//01.主键PrimaryKey
- 数据库的特点: 海量数据存储,查询速度快,并发性问题控制,安全性,数据完整性。
- 什么是主键PrimaryKey:
主键就是数据行的唯一标识。不会重复的列才能当主键,一个表可以没有主键,但是会非常难以处理,所以没有特殊理由都要设置主键。 - 主键的作用:唯一标识表中的一条记录。
- 主键的特点:1.不能重复 2.主键不能为空null
- 选择主键的时候,根据列存储的信息不同,可以分为:业务主键和逻辑主键(推荐使用逻辑主键)
- 什么是业务主键? 业务主键是使用有业务意义的字段做主键。
- 什么是逻辑主键?逻辑主键是使用没有任何业务意义的字段当做主键。
- 选择什么样的列作为主键? (1).不能为空的列 (2).没有重复的列 (3).与实际业务没有关系的列(逻辑主键)
(4).稳定的列(列中的数据不经常改变)
(5).选择单列作为主键(当通过多列共同标识表中一条记录的时候,此时可以选择多列来共同组成一个主键,这种主键叫做复合主键,组合主键,联合主键),一般不推荐使用组合主键。
(6).尽量选择数字类型作为主键。 - 一个表中可以有几个主键? 一个表中只能有一个主键。
//02.外键ForeignKey
- 什么是外键?如何通过主外键将两张表中的数据关联起来?
当把数据拆分成两张表来存储的时候,每个表中都有自己的主键,其中一张表中除了主键,又多了一列,这列用来引用另外一张表中的主键,那么这列就是第一张表中的“外键列”,有外键列的表就叫做外键表。相对来说,主键被引用的那张表就是“主键表”。因为外键列中引用的是另外一张表中的主键列的数据,所以外键列中的数据是不能随便写的,必须是在另一张表的主键列中已存在的数据。
//03.通过设计器创建数据库和表
- 创建一个新的数据库之后,会在磁盘上创建一个mdf格式的主数据文件和一个ldf的日志文件。另外一个数据库可以包含任意多个次要数据文件(.ndf)和多个事务日志文件。
- 创建表的时候字段自增:选中数值字段–>点击列属性中的标识规范–>是否标识选择是,种子为初始值,增量为增值
- 数据库中的字符串可以用多种数据类型表示:char(10) nchar(10) varchar(10) nvarchar(10) text
ntext 数字也可以是varchar(max) nvarchar(max) ,一般用nvarchar(10)。 - 数据库中的bool类型的数据类型bit,在设计器中它的值只能是true或者false,在其他地方是1或者0。
- 数据库中的日期时间类型:date只表示日期 time只表示时间 datetime表示日期和时间
datetime2表示的日期和时间更精确。 - 在分离数据库的时候一定要将删除连接勾选上。
//04.SQL数据库数据类型
- 二进制数据类型image:image类型可以存储任何文件的二进制字节(对于一些特殊情况,我们不能将文件只保存在硬盘上,这样安全性无法保证,所以要将文件直接保存在数据库中)。
- char(50) nchar(50) varchar(50) nvarchar(50) text ntext varchar(max)
nvarchar(max) 以上这些数据类型都表示字符串。 - 带n的和不带n的区别:
char(2)表示可以存储2个字节,列如“12”,“ab”“刘”,不带n的存储中文等双字节字符,占用两个2个字节,存储英文数字等每个字符占用1个字节。使用char和varchar时,当数据库环境排序规则为中文时,不会出现乱码,否则会出现乱码。
nchar(2)带n的,无论存储中文,英文还是数字,每个字符都是占用2个字节,nchar(2)表示可以存储两个字符,例如“哈哈”,“ab”,“12”。使用nchar和nvarchar时,无论数据库环境排序规则是否支持中文,都不会出现乱码。
带n的数据类型长度最长可以设置为8000,而带n的这些数据类型长度最长可以设置为4000。比如char(8000) varchar(80000) nchar(4000) nvarchar(4000)。 - 带var和不带var的区别:带var的表示长度可变,不带var的表示长度固定。
char(10)表示固定长度,存储1个字符也是要占用十个字节的,会自动补9个空格。
varchar(10)表示可变长度,会根据实际存储数据的大小动态的重新分配存储空间,相对来说节省存储空间。 - text和ntext等价于varchar(max)和nvarchar(max),用于存储大量的文字,比如文章。
- 日期和时间:datetime
- 整数:int
- 小数:float
- 二进制字节:image
- 在附加数据库的时候,如果出现提示“拒绝访问”的错误,那就是说明权限不够,需要将数据库的*.mdf和*.ldf文件的访问权限改为完全控制(右键属性–>安全–>添加用户–>完全控制)。
- 表中的自增字段的值是不会回头的,是一直增加的。(当某行记录输入错误重新录入后,会发现自增字段的值多加了1)
- 在附加数据库的时候,高版本数据库可以兼容低版本数据库,而低版本不能兼容高版本数据库,此时想要附加的话,只能将高版本的数据库编写成脚本,然后将脚本在低版本数据库中执行。(在编写成脚本的时候一定要设置好目标数据库版本以及编写脚本的数据类型选项为“架构以及数据”)
- nvarchar并不是专门为中文设置的,而是为世界上所有的像中文一样的双字节文字设置的。
//05.用sql命令创建并配置数据库
create database MyDatabaseOne--创建一个数据库并配置
on primary--这里进行主数据文件的配置
(
name='MyDatabaseOne',--主数据文件名称
filename='C:\test\MyDatabaseOne.dbf',--主数据文件路径,确保所在文件夹有权限
size=5mb,--主数据文件初始大小
