射影变换及其matlab实现

上述变换可以转换为:
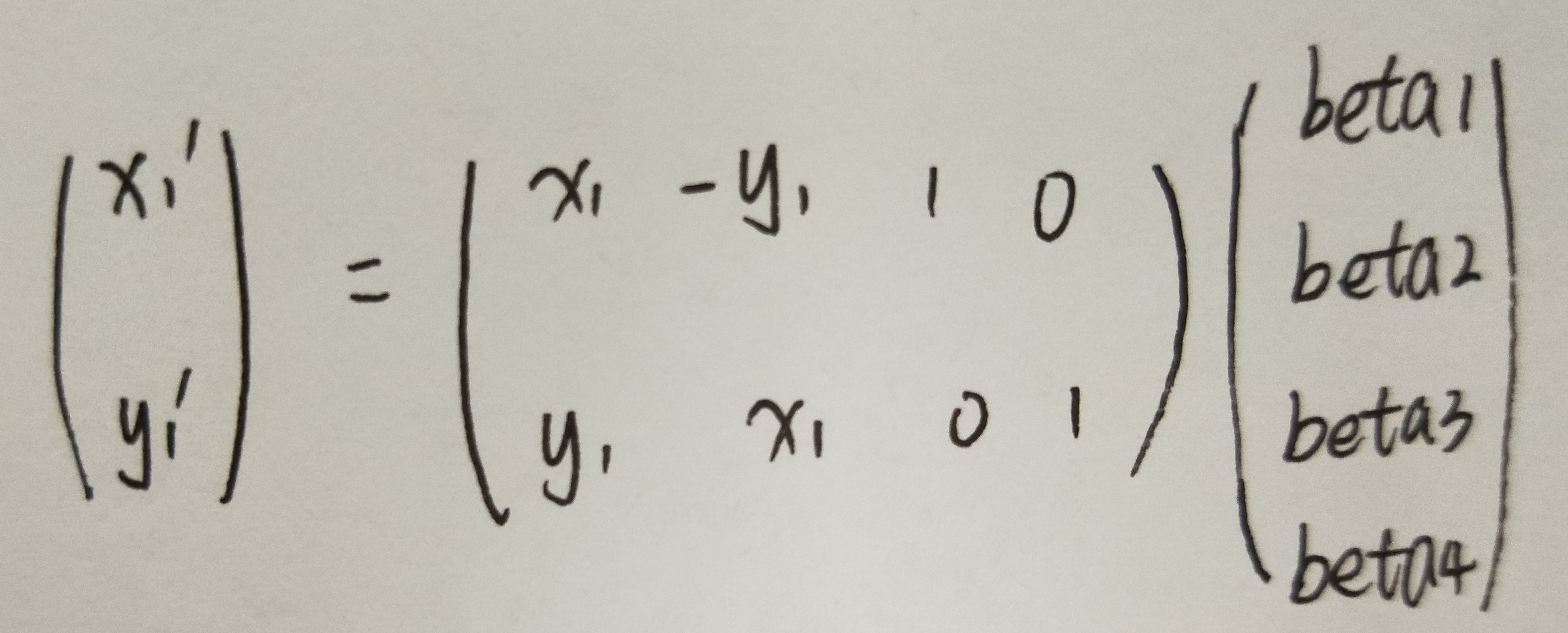
对应代码:
for idx = 1:size(x,2)
A = [A; x(idx) -y(idx) 1 0;
y(idx) x(idx) 0 1];
b = [b;x_(idx);
y_(idx)];
end
beta = A\b;
S_segment{i} = [beta(1) -beta(2) beta(3);
beta(2) beta(1) beta(4);
0 0 1];ransac_global_similarity(data,data_orig,img1,img2)函数:
作用:查找旋转角度最小的相似矩阵
function S = ransac_global_similarity(data,data_orig,img1,img2)
thr_l = 0.001;
M = 500;
figure(1);
imshow([img1 img2]);
title('Ransac''s results');
hold on;
plot(data_orig(1,:),data_orig(2,:),'go','LineWidth',2);
plot(data_orig(4,:)+size(img1,2),data_orig(5,:),'go','LineWidth',2);
hold on;
pause(0.5)
%通过门限值thr_l获取内点inliers
for i = 1:20
[ ~,res,~,~ ] = multigsSampling(100,data,M,10);
con = sum(res<=thr_l);
[ ~, maxinx ] = max(con);
inliers = find(res(:,maxinx)<=thr_l);
if size(inliers) < 50
break;
end
data_inliers = data(:,inliers);
x = data_inliers(1,:);
y = data_inliers(2,:);
x_ = data_inliers(4,:);
y_ = data_inliers(5,:);
A = [];
b = [];
for idx = 1:size(x,2)
A = [A; x(idx) -y(idx) 1 0;
y(idx) x(idx) 0 1];
b = [b;x_(idx);
y_(idx)];
end
beta = A\b;
%通过inliers计算相似矩阵
S_segment{i} = [beta(1) -beta(2) beta(3);
beta(2) beta(1) beta(4);
0 0 1];
%计算旋转角度
theta(i) = atan(beta(2)/beta(1));
clr = [rand(),0,rand()];
plot(data_orig(1,inliers),data_orig(2,inliers),...
'o','color',clr,'LineWidth',2);
plot(data_orig(4,inliers)+size(img1,2),data_orig(5,inliers),...
'o','color',clr,'LineWidth',2);
hold on;
pause(0.5);
%查找outliners,删除内点inliers
outliers = find(res(:,maxinx)>thr_l);
data = data(:,outliers);
data_orig = data_orig(:,outliers);
end
index = find(abs(theta) == min(abs(theta)));
S = S_segment{index};
end
这一段代码对应论文:
for i = 1:20
……
end
循环:
i=1时:

