文章目录
- 1. Cmd on Docker Client
- 2. Overriding Default Commands
- 3. Listing Running Containers
- 4. Container LifeCycle
- 5. Restarting Stopped Containers
- 6. Removing Stopped Containers
- 7. Stopping Containers
- 8. Multi-Command Containers
- 9. Executing Commands in Running Containers
- 10. The Purpose of the IT Flag
- 11. Getting a Command Prompt in a Container
- 12. Starting with a Shell
- 13. Container Isolation
- 14. Conclusions
This article typically focuses on Docker Client.Only with simple use ,actually ,not in detailed description,by the way.
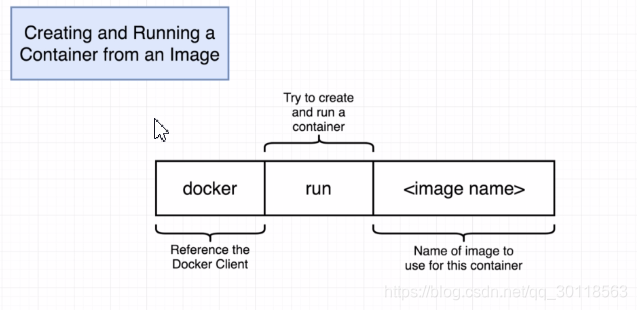
1. Cmd on Docker Client
That’s the standard way to run a cmd on Docker Client .
2. Overriding Default Commands
We use some cmds just after < image name>,thus overriding the default cmd .It’s nice for you to notice that in last section,there 's no ,obviously ,a cmd afterwards.But let’s not
spin over this detail.Appending a cmd also can be assgined as ‘override the default cmd’.
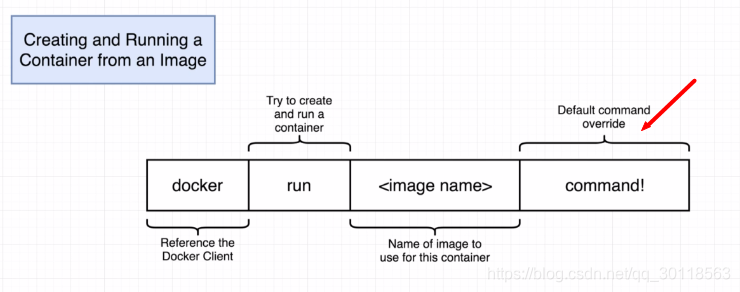
Here’s an interesting example:
$ docker run busybox echo 'yes'
yes
$ docker run hello-world ls
C:\Program Files\Docker\Docker\Resources\bin\docker.exe: Error response from daemon: OCI runtime
create faed: container_linux.go:344: starting container process caused "exec: \"ls\":
executable file not found in ATH": unknown.
$ docker run busybox ls
bin
dev
etc
home
proc
root
sys
tmp
usr
var
Before you make it clear ,you had better know a little bit more on how a container works.
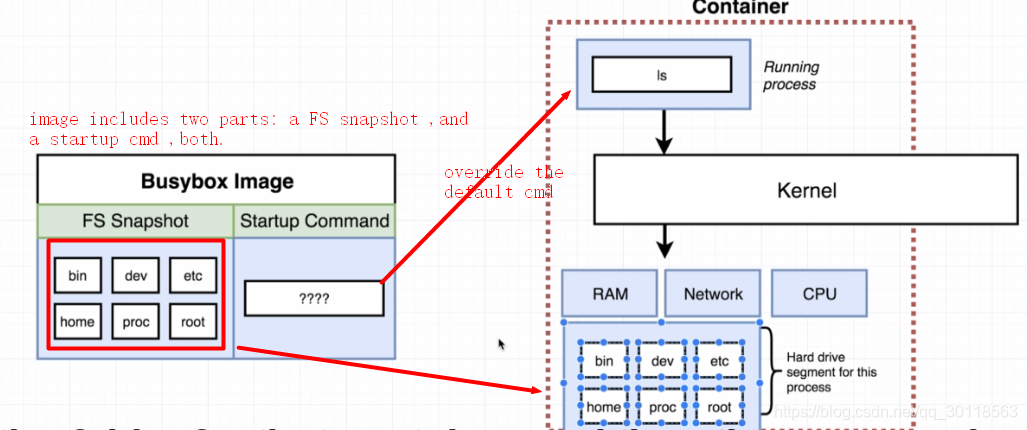
As we see from this diagram,we try to create and run a container from the BusyBox image.Overall , we may concentrate on the following facts.