filegrowth=20%--主数据文件增长率
)
log on--这里进行日志文件的配置
(
name='MyDatabaseOne_log',--日志文件名称
filename='C:\test\MyDatabaseOne_log.ldf',--日志文件存储路径,确保所在文件夹有权限
size=5mb,--日志文件初始大小
filegrowth=2mb--日志文件增长率
)
--删除数据库
drop database MyDatabaseOne;
--切换数据库
use MyDatabaseOne;
--创建一张表
create table Departments
(
AutoID int identity(1,1) primary key,
DepartmentName nvarchar(50) not null
)
--删除表
drop table Departments;
--创建一张员工表
create table Employees
(
AutoID int identity(1,1) primary key,
EmpID nvarchar(50) not null,
EmpName nvarchar(10) not null,
EmpGender bit not null,
EmpJoinDate datetime not null,
EmpAge int not null,
EmpAddress nvarchar(100) not null,
EmpPhone nvarchar(50) not null,
DepartmentID int not null,
EmpEmail nvarchar(50) not null
)
//06.insert语句介绍
- –在sql语言中表示字符串用单引号,如果想转义一个单引号,就在单引号前面再加一个单引号
–在sql中使用单等号用来判断两个值是否相等。
–sql数据库在默认简体中文的排序规则下是不区分大小写的。
–sql中两个单引号转义成一个单引号。 - –插入记录 语法格式 insert into 表名称(列名1,列名2,列名3…) values(值1,值2,值3…);
–插入记录的时候自增列不可以对其插入值,如果要插入,必须提前打开开关,插入完成后,关闭。
insert into --指定列名
TblStudent(studentName,studentGender,studentAddress,studentAge,studentBirthday,studentCardID,studentClassID)
values
('张三','男','山东济南',15,'1997-9-2','370923199709022230',1);
insert into--不指定列名
TblStudent
values('李四','男','山东青岛',18,'1997-9-1','370923199709012230',1);
- –对自增列插入值的写法,在插入之前应将自增列插入值开关打开,插入完成后然后关闭
set identity_insert TblStudent on;--打开开关
insert into TblStudent
(studentID,studentName,studentGender,studentAddress,studentAge,studentBirthday,studentCardID,studentClassID)
values('100','王五','男','山东淄博',20,'1997-10-12','370923199709032230',2);
set identity_insert TblStudent off;--关闭
- –如果在非中文排序规则的数据库中直接插入字符串的时候一定要在字符串前面加N
insert into TblStudent
(studentName,studentGender,studentAddress,studentAge,studentBirthday,studentCardID,studentClassID)
values(N'赵六',N'男',N'山东济南',20,'1998-08-01','370923199709042230',2);
//07.update数据更新语句
- –update更新操作 语法: update 表名称 set 列名1=value1,列名2=value2,列名3=value3 where 条件表达式
- –如果不加where条件则表示对表中的每一条记录都进行修改
- –sql中and表示且,or表示或,not表示非
update TblStudent set studentName='张三' where studentID=1;
update TblStudent set studentAge+=20 where studentAge<15;
update TblStudent set studentName+='(男)' where studentID<10 and studentAge<18;
//08.删除语句delete
- –delete删除语句 语法:delete from 表名称 where 条件表达式
- –如果不加where条件,则表示将表中的所有记录都删除
delete from TblStudent where studentAge<18;
- –如果想要删除表中的所有数据,使用truncate要比delete效率高,truncate不能添加where条件
–truncate删除表中所有数据 语法:truncate table 表名称
truncate table TblStudent;
- –truncate的特点:
–1.truncate语句执行效率非常高,对于几百万条数据使用truncate操作几秒钟就可以完成删除,而使用delete可能要耗费几小时。
–2.使用truncate操作删除后,表中的自增列会重置。