相似矩阵S:

7、计算pano大小
%% Obtaining size of canvas (using global Homography).%img2映射到canvas的坐标-->H\x2
TL = Hg\[1;1;1];
TL = round([ TL(1)/TL(3) ; TL(2)/TL(3) ]);
BL = Hg\[1;size(img2,1);1];
BL = round([ BL(1)/BL(3) ; BL(2)/BL(3) ]);
TR = Hg\[size(img2,2);1;1];
TR = round([ TR(1)/TR(3) ; TR(2)/TR(3) ]);
BR = Hg\[size(img2,2);size(img2,1);1];
BR = round([ BR(1)/BR(3) ; BR(2)/BR(3) ]);
% Canvas size.
cw = max([1 size(img1,2) TL(1) BL(1) TR(1) BR(1)]) - min([1 size(img1,2) TL(1) BL(1) TR(1) BR(1)]) + 1;
ch = max([1 size(img1,1) TL(2) BL(2) TR(2) BR(2)]) - min([1 size(img1,1) TL(2) BL(2) TR(2) BR(2)]) + 1;
% Offset for left image.
off = [ 1 - min([1 size(img1,2) TL(1) BL(1) TR(1) BR(1)]) + 1 ;
1 - min([1 size(img1,1) TL(2) BL(2) TR(2) BR(2)]) + 1 ];
img2**映射前**的TL,BL,TR,BR如下图所示:
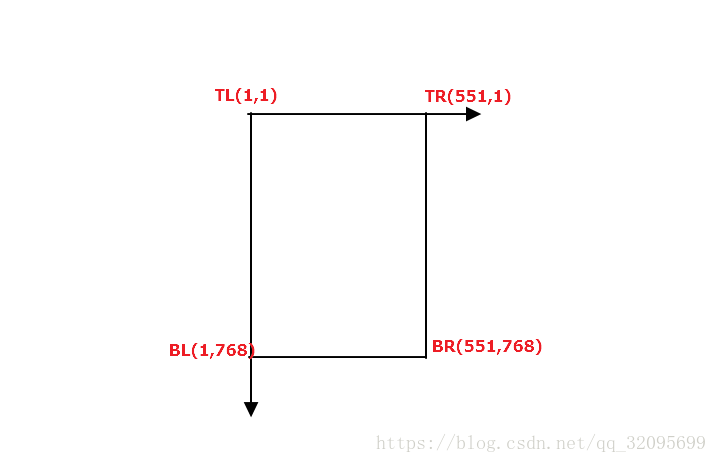
img2**映射后**的TL,BL,TR,BR:

8、把img1框起来
%% Generate anchor points in the boundary,20 in each size, 80 in total
anchor_points = [];
anchor_num = 20;
hx = linspace(1,size(img1,2),anchor_num);
hy = linspace(1,size(img1,1),anchor_num);
for i = 1:anchor_num
anchor_points = [anchor_points;
1, round(hy(i))];
anchor_points = [anchor_points;
size(img1,2), round(hy(i))];
anchor_points = [anchor_points;
round(hx(i)), 1];
anchor_points = [anchor_points;
round(hx(i)), size(img1,1)];
end
将img1用为20*20的圆点框起来的网格
[hx;hy]:


9、计算权重
%% Compute weight for Integration
% (x,y): K_min -> K_1 -> K_2 -> K_max
Or = [size(img1,2)/2;size(img1,1)/2];
Ot = Hg\[size(img2,2)/2;size(img2,1)/2;1];
Ot = [Ot(1)/Ot(3);Ot(2)/Ot(3)];
% solve linear problem
k = (Ot(2) - Or(2))/(Ot(1) - Or(1));%斜率
b = Or(2) - k * Or(1);%截距
K_min(1) = min([TL(1) BL(1) TR(1) BR(1)]);
K_max(1) = max([TL(1) BL(1) TR(1) BR(1)]);
K_1(1) = size(img1,2);
K_2(1) = K_1(1) + (K_max(1) - K_1(1))/2;%img2投影后的中点横坐标
K_min(2) = k * K_min(1) + b;
K_max(2) = k * K_max(1) + b;
K_1(2) = k * K_1(1) + b;
K_2(2) = k * K_2(1) + b;
% Image keypoints coordinates
Kp = [data_orig(1,inliers)' data_orig(2,inliers)'];
[ X,Y ] = meshgrid(linspace(1,cw,C1),linspace(1,ch,C2));
% Mesh (cells) vertices' coordinates.
Mv = [X(:)-off(1), Y(:)-off(2)];
% Perform Moving DLT
fprintf(' Moving DLT main loop...');tic;
Ht = zeros(size(Mv,1),9);
Hr = zeros(size(Mv,1),9);




















 2万+
2万+