- Firstly,a busybox image includes two main parts: a FS snaphot that is a file set,and some startup cmd that is off top of my head.Whatever ,Docker server pulls this image.
- Secondly,as Docker server creates a new container out of that image,it takes the file system snapshot ,and sticks it in as the folder for the container . Say,the fs snapshot is part of the container!
- Thirdly,the cmd overriding the default one is ’
ls’ . ‘ls’ is exactly the cmd from some file of the file system snapshot! Therefore ,as the container runs process of'ls', it actually runs the binary file of bin originated from the file system snapshot! - Fourthly, as we type ‘
docker run hello-world ls’, no file system snapshot resembling that of ‘docker run busybox’ would be stuck in. So there 's no executable file matchingls. Then ,error message apeared as the example above.
3. Listing Running Containers
So this title easily reminds us of Linux cmd ,i.e. ps .Yep, Dockers cmd to show the running processes really resembles the one of Linux .
At first ,we start to ping some website which lasts for a longer time than ls or echo cmd.
$ docker run busybox ping www.baidu.com
Then ,we open another window ,and make a new docker cmd ,as follows:
$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
ae74118f9516 busybox "ping www.baidu.com" 3 minutes ago Up 3 minutes angry_pascal
Ok ,we presently see the containers!
We look at the first row .You believe that ? The last one :‘NAMES’, is a randomly generated name identifying the container!
What if we want to see all the docker cmd history?
Here 's is the very cmd ,and -a suffix means ‘all’.
$ docker ps -a
4. Container LifeCycle
When we call docker ps -a,we see a lot of processes which have exited.Then why does a container exit?
This question just invokes a point over container lifecycle.
Before,we learned a cmd:
$ docker run hello-world
But docker runis ,as a matter of fact ,a short cmd for docker create and docker start containerID:There we go.
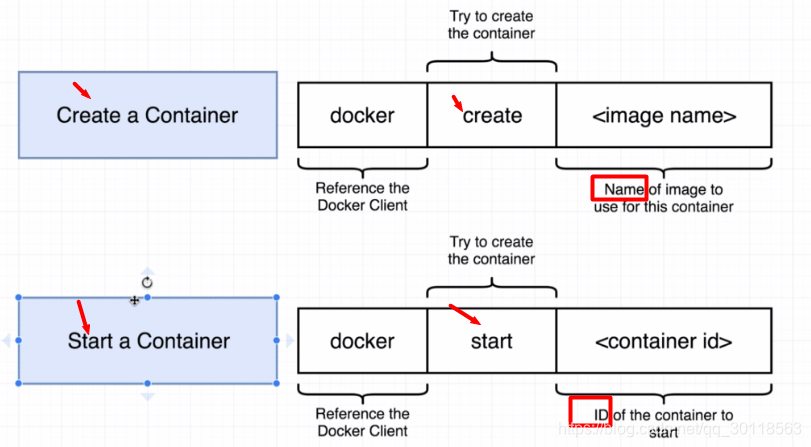
and we also get the example:
----------
ht@Lenovo-PC MINGW64 ~
$ docker create hello-world
699f43b5a63d17946e87403298a0e63e3d5575c88889cd3f473c786b53c04bb0
ht@Lenovo-PC MINGW64 ~
$ docker start 699f43b5a63d17946e87403298a0e63e3d5575c88889cd3f473c786b53c04bb0
699f43b5a63d17946e87403298a0e63e3d5575c88889cd3f473c786b53c04bb0
5. Restarting Stopped Containers
$ docker start -a ae74118f9516
64 bytes from 14.215.177.38: seq=3426 ttl=37 time=11.360 ms
......
ae74118f9516 is the containerID!