–3.truncate删除不能添加where条件,只能进行全部删除。
–4.truncate语句不触发delete触发器。
//08.sql中常见约束
–数据库约束是为了保证数据的完整性(正确性)而实现的一套机制。
–主要的几个约束:非空约束,主键约束,唯一约束,默认约束,检查约束,外键约束
–len()函数是返回字段值的长度
–如果两张表之间有引用关系,那么在删除的时候先删除外键表,再删除主键表。默认情况下,如果主键表中的某条记录被外键表引用,那么这条记录无法删除,如果将外键约束的删除规则改为“级联”,那么就可以连同引用他的数据一块删除掉。
//09.通过t-sql实现约束
-
–创建好一个表后,如果想要增加、删除、或者是修改表中的列,是对表的结构进行修改,使用alter关键字
-
–删除表中的某个列 语法:alter table 表名称 drop column 列名称
alter table TblStudent drop column studentClassID
- –手动增加某个列 语法:alter table 表名称 add 列名称 数据类型
alter table TblStudent add studentClassID int
- –手动修改某个列的数据类型 语法:alter table 表名称 alter column 列名称 数据类型
alter table TblStudent alter column studentClassID nvarchar(200);
- –手动添加主键约束 语法 alter table 表名称 add constraint 约束名称 primary key(列名称)
alter table TblStudent add constraint PK_TblStudent_StudentId primary key(StudentId);
- –手动修改非空约束 语法 alter table 表名称 alter column 列名称 数据类型 not null
alter table TblStudent alter column StudentName nvarchar(50) not null;
- –手动增加一个唯一约束 语法 alter table 表名称 add constraint 约束名称 unique(列名称)
alter table TblStudent add constraint UQ_TblStudent_studentCardID unique(studentCardID);
- –手动增加一个默认值 语法 alter table 表名称 add constraint 约束名称 default(‘男’) for 列名称
alter table TblStudent add constraint DF_TblStudent_studentGender default('男') for studentGender;
- –手动增加一个检查约束 语法 alter table 表名称 add constraint 约束名称 check(表达式)
alter table TblStudent add constraint Ck_TblStudent_studnetGender check(studentGender='男' or studentGender='女')
- –手动增加一个外键约束 语法 alter table 外键表名称 add constraint 外键约束名称 foreign key(外键列名称) references 主键表名称(主键列名称)
alter table TblStudent add constraint FK_TblStudent_studentClassID foreign key(studentClassID) references TblClass(classID);--如果想要设置为级联删除 on delete cascade
- –通过一句话手动删除多个约束 语法 alter table 表名称 drop constraint 约束名称1,约束名称2,约束名称3
alter table TblStudent drop constraint UQ_TblStudent_studentCardID,DF_TblStudent_studentGender;
- –通过一句话同时增加多个约束
alter table TblStudent add constraint UQ_TblStudent_studentCardID unique(studentCardID),
constraint DF_TblStudent_studentGender default('男') for studentGender;
//10.创建表的同时把约束也创建好
- –建表的同时把约束创建好
create table Departments
(
DepID int primary key,
DepName nvarchar(50) unique not null
)
create table Employees
(
EmpID int primary key,
EmpName nvarchar(50) check(len(EmpName)>1) not null,
EmpGender char(1) default('男') check(EmpGender='男' or EmpGender='女'),
EmpAge int check(EmpAge>0 and EmpAge<120),
EmpEmail nvarchar(50) unique not null,
EmpAddress nvarchar(500) not null,
EmpDepID int foreign key references Departments(DepID) on delete cascade--设置为级联删除
