先看interface例子
interface Animal{
public void eat();
public void sayhello();
}
class human implements Animal{
public void eat(){
}
}
public class interface_test{
public static void main(String[] args){
human h = new human();
}
}
运行结果:

编译错误。跟继承抽象类相似,子类必须实现接口所有方法,或者将其定义成抽象类,通过子类的子类来实现
interface Animal{
public void eat();
public void sayhello();
}
abstract class human implements Animal{
public void eat(){
}
}
class chirld extends human{
public void sayhello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
}
public class interface_test{
public static void main(String[] args){
chirld c = new chirld();
c.sayhello();
}
}运行结果:
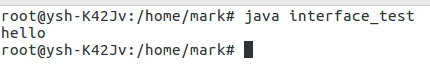
实现接口的方式,与类继承差不多,那接口与类有如下区别
- 接口不能用于实例化对象。
- 接口没有构造方法。
- 接口中所有的方法必须是抽象方法(默认为抽象的)。
- 接口不能包含成员变量,除了 static 和 final 变量。
- 接口支持多继承。
接口和抽象类的区别
- 抽象类中的方法可以有方法体,就是能实现方法的具体功能,但是接口中的方法不行。
- 抽象类中的成员变量可以是各种类型的,而接口中的成员变量只能是 public static final 类型的。
- 接口中不能含有静态代码块以及静态方法(用 static 修饰的方法),而抽象类是可以有静态代码块和静态方法。
- 一个类只能继承一个抽象类,而一个类却可以实现多个接口
interface Animal{
public void eat();
}
interface human extends Animal{
public void sayhello();
}
interface man extends Animal,human{
public void saybye();
}
class chirld implements man{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("eat");
}
public void sayhello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
public void saybye(){
System.out.println("bye");
}
}
public class interface_test{
public static void main(String[] args){
chirld c = new chirld();
c.eat();
c.sayhello();
c.saybye();
}
}
运行结果:
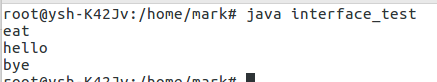





















 1658
1658

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








