2018年09月24日
目录
目录
一、java反射机制概念
反射 (Reflection) 是 Java 的特征之一,它允许运行中的 Java 程序获取自身的信息,并且可以操作类或对象的内部属性。
Reflection enables Java code to discover information about the fields, methods and constructors of loaded classes, and to use reflected fields, methods, and constructors to operate on their underlying counterparts, within security restrictions.
The API accommodates applications that need access to either the public members of a target object (based on its runtime class) or the members declared by a given class. It also allows programs to suppress default reflective access control.
Java反射机制可以让我们在编译期(Compile Time)之外的运行期(Runtime)获得任何一个类的字节码。包括接口、变量、方法等信息。还可以让我们在运行期实例化对象,通过调用get/set方法获取变量的值。
简而言之,通过反射,我们可以在运行时获得程序或程序集中每一个类型的成员和成员的信息。程序中一般的对象的类型都是在编译期就确定下来的,而 Java 反射机制可以动态地创建对象并调用其属性,这样的对象的类型在编译期是未知的。所以我们可以通过反射机制直接创建对象,即使这个对象的类型在编译期是未知的。
反射的核心是 JVM 在运行时才动态加载类或调用方法/访问属性,它不需要事先(写代码的时候或编译期)知道运行对象是谁。
二、反射的用途
Java 反射主要提供以下功能:
- 在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类;
- 在运行时构造任意一个类的对象;
- 在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法(通过反射甚至可以调用private方法);
- 在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法
反射最重要的用途就是开发各种通用框架。很多框架(比如 Spring)都是配置化的(比如通过 XML 文件配置 Bean),为了保证框架的通用性,它们可能需要根据配置文件加载不同的对象或类,调用不同的方法,这个时候就必须用到反射,运行时动态加载需要加载的对象。
三、reflectionDemoTest
3.1 新建一个测试bo
package classReflection;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
×××getter and setter();
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
}
3.2 写测试Demo
package classReflection;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class ClassForName {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new ClassForName();
}
public ClassForName() {
super();
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
String classInfo=JOptionPane.showInputDialog(null,"输入类全路径");//要求用户输入类的全路径
try {
Class<?> cla=Class.forName(classInfo);//根据类的全路径进行类加载,返回该类的Class对象
Method[] method=cla.getDeclaredMethods();//利用得到的Class对象的自审,返回方法对象集合
System.out.println("forName:"+cla);
for(Method me:method){//遍历该类方法的集合
System.out.println("方法有:"+me.toString());//打印方法信息
}
System.out.println("*****************************************************");
Field[] field=cla.getDeclaredFields();//利用得到的Class对象的自审,返回属性对象集合
for(Field me:field){ //遍历该类属性的集合
System.out.println("属性有:"+me.toString());//打印属性信息
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3.3 运行demo
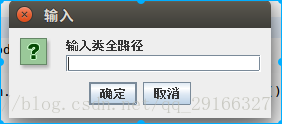
输入“classReflection.Person”;
结果:
forName:class classReflection.Person
方法有:public void classReflection.Person.setAge(int)
方法有:public int classReflection.Person.getAge()
方法有:public java.lang.String classReflection.Person.toString()
方法有:public java.lang.String classReflection.Person.getName()
方法有:public void classReflection.Person.setName(java.lang.String)
*****************************************************
属性有:private java.lang.String classReflection.Person.name
属性有:private int classReflection.Person.age







 本文深入讲解Java反射机制的概念,探讨其在运行时判断对象、构造类、调用方法及访问属性的强大功能。通过实例演示如何使用反射加载类、获取方法和字段信息。
本文深入讲解Java反射机制的概念,探讨其在运行时判断对象、构造类、调用方法及访问属性的强大功能。通过实例演示如何使用反射加载类、获取方法和字段信息。

















 1209
1209

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