)
//11.查询语句
- –查询语句
- –*号表示显示所有列,查询语句没有where条件表示查询所有行
select * from Tblstudent;
- –只查询表中的部分列
select studentName,studentAge from Tblstudent;
- –根据条件,只查询部分行(使用where条件筛选)
select * from Tblstudent where studentName='李四';
- –为查询结果中的列起别名
select studentName as '学生姓名',studentAge as '年龄' from TblStudent;
- –另一种起别名的方式
select
'学生姓名'=studentName,
'年龄'=studentName
from TblStudent;
- –获取当前系统的日期,使用getdate()方法
select '当前系统的日期'=GETDATE();
- –select语句是可以单独使用的
select '班长'='张三','班主任'='李四';
//12.去重,排序
- –distinct关键字,对已经查询出的结果集进行去除重复
select distinct studentAge from TblStudent;
- –top关键字和order by配合使用,order…by…一定是在语句的最后边,mysql中不支持top相关语法,而是使用limit n语法
- –对年龄进行降序排列,使用desc关键字
select top 2 * from TblStudent order by studentAge desc;
select * from TblStudent order by studentAge desc limit 2;--mysql
- –对年龄进行升序排列,使用asc关键字
select top 2 * from TblStudent order by studentAge asc;
select * from TblStudent order by studentAge asc limit 2;
- –取前10%
select top 20 percent * from TblStudent order by studentAge asc;
- –order by 补充
–order by 多列排序 - –先根据数学成绩降序排序,再根据英语成绩降序排序
select * from TblScore order by mathScore desc,englishScore desc;
- –查询结果加一列平均分,通过平均分进行降序排序
select *,平均分=(matnScore+englishScore)*1.0/2 from TblScore order by 平均分 desc;
- –查询结果不显示平均分,但是要通过平均分进行降序排序(可以直接通过表达式来排序)
select * from TblScore order by (mathScore+englishScore)*1.0/2 desc;
- –表中的数据是集合,集合是没有顺序的。order by返回的数据是有顺序的,所以他返回的数据集合叫‘游标’,所以含有order by的语句不能作为子查询语句来使用。
//13.聚合函数
- –聚合函数
- –统计所有人的年龄总和
select sum(studentAge) as '年龄总和' from TblStudent;
- –统计一下当前表中共有多少条记录
select count(*) from TblStudent;
- –计算平均年龄
select (sum(studentAge)*1.0/count(*)) as '平均年龄' from TblStudent;
- –求出最大年龄
select max(studentAge) from TblStudent;
- –求出最小年龄
select min(studentAge) from TblStudent;
- –使用avg聚合函数计算平均年龄
select avg(studentAge*1.0) from TblStudent;
- –聚合函数的一些问题:1.聚合函数是不统计空值(null)的。 2.如果使用聚合函数的时候没有进行手动分组,那么默认将整个表中的所有记录分为一组。
//14.条件查询
- –条件查询
- –查询出年龄在13-15之间的学生(between…and…)
select * from TblStudent where studentAge>=13 and studentAge<=15;
select * from TblStudent where studentAge between 13 and 15;
- –查询出班级id为1,2的所有学生 in(1,2)
select * from TblStudent where studentClassID=1 or studentClassID=2;
select * from TblStudent where studentClassID in(1,2);
//15.模糊查询
- –模糊查询,使用like关键字
- –通配符:_ % [] ^
- –下划线_表示任意的单个字符
--匹配出姓张的两个字的
select * from TblStudent where studentName like '张_';
- –百分号%表示匹配多个任意字符
--匹配出姓张的,不管几个字
select * from TblStudent where studentName like '张%';
- –中括号[]表示筛选范围的单个字符
--筛选出张三两个字中间有单个字母或者单个数字的
select * from TblStudent where studentName like '张[0-9a-z]三';