6. Removing Stopped Containers
$ docker system prune
WARNING! This will remove:
- all stopped containers
- all networks not used by at least one container
- all dangling images
- all dangling build cache
Are you sure you want to continue? [y/N] y
It is noticeable that as you run this cmd, you are not only removing stopped containers, but also several other items .And you are reclaiming disk usages ,by the way.
7. Stopping Containers
We 've known steps to create and start a new container.However ,as the container runs background,which we see from the docker logs containerID,we even fail to stop one yet.
ht@Lenovo-PC MINGW64 /f
$ docker create busybox ping baidu.com
f2f6b4d50907be99dcd5d3de4b5b19fe4ea27ae1705bdfddb702147a7c7918eb
ht@Lenovo-PC MINGW64 /f
$ docker start ca79db23880ac09b4427428708dab5557043eb02ee46d20a63dc2e66cc6c5c18
ca79db23880ac09b4427428708dab5557043eb02ee46d20a63dc2e66cc6c5c18
ht@Lenovo-PC MINGW64 /f
$ docker logs ca79db23880ac09b4427428708dab5557043eb02ee46d20a63dc2e66cc6c5c18
PING baidu.com (220.181.57.216): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 220.181.57.216: seq=0 ttl=37 time=40.523 ms
64 bytes from 220.181.57.216: seq=1 ttl=37 time=40.166 ms
All right,here we put forward cmds to stop containers.
Here is the point: there are two cmds to really stop a container :
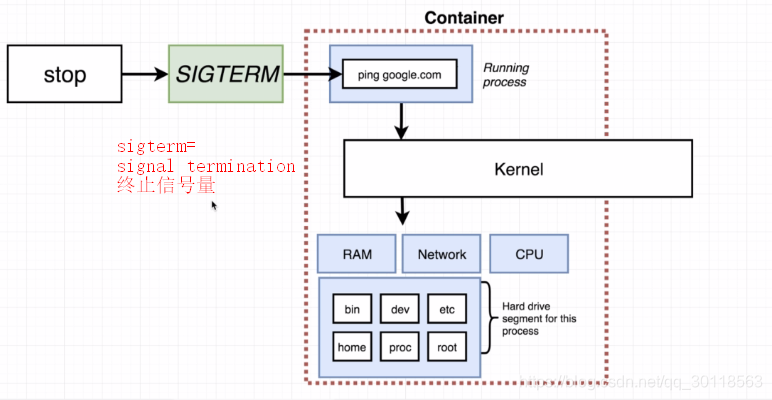
- stop a container (pic1)
- kill a container (pic2)
pic1:SIGTERM is short for signal termination,which means, this cmd will signal the container a message to shutdown itself after doing some cleanup or emitting messages,etc.
pic2:
SIGKILL: this cmd tells the container to shutdown right now ,and do not do any additional work at all,not even to do cleanup.
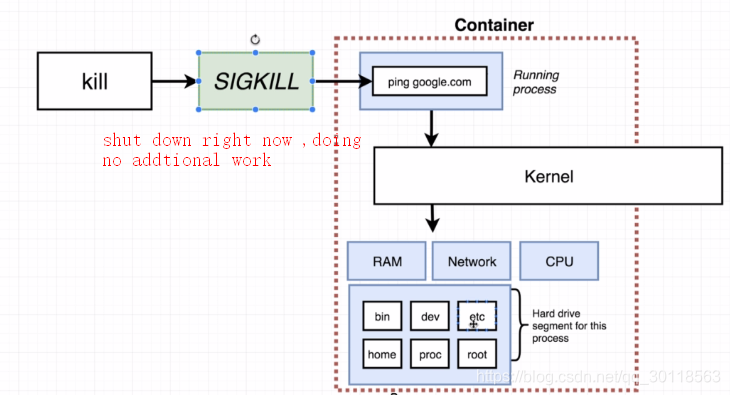
This two stop ways are no more rare stuff. Just try to remember singals in Linux.Don’t you ever know the differences between kill -9 PID and kill -15 PID in bash?