- –亦或符号表示非
--筛选出张三两个字中间不是字母和数字的
select * from Tblstudent where studentName like '张[^0-9a-z]三';
- –转义字符,将通配符放到中括号中就将通配符转义了
--筛选出姓名中包含%的
select * from TblStudent where studentName like '%[%]%';
//16.空值处理
- –空值处理
- –null值无法使用=或者!=来比较的
–判断null值必须使用is null关键字或者is not null关键字来判断
select * from TblStudent where studentAge is null;
select * from TblStudent where studentAge is not null;
- –任何值和null计算结果都是null
select 2+null;
//17.分组group by
- –分组group by
- –请查询出每个班的班级id和人数
select studentClassID,班级人数=count(*) from TblStudent group by studentClassID;
- –请查询出男女生各有多少
select studentGender,人数=count(*) from TblStudent group by studentGender;
- –请查询出每个班的班级id和男同学人数(先过滤,再分组)
select 班级ID=studentClassID,男人数=count(*) from TblStudent where studentGender='男' group by studentClassID;
- –当使用了分组或者聚合函数的时候,在select的查询列表中不能再包含其他的列名,除非该列同时也出现在了group by子句中,或者该列也出现在了聚合函数中。
- –对分组后的数据进行筛选使用having
- –where和having都是数据进行筛选,不同的是,where是对分组之前的数据进行筛选,having是对分组后的每一组数据进行筛选。
- –由于having子句在整个语句中的的执行顺序不同,所以不能使用select列表中的别名,只能使用表达式
select 班级ID=studentClassID,班级人数=count(*) from TblStudent group by studentClassID having count(*)>5;
//18.数据类型转换方法
- –数据类型转换函数cast()和convert()
–cast(待转换数据 as 数据类型) convert(数据类型,待转换数据)
select '哈哈'+cast('1000' as nvarchar(10));
select '哈哈'+convert(nvarchar(20),'1000');
//19.union联合
- –统计每班的人数并计算总人数
select
班级ID=convert(nvarchar(20),studentClassID),
班级人数=count(*)
from TblStudent
group by studentClassID
union all
select
'年级总人数',
count(*)
from TblStudent
- –union all和union的区别:二者都能进行数据集的联合,使用union联合会去除重复数据,重新排列顺序。而使用union all不会去除重复也不会重新排列。
–大多数情况下,联合的时候不需要去除重复数据,同时要保持数据的顺序,所以一般建议使用union all.
–语法:数据集1 union all 数据集2 union 数据集3… - –使用union all联合两个结果集
select
studentName,
studentAge
from TblStudent
union all
select
studentName,
studentAge
from TblStudent
- –使用union联合两个结果集
select
studentName,
studentAge
from TblStudent
union
select
studentName,
studentAge
from TblStudent
- –使用union all的时候注意,如果想要对联合之后的数据进行排序,那么order by子句一定写在最后一个数据集的后面。因为是在联合完成之后才执行排序的。
- –使用union all一次性向表中插入多条数据
insert into TblStudent
select '王五1','男','山东青岛',20,'1994-02-03','370923199602034456',2
union all
select '王五2','女','山东青岛',40,'1992-02-03','370923199696034456',1
union all
select '王五3','男','山东青岛',35,'1999-02-03','370996099602034456',3
union all
select '王五4','女','山东青岛',25,'1994-02-03','370960199602034456',2
//20.向表中插入多条数据
-
–将TblStudent表中的结构和数据备份到TblTemp中
-
–TblTemp表是在select * into执行的时候创建的,所以select into语句不能重复执行,因为每次都会创建一张表,会有冲突。
-
–TblStudent表的结构和自动编号列都会在TblTemp中创建,但是TblStudent中的约束不会出现在TblTemp中。
select * into TblTemp from TblStudent;
select * from TblTemp;
- –只拷贝表的结构,不拷贝数据
select top 0 * into TblBackup from TblStudent;
向表中插入多条数据,使用insert into…select …from
insert into TempTable
select EmpID,EmpName,EmpGender,EmpAge,EmpEmail,EmpAddress,DepartmentID
from Employees
where EmpGender='女'
常用的字符串函数
--常用的字符串函数
select len('哈喽,你好吗,kitty?')--len()函数返回字符串的字符个数
select DATALENGTH('哈喽,你好吗,kitty?')--datalength()函数返回字符换的字节数
select UPPER('hello')--upper()函数是将字母转成大写
select LOWER('HELLO')--lower()函数是将字母转成小写
select '========='+LTRIM(' hello ')+'========='--ltrim()函数是去掉左边空格
select '========='+rTRIM(' hello ')+'========='--rtrim()函数是去掉右边空格
select '========='+rtrim(LTRIM(' hello '))+'========='--去掉两边的空格
select LEFT('中华人民共和国成立了',5)--left()函数是将字符串从左边开始截取
select RIGHT('中华人民共和国成立了',5)--right()函数是将字符串从右边开始截取
select SUBSTRING('中华人民共和国成立了',1,5)--substring()是截取字符串
常用的日期和时间函数
--日期和时间的函数
select GETDATE()--获取当前的日期和时间
select SYSDATETIME()--获取精度更高的日期和时间
select DATEADD(DAY,3,GETDATE())--得到增加后的时间:(时间单位,增量,种子时间)
select DATEDIFF(YEAR,JoinDate,GETDATE()) from DateTable--datediff()函数能够得到两个日期的差
select DATEPART(YEAR,GETDATE())--datepart()函数能够得到日期的某个部分,返回的数据类型是数值型
select '年'=YEAR(GETDATE()),'月'=MONTH(GETDATE()),'日'=DAY(GETDATE())--获取时间的年月日
select DATENAME(YEAR,GETDATE())--datename()函数同样是返回日期的某个部分,但是返回的是字符串类型的
--筛选出工龄大于等于三年的
select * from Datetable where DATEADD(YEAR,3,JoinDate)<=GETDATE()
--查询出入职几年的各多少人
select '工龄'=DATEDIFF(YEAR,JoinDate,GETDATE()),'人数'=COUNT(*) from DateTable group by DATEDIFF(YEAR,JoinDate,GETDATE())
--统计出不同年份入职的人数
select 入职年份=DATEPART(YEAR,JoinDate),人数=COUNT(*) from DateTable group by DATEPART(YEAR,JoinDate)
日期函数练习
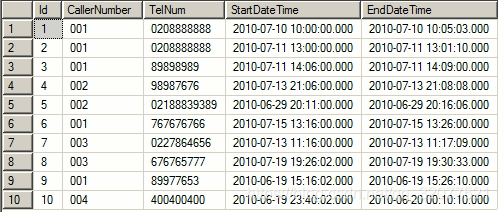
--输出所有通话数据中通话时间最长的5条记录
select top 5 *
from CallRecords
order by DATEDIFF(SECOND,StartDateTime,EndDataTime) desc
--输出所有通话数据中拨打长途号码的总时长
select 总时长=sum(DATEDIFF(SECOND,StartDateTime,EndDataTime))
from CallRecords
where TellNum like '0%'
--输出本月通话总时长最多的前三个呼叫员的编号
select top 3 CallerNumber
from CallRecords
where DATEDIFF(MONTH,StartDateTime,GETDATE())=0
group by CallerNumber
order by sum(DATEDIFF(SECOND,StartDateTime,EndDataTime)) desc
--输出本月拨打电话次数最多的前三个呼叫员的编号
select top 3 CallerNumber
from CallRecords
where DATEDIFF(MONTH,StartDateTime,EndDataTime)=0
group by CallerNumber
order by COUNT(*) desc
ADO.NET介绍
ADO.NET常用类:Connection、Command、DataReader、DataAdapter、DataSet
Connection类用来连接数据库
Command类用来执行SQL语句
DataReader类是只读、只进的结果集,一条一条读取数据
DataAdapter类是封装了上面三个对象的对象
DateSet类是数据集,是一个临时数据库
数据库连接的步骤
//1.创建连接字符串(两种方式)
//Data Source是数据库服务器名称,在自己电脑上的话就是电脑机器名,或者是直接用一个点表示,或者写localhost.