Still ,you have a tip to keep in mind:
- If
stopcan’t make it to shutdown the container in 10 seconds,Docker will fall back tokillmode to kill the container.
Last but not least,here we post the two cmds:
$ docker ps
$ docker kill containerID
---
$ docker ps
$ docker stop containerID
8. Multi-Command Containers
In this section ,we run a Redis container.The procedures are simple and straightforward:
$ docker run redis
But,as you try to open redis-cli in the terminal,you will fail:
huting@Lenovo-PC MINGW64 ~
$ redis-cli
bash: redis-cli: command not found
Why ?
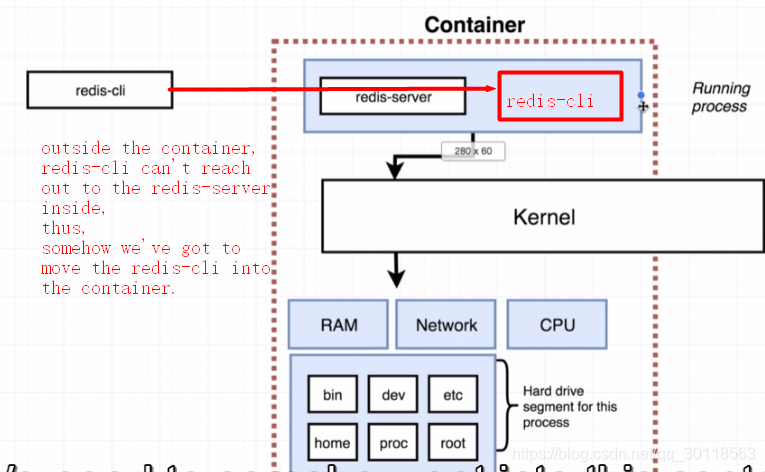
So ,here we have a good look at the diagram :
It is essentially a matter of process communication problem, as i see it.Redis-cli outside the container is not able to link to redis-server that is located inside the container.
9. Executing Commands in Running Containers
We still continue the topic extended from last section.Then how do we start up a redis-cli which interacts with redis-server inside the container?
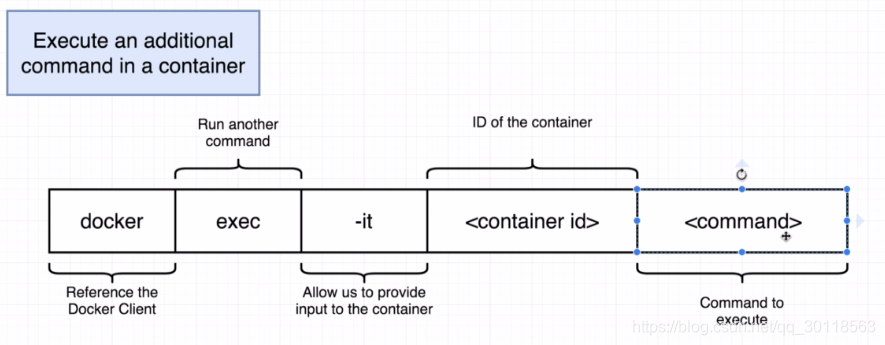
Here,we introduce a new cmd ,and the diagram shows the grammar.
$ winpty docker exec -it 890ca57159fb redis-cli
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
PONG
You just ignore winpty ,which makes it OK to run a Linux cmd on Windows OS.
Also, if we ignore -it (a flag),we would get kicked to the terminal again.Of course we would.And we will talk about the answer later.