//Initial Catalog是要连接的数据库的名称
//Integrated Security是集成连接的方式
//UserID和Password是指sqlserver用户名称和密码
//使用电脑账户登录
string constr1 = "Data Source=lenovo;Initial Catalog=MyTestDatabase;Integrated Security=true";
//使用SQLserver账户登录
string constr2 = "Data Source=Lenovo;Initial Catalog=MyTestDatabase;UID=1911499587;PWD=19970902@@@";
//2.创建连接对象
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(constr2))
{
//3.打开连接
conn.Open();
MessageBox.Show("数据库连接成功!");
//4.关闭连接,释放资源,因为这里使用了using,所以就不用手动关闭连接释放资源了
}
增删改示例
1.ExecuteNonQuery()方法适合执行insert、delete、update等语句,这个方法返回一个int类型的值表示受影响的行数,除了执行insert、delete、update这三类语句以外的其他语句时返回-1.
2.command.ExecuteScalar();//ExecuteScalar()方法适合执行返回单个结果的语句
3.command.ExecuteReader();//ExecuteReader()方法适合执行返回多条数据的语句
//连接字符串
string constr = "Data Source=Lenovo;Initial Catalog=MyTestDatabase;UID=1911499587;PWD=19970902@@@";
//创建连接对象
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(constr))
{
//sql语句
//string sqlStr = "insert into Employees values(20,'刘冬雪','女',22,'9555245555@qq.com','山东泰安',3)";
//string sqlStr = "delete from Employees where EmpID=20";
string sqlStr = "update Employees set EmpName='张四' where EmpID=1";
using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sqlStr, conn))
{
//打开连接
conn.Open();
//执行sql
int count = command.ExecuteNonQuery();
MessageBox.Show(count.ToString() + "行受影响");
}
}
SqlDataReader使用
SqlDataReader对象的特点:
1.只读、只进。只能通过reader读取数据,不能修改数据。reader只能一条一条向前移动,不能向后也不能跳跃。
2.使用reader时必须保证连接是打开状态,当reader使用完毕后,必须把reader关闭,释放。同时关闭释放连接对象。
3.默认情况下SqlDataReader对象要求独占一个连接对象。
reader[i]和reader.getValue(i)方法的区别和联系:
reader索引器有int和string两个重载,而reader.getValue()方法没有重载。其实在reader索引器的int类型的这个重载中,内部实现的时候,也是调用的reader.getValue()方法。reader索引器的string类型的重载的内部实现是调用了reader.getOrdinal(‘列名’)方法,返回已知列名的索引,然后再调用reader索引器的int类型的重载方法。
从SqlDataReader对象中获取数据的时候通过强类型获取数据,而不去使用getValue()方法,例如:
reader.GetInt32(i);
reader.GetString(i);
reader.GetDateTime(i);诸如此类,还有很多。
通过上面这种强类型的方式获取数据,可以直接得到对应的数据类型(注:reader.getValue()方法返回值为object类型的,使用不方便)
表中的null值
当查询到数据库表中的null值的时候,通过reader索引器和reader.getValue()方法获取的值返回的不是null,而是一个空的字符串,所以此时不会抛异常。但是当通过强类型获取数据的的时候,遇到null值则会抛异常。
//连接字符串
string constr = "Data Source=Lenovo;Initial Catalog=MyTestDatabase;UID=1911499587;PWD=19970902@@@";
//创建连接对象
using (SqlConnection conn = new SqlConnection(constr))
{
//sql语句
string sqlstr = "select * from Employees";
//创建命令对象
using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(sqlstr, conn))
{
//打开连接
conn.Open();
//执行,创建reader对象
//通过调用ExecuteReader()方法将给定的sql语句在服务器端执行
//执行完毕后,服务器就已经查询出了数据,但是数据此时是保存在服务器的内存中,并没有返回给应用程序,只是返回给应用程序一个reader对象,这个对象就是用来获取数据的对象。
using (SqlDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader())
{
//接下来就要通过reader一条一条的获取数据
//在获取数据之前,首先判断一下此次查询有没有查询到数据
if (reader.HasRows)//如果有数据,返回true,没有返回false
{
//循环一条一条的读取
//每次获取数据之前都要执行read()方法向后移动一条数据,如果成功移动到了某条数据上,返回true,否则返回false.