$ winpty docker exec 890ca57159fb redis-cli
10. The Purpose of the IT Flag
You might wonder what -it means in the cmd above.
Well, just associate it with Linux Bash.-it can be interpreted as -i -t.
- -i ,means the cmd you type in will be directed to redis-cli inside the container, instead of outside
- -t , means the characters on the screen will be in a formatted manner, thus being more human readable.
Even though you already know -i -t clearly,you still need a few minutes to enhance your awareness of stdin\stdout\stderr on Linux. The disgram below is meaningful ,which describes how -i makes effects on stdin\stdout\stderr.
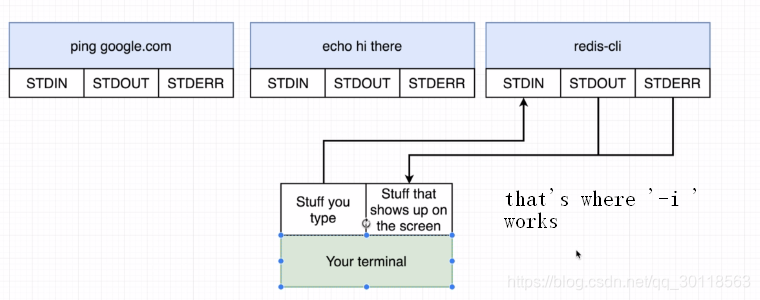
11. Getting a Command Prompt in a Container
Well ,i am not going to spend so much time on this cmd.Just keep it in your mind,as you will use it very frequently.
$ winpty docker exec -it 890ca57159fb sh
# ls
bin data etc lib media opt root sbin sys usr
boot dev home lib64 mnt proc run srv tmp var
See,with sh , this cmd works like a Bash shell ,which ,by the way ,is not Bash shell whatsoever, though they do look like each other.
But, for bashreally appears here and there,with most of its cmds included by many other shells , Docker shell of course,supports pretty a lot of shell cmds of bash,too.
This cmd is useful because it is the entry point to shell environment inside the containers ,where you can manipulate your softwares directly.Sounds like a big feature!
12. Starting with a Shell
OK,to be simple ,this cmd is made use of to start up a new container out of the image, along with a cmd prompt.That is an alternative use of Docker run.
$ winpty docker run -it busybox sh
/ # cd
~ # ll
sh: ll: not found
~ # ls
~ # ls /
bin dev etc home proc root sys tmp usr var
~ #
13. Container Isolation
We are very close to the end of this article,and here is a crystal-clear gotcha that we better know.
Containers do not share their file systems at all ,neither do they share their data.
You might do some demo to test this conclusion .You open two terminals ,with both
typed in :
$ winpty docker run -it busybox sh
/ # ls
bin dev etc home proc root sys tmp usr var
/ #
and at one of them ,you touch a new file in the root directory ,easily .
Then you turn to the other ,and list the files in the root directory,and definitely you find the new file.
Ok ,that’ pretty much it.
14. Conclusions
Here in this very article,we discuss some basics of Docker.Thank you for reading it all.!
And at this time,I collect all the cmds mentioned before,and make a list of them, for the sake of memorising and review.
docker run hello-world
docker run -it busybox sh
docker create busybox
docker ps
docker ps -a
docker start ContainerID
docker logs
docker stop ContainerID
docker kill ContainerID
docker system prune
docker exec -it 890ca57159fb(ContainerID) redis-cli





 本文深入探讨Docker客户端的使用技巧,包括覆盖默认命令、运行、停止及重启容器、执行多命令容器、容器生命周期管理等核心操作。通过实例解析,帮助读者理解容器内部工作原理及隔离特性。
本文深入探讨Docker客户端的使用技巧,包括覆盖默认命令、运行、停止及重启容器、执行多命令容器、容器生命周期管理等核心操作。通过实例解析,帮助读者理解容器内部工作原理及隔离特性。
















 3162
3162

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