while (reader.Read())
{
string str = null;
//获取当前reader指向的数据
//reader.FieldCount属性返回当前查询数据的列数
for (int i = 0; i < reader.FieldCount; i++)
{
//还可以通过reader.GetValue(i)获取数据,这个方法只能通过int类型的索引获取,而通过索引器获取可以通过int类型和string的字段名称两种方式获取数据,例如:reader[i]或者reader['字段名称']。
str += (reader[i].ToString()+"\t");
//reader.Getordinal('列名')方法还能根据已知列名获取它的索引
}
textBox1.AppendText(str + "\r\n");
}
}
}
}
}
SqlDataReader对象使用原理图
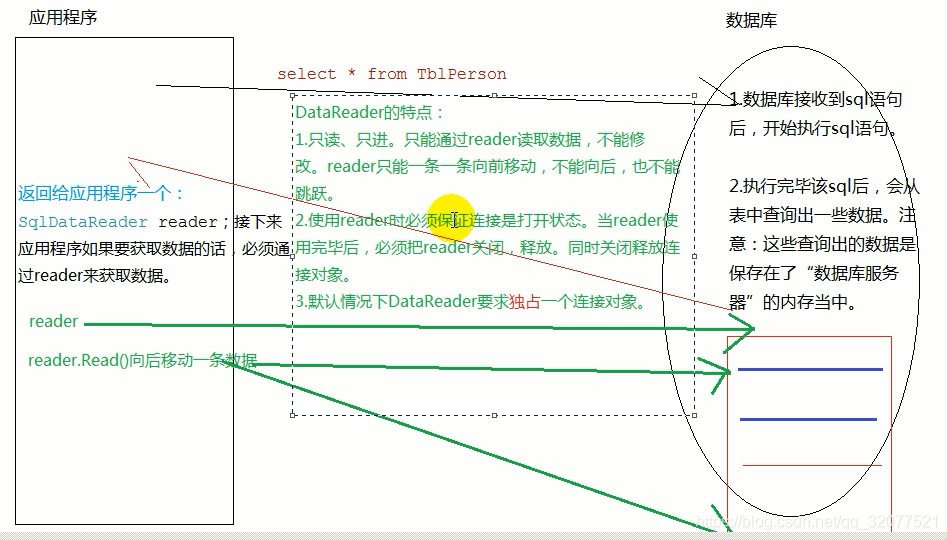
通过reader.getXXX()这种方式获取数据
通过reader.getValue()获取数据返回object类型,查询到数据库表中的null值返回一个空字符串,但是使用强类型获取数据返回对应的数据类型,查询到数据库表中的null值会抛异常。所以,在使用强类型获取数据的时候,要先使用reader.IsDbNull()方法判断一下当前查询到的数据是否为null值。
//通过强类型获取数据,首先要判断是否为null
string EmpID = reader.IsDBNull(0) ? "null" : reader.GetInt32(0).ToString();
string EmpName = reader.IsDBNull(1) ? "null" : reader.GetString(1);
string EmpGender = reader.IsDBNull(2) ? "null" : reader.GetString(2);
string EmpAge = reader.IsDBNull(3) ? "null" : reader.GetInt32(3).ToString();
string EmpEmail = reader.IsDBNull(4) ? "null" : reader.GetString(4);
string EmpAddress = reader.IsDBNull(5) ? "null" : reader.GetString(5);
string DepartmentID = reader.IsDBNull(6) ? "null" : reader.GetInt32(6).ToString();
插入记录返回自动编号
在values关键字前面加上关键字:output inserted.自动编号的列名
此时就得使用ExecuteScalar()方法来执行插入语句了。
insert into myclasstable output inserted.classID values('地信165','地信')





















 177
177

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








